* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alkene Addition Reactions
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
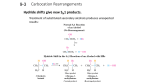
Chem 343 – Organic Reactions Chapters 4, 5 & 7 Prepared by José Laboy, MS http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Alkene Reactions #1: Summary of Addition Reactions to Alkenes H H H C HX C H CH 3 H CH 3 substituted alkane racemic H H alkene X X = Cl, Br, I Mechanism There are two possible products when HX is added across a double bond. If there is a preference of one product over the other the reaction is said to be regioselective. The regiochemistry of addition of HX to an alkene follows Markovnikov’s Rule, that is, the hydrogen atom adds to the carbon atom (in the double bond) that has the most hydrogen atoms, the X group adds to the carbon atom that has the least number of hydrogen atoms. The rate-‐determining step of the reaction is the formation of a carbocation, which represents the most stable on the immediate double bond. The order of carbocation stability is 3o > 2o > 1o. Carbocations can undergo rearrangement to produce a more stable carbocation (2o to 3o) as shown below. These are called 1,2-‐shifts. H 3C H 1,2 hydride shift H 3C 2o carbocation 3o carbocation H 3C CH 3 1,2 methide shift H 3C 2o carbocation 3o carbocation The shifting group migrates with its pair of electrons therefore the name hydride (H-‐) or methide (CH3-‐). The order of migrating groups is H > CH3. Alcohols can be produced by addition of water around the double bond in the process called hydration. This is accomplished by using an acid catalyst such as H2SO4. OH H2O / H2SO 4 catalytic alkene secondary alcohol Best to use this reaction when the carbocation formed as the intermediate does not rearrange. There are better ways to prepare alcohols that result in a predicted regiochemistry. Mechanism H + O rate determining step O H H H H + H3O+ O + OH O H H H H