* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nonspecific defense
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
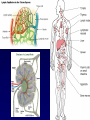
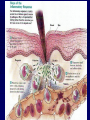
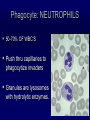
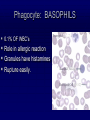
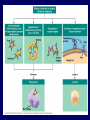
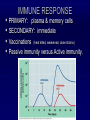
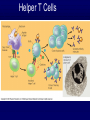
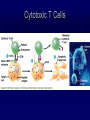
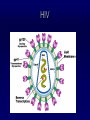
The Lymphatic System Function 1: to return interstitial fluid to blood stream Function 2: to provide working location for immune system IMMUNE SYSTEM Immunity is the ability to defend against pathogens. Pathogen: an organism or virus that causes disease. ex. infectious agents, foreign cells, even abnormal body cells (cancer). NONSPECIFIC DEFENSE SKIN keratin CILIA MUCOUS MEMBRANES STOMACH ACID RESIDENTIAL BACTERIA Sweat, tears, saliva have lysozyme. INTERFERONS Small proteins Active only against viruses Released by invaded cell To “warn” neighbor cells Inhibit reproduction of viruses. Inflammatory response Skin is cut Histamines released by damaged cells WBC’s attracted (phagocytes) Blood flow increased Capillaries permeable to phagocytes Phagocytes ingest pathogens by endocytosis Local temp rises Blood clot forms with platelets Hot, red, swollen, painful. :( BLOOD CELLS 1 in 1000 blood cells is a leukocyte A. ERYTHROCYTES B. LEUKOCYTES Phagocytes Lymphocytes. Phagocyte: NEUTROPHILS 50-70% OF WBC’S Push thru capillaries to phagocytize invaders Granules are lysosomes with hydrolytic enzymes. Phagocyte: BASOPHILS 0.1% OF WBC’s Role in allergic reaction Granules have histamines Rupture easily. Phagocyte: EOSINOPHILS 1-4% of WBC’s Infections with parasites Granules have toxins. Phagocyte: Monocytes Transformed into MACROPHAGES Ingest bacteria and viruses Circulate & Lodge in spleen, liver, lungs, nodes 2-8% of WBC’s Activate Helper T cells (lymphocytes). Major Histocompatability Complex MHC Class I for body cells (nucleated) Class II for immune cells 20 different glycoproteins each with 8-10 choices. Lymphocytes: 20 - 40% of WBC’s 2 types: B (bone) cells T (thymus) cells Specific defense B lymphocytes Mature in the bone Have antigen receptors Produce antibodies (proteins) Humoral immunity Antibody activity 1. Coat & Clump “agglutination” 2. Combine & Interfere “neutralization” 3. With complement, lyse & destroy. antibody Clonal selection theory of B lymphocytes IMMUNE RESPONSE PRIMARY: plasma & memory cells SECONDARY: immediate Vaccinations (heat killed, weakened, close strains) Passive immunity versus Active immunity. T Lymphocytes Mature in the thymus 3 types Helper T cells (recognize Class II MHC) Activate B plasma cells with receptor Cytotoxic T cells (recognize Class I MHC) Attack and lyse invader Or make clones & memory cells Or release chemicals to attract monocytes Or release toxins or interferons Supressor T cells turn off immune response. Helper T Cells Cytotoxic T Cells Cytotoxic T-cell attacking a body cell infected with a virus. Central Role of Helper T Cells Immune system Nonspecific: anatomic barriers,inflammatory, interferons Specific: Humoral with B-cells and antibodies Cell mediated with T-cells. HIV - AIDS Human Immunodeficiency Virus is responsible for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome HIV infects the helper T-cells. Body is vulnerable to opportunistic pathogens. Transmission: bodily fluids i.e. blood, sex, breast milk, across placenta HIV Helper T Cell releasing HIV