* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TOPIC 4.4 Genetic Engineering Worksheet
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
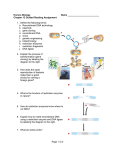
TOPIC 4.4: GENETIC ENGINEERING 1 2 3 4.4.1: POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTIONS 1. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used where DNA samples are too small to be useful. a) State the purpose of PCR: why is it so useful? b) Identify the cellular process which PCR mimics c) Explain the role of a thermal cycler in PCR. What happens during the high temperature cycle? d) State the role of complementary base pairing in PCR e) Explain why PCR is called a chain reaction 4 4.4.1: GEL ELECTROPHORESIS AND DNA PROFILING 2. What is the technique of gel electrophoresis used fo 3. State the roles of the following components of gel electrophoresis Restriction enzymes Gel Electric current Fluorescent DNA markers 4. Annotate the image below to show how gel electrophoresis works, including how the size of fragments affects their position on the gel. 5 5. State two main uses of DNA profiling by gel electrophoresis 6. State some other names (synonyms) for DNA profiling 7. Use the gel electrophoresis results below to answer the following questions: In this case, a DNA sample was taken from a cigarette at a crime scene (in a no smoking zone): a) State the process used to amplify the small amounts of DNA collected at the crime scene to a quantity adequate for identification by DNA proflining. b) Deduce which criminal, Robb McCarr or Nick Allott, left their cigarette at the crime scene. Explain your answer. c) Draw bands to show where the standard fragments would be observed. d) State the role of the standard fragment. 6 e) Outline the evidence in the sample that suggests that Nick and Rob are related. 7 4.4.6: THE HUMAN GENOME PROJECT Key resources: This link is to the Wellcome Institute Sanger Centre’s Genome website:http://www.yourgenome.org This link is to the US Government National Human Genome Website: http://www.genome.gov 1. What is the the Human Genome project? When did it begin, and when was the ‘first draft’ published? 2. Outline the aims of the Human Genome project 3. Look at some of the HGP resources on the websites above Name other organisms which have had their genomes sequenced. What is the role of E. Coli in the HGP? 8 4. Outline how the HGP developed knowledge in the following fields: Medicine Pharmacogenomics Bioinformatics Evolutionary Research Ethical, Legal and Social issues 9 4.4.7 – 4.4.10: GENETICALLY MODIFIED ORGANISMS Genetically modified organisms (GMO’s) are created using gene transfer. 1. Outline gene transfer 2. Explain how the universality of the genetic code is central to gene transfer applications 3. Define transgenic organism 4. State the role of the following in gene transfer: Restriction enzymes E. Coli plasmids Ligase Vector 10 5. Annotate the diagram below to outline the process of gene transfer 6. Explain how gene transfer is used in the industrial production of insulin 7. Outline the use of gene transfer techniques in gene therapy for the treatment of SCID What is SCID? What is the prognosis for management of SCID through gene therapy> 11 8. Outline how genetically modified sheep are used for the treatment of inherited haemophilia due to Factor IX deficiency in humans 9. Give at least 3 examples of genetically modified (GM) plant crops, and the effects of their new genes. GM CROP 1. ‘Golden rice’ New properties Advantages 2. 3. 12 4.4.11 – 4.4.13: CLONING 1. Define clone 2. State three examples of naturally occurring clones 4. Dolly the sheep was produced by cloning using a differentiated nucleus Use the Dolly resources: The Official Roslin site: http://www.roslin.ed.ac.uk/public-interest/dolly-thesheep/ Utah Genetics Cloning site: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/cloning/ Why was the differentiated nucleus taken from an udder cell? Suggest reasons why Dolly died ‘young’ from age-related diseases Outline the method used to clone Dolly 13 4. Outline the difference between therapeutic cloning and reproductive cloning 5. State four potential medical applications and benefits of therapeutic cloning 6. Discuss the ethical implications of therapeutic cloning in humans: Advantages Disadvantages 14 7. Suggest why reprogrammed IPS stem cells might mitigate the negative perception of human therapeutic cloning: Define IPS cells Explain the process of producing IPS cells Explain the benefits of using IPS cells in medical research and treatment 15