* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plant tissue - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Hyaluronic acid wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
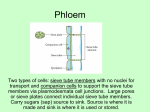
PLANT TISSUE SMAK BPK PENABUR SUKABUMI GRADE XI – SCIENCE CLASS Lectures by : Agustina Eka H.,S.SI. TISSUE ?? cells the smallest basic unit of cells tissue a group of cells that have similar forms, composition, and function organ a unit of several types of tissues that are close to each other and support certain functions Organ system organism some organs which are coordinate each other and conducting certain functions Meristematic & Permanent Tissue A. Meristematic Tissue Apical meristem Lateral meristem Intercalary meristem B. Permanent Tissue 1. Simple permanent tissue Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma 2. Complex permanent tissue Xylem Phloem 3. Protective tissue Epidermis Cork (phellem) Meristematic Tissue 1. have thin cellulose cell walls. 2. The meristematic cells may be spherical,oval,polygonal or rectangular in shape. 3. compactly arranged & do not contain any intercellular space between them. 4. contains dense or abundant cytoplasm & a single large nucleus. 5. contain few vacuoles or no vacuoles at all Apical meristems Are located at the tips of roots and in the buds of shoots Elongate shoots and roots through primary growth The root tip is covered by a root cap Primary meristem Lateral Meristem Add thickness to woody plants through secondary growth Secondary meristem cambium : 1) Vascular cambium 2) Cork cambium Vascular cambium Located between xylem and phloem Vascular cambium (a) Types of cell division. An initial can divide transversely to form two cambial initials (C) or radially to form an initial and either a xylem (X) or phloem (P) cell. C (b) Accumulation of secondary growth. Although shown here as alternately adding xylem and phloem, a cambial initial usually produces much more xylem. • An overview of primary and secondary growth Primary growth in stems Shoot apical meristems (in buds) Epidermis Cortex Primary phloem In woody plants, there are lateral meristems that add secondary growth, increasing the girth of roots and stems. Vascular cambium Cork cambium Primary xylem Lateral meristems Pith Secondary growth in stems Apical meristems add primary growth, or growth in length. Pith Primary xylem Root apical meristems Secondary xylem Periderm Cork cambium The cork cambium adds secondary dermal tissue. Cortex Primary phloem The vascular cambium adds Secondary secondary phloem xylem and Vascular cambium phloem. Intercalary meristem • Intercalary meristem : located between mature tissues, ex : base of nodes in grass stem • Gramineae or Poaceae (rice, corn, sugar cane) Epidermis • Outer layer • Tightly cell • Function : to protect the underlying cell • Modification : hair, spine, trichome, stomata, lenticell, root hair, cuticule Epidermis – stoma, trichomes, & root hairs http://www.ucd.ie/botany/Steer/hair/roothairs.html Periderm – cork & parenchyma TWIG WITH LENTICELS Parenchyma • Large cell, thin wall, large vacuoles Types : 1 ) aerenchyma : aquatic plant 2) Chlorenchyma : containing chloroplast Parenchyma Chollenchyma Function : supporting and strengthening tissue • Cellulose and pectin thickening in the corner of the cell Sclerenchyma • Function : organ support • Inactive cell • Cellulose and lignin thickening Sclereids : Hard and rigid Stem cortex, leaf venetin, root, fruit, and seed Fiber: hard elongated cells Gymnosperm woody fiber, bark, leaf fiber, seed fiber Sclerenchyma SCLERIDS Right-hand illustration modified from: Weier, Stocking & Barbour, 1974, Botany: An Introduction to Plant Biology, 5th Ed. FIBERS Secretory Cell • Secrete various substances Xylem • Water and mineral transportation • Lignin thickening Consists of : 1) Trachea/vessel element 2) Tracheid 3) Xylem fiber 4) Xylem parenchyma Fig. 35.8 Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Phloem • Conduction of nutrition Consists of : 1) Sieve tube 2) Companion cell 3) Phloem fiber 4) Phloem parenchyma