* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
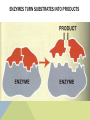
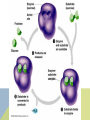
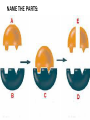
ENZYME STRUCTURE • Enzymes are proteins found in cells • Like all proteins, they are made out of amino acids • The most important part of an enzyme is its ACTIVE SITE The active site is the area where the substrate bonds • (A substrate is the stuff that is used in a reaction) ENZYMES TURN SUBSTRATES INTO PRODUCTS FUNCTION OF ENZYMES • A catalyst is anything that makes a reaction go faster • Heat is the best catalyst but it would kill our cells! • An enzyme is a catalyst made out of protein • When a chemical reaction is helped by an enzyme, the enzyme is not changed or used up. When the job is done, the enzyme will still be there, ready to be used again. ENZYMES ARE SPECIFIC • Every enzyme can only be used for one reaction. Each one can only bond with one substrate • So every time you have a new substrate, you need a new enzyme • This is called being SUBSTRATE SPECIFIC http://www.dnatube.com/video/4999/EnzymeAnimation DISCOVERY CHANNEL VIDEO Review from EPS….. (or the video won’t make sense!) Exergonic: a reaction that gives off energy • (the reactants have more energy in their bonds than the products) Endergonic: a reaction that needs energy • (the reactants have less energy in their bonds than the products) http://videos.howstuffworks.com/discovery/28733-assignment-discovery-enzymecatalysts-video.htm BREAKERS AND BUILDERS Some enzymes break down molecules into smaller pieces Some enzymes create large molecules by joining smaller ones Like in digesting your food Like when you build muscle or a plant makes sugar NAME THE PARTS: ACTIVITY OF ENZYMES • When an enzyme is doing its best job, that is called it’s optimum • Many things can affect how good an enzyme is at doing it’s job. Heat (too much or too little) pH and/or salts (interfere with the chemical bonds of the enzyme and change its shape) Even things like enough vitamins and minerals in your diet (not enough makes enzymes work slower) http://lpscience.fatcow.com/jwanamaker/animati ons/Enzyme%20activity.html