* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
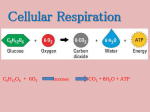
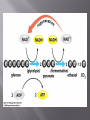
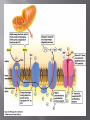
A key energy-storing molecule: Nearly all cells metabolize glucose for energy Other organic molecules are converted to glucose for energy harvesting C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP + (heat E) The main stages of glucose metabolism are: Glycolysis Cellular respiration Glycolysis Occurs in cytosol Does not require oxygen Breaks glucose into pyruvate Yields two molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose If oxygen is absent fermentation occurs pyruvate is converted into either lactate, or into ethanol and CO2 If oxygen is present, cellular respiration occurs Occurs in mitochondria (in eukaryotes) In cytosol (in prokaryotes) Requires oxygen Breaks down pyruvate into carbon dioxide and water Produces an additional 32 or 34 ATP molecules, depending on the cell type Each molecule of glucose is broken down to 2 molecules of pyruvate. A net of 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules are formed. Occurs under anaerobic conditions Pyruvate is converted into lactate or ethanol and CO2 Fermentation does not directly produce more ATP But is necessary to regenerate NAD+, which must be available for glycolysis to continue Some cells ferment pyruvate to form acids Human muscle cells can perform fermentation Anaerobic conditions produced when muscles use up O2 faster than it can be delivered (e.g. while sprinting) Lactate (lactic acid) produced from pyruvate Some microbes ferment pyruvate to other acids (as seen in making of cheese, yogurt, sour cream) Some microbes perform fermentation exclusively (instead of aerobic respiration) recipes.howstuffworks.com preparednesspro.files.wordpress.com/2009/08/c... Yeast cells perform alcoholic fermentation Glucose is fermented to ethanol and CO2 Occurs within mitochondria in eukaryotic cells Most of energy in glucose is stored in electron carriers NADH and FADH2 Only 4 total ATP produced per glucose after complete breakdown in the Krebs Cycle NADH and FADH2 deposit electrons into electron transport chains in the inner mitochondrial membrane Electrons join with oxygen gas and hydrogen ions to make H2O at the end of the ETCs 1. Energy released from electrons as they are passed down the ETC 2. Released energy used to pump H+ across inner membrane H+ accumulate in intermembrane space 3. H+ form a concentration gradient across the membrane (a form of stored energy) 4. H+ flow back into the matrix through an ATP synthesizing enzyme Flow of H+ provides energy to link 32-34 molecules of ADP with phosphate, forming 3234 ATP ATP then diffuses out of mitochondrion and used for energy-requiring activities in the cell Metabolic processes in cells are heavily dependent on ATP generation Muscle cells switch between fermentation and aerobic cell respiration depending on O2 availability vitalsigns-health.co.uk news.bbc.co.uk













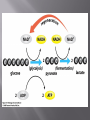














![fermentation[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008290469_1-3a25eae6a4ca657233c4e21cf2e1a1bb-150x150.png)