* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nuclear Radiation
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear fission wikipedia , lookup
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Ionizing radiation wikipedia , lookup
Background radiation wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
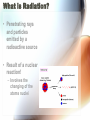
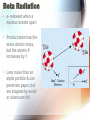
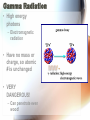
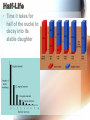
Nuclear Radiation Half-Life What is Radiation? • Penetrating rays and particles emitted by a radioactive source • Result of a nuclear reaction! – Involves the changing of the atoms nuclei Radioisotopes • Isotopes – Elements with the same # of protons & electrons, but a different # of neutrons! • Radioisotopes – Unstable isotopes – In nuclear rxns their nuclei undergo changes to become stable Chemical vs. Nuclear rxns Chemical Rxns Nuclear Rxns • Involve the transfer or sharing of e- • Nuclei are changed to become stable • Nuclei are unchanged • Involve large amounts of energy being emitted • Affected by ∆ in temp, pressure & catalyst • Not affected by anything & cannot be stopped Nuclear Stability • Depends on the ratio of neutrons to protons in the nucleus & the overall size of the nucleus • Too many or too few neutrons makes the nucleus unstable • Unstable nucleus releases energy by emitting radiation during radioactive decay! Types of Radiation • 3 main types: • Alpha Radiation • Beta Radiation • Gamma Radiation Alpha Radiation • Occurs when a helium nuclei is emitted – Called “alpha” particals • Product atoms atomic # is lower by 2 & its mass # is lower by 4 • Are stopped by paper! Beta Radiation • e- released when a nucleus breaks apart • Product atom has the same atomic mass, but the atomic # increases by 1 • Less mass than an alpha particle & can penetrate paper, but are stopped by wood or aluminum foil Gamma Radiation • High energy photons – Electromagnetic radiation • Have no mass or charge, so atomic # is unchanged • VERY DANGEROUS! – Can penetrate even wood! Nuclear Decay • Nuclear force Attractive force between protons & neutrons that are really close together in the nucleus • Stronger than the electromagnetic repulsions • Keeps nucleus together! Half-Life • Time it takes for half of the nuclei to decay into its stable daughter