* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Innate lymphocytes_LÁ_optional
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
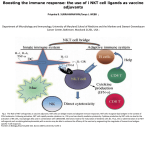
Unconventional (T)-lymphocytes Arpad Lanyi, LSB 2.201 [email protected] Main Characteristics of innate lymphocytes Subsets: • γδT-cells • iNKT cells • MAIT (mucosa associated invariant Tcells) Main characteristics: • Very rapid response to pathogens or to tissue dysregulation • No MHC-restriction • Non-reactive to peptide-MHC complexes • Antigen presentation by MHC-like proteins • May especially be important early in life, when the adaptove system is not fully functional Innate lymphocytes: γδT cells B-cells, αβ T-cells and γδ T-cells are remarkably similar by appearance αβ T-cell γδ T-cell B-cell Innate Immune cells in the murine skin Langerhans cells (Langerin) γδ T-cell receptor Dendritic Epidermal T-cells (DETC) merge Human Intraepithelial lymphocytes have a very limited receptor repertoire Intraepithelial lymphocytes TCR γ1δ1 Immunol rev 2007 γδ T Cells and the Lymphoid StressSurveillance Response Adrian C. Hayday http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2009.08.006 A distinct population of T-cells expresses a second class of TCR with γδT cell receptors • • • • • The two types of receptors are similar, Similar gene rearrangement process Small to medium diversity CD8-/CD4- (double negative) None-peptide small molecules, stress proteins, presentation by class I like molecules • Abundant in tissues • Maintenance of homeostasis, tissue repair γδ T-cells •MHC-independent, CD1c and CD1d dependent. •Double megative. •Comprise about 1-5% of the T-cells found in the circulation, but can be the dominant (20 to 50%) T-cell population in epithelial tissue (intestine and dermis). •A population that is expanded in intra- (Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Listeria monocytogenes) and extracellular infections (Borrelia burgdorferi) and certain disease states such as celiac disease. •Many of the receptors are shared with NK cells Development of unconventional T cells in the thymus γδ T-cells, NKT-cells Subsets of γδT-cells: Vγ9:Vδ2 receptors of blood γ:δ T cells recognize phosphoantigens. • γγδTcells in various tissues express different γ:δ TCR. • Killing and cytokine production (IFNg for example) IPP, made by the host cells • γ:δ T cells recognize phosphoantigens HMBPP, Produced by Bacteria Drug approved for the treatment of osteoporosis patients Butyrophilin 3A1 on tissue cells binds phosphoantigens and presents them to γ:δ T cells. Butyrophilin 3A1 The endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) is a ligand for Vγ4:Vδ5 T cells. • Recognition of virus-infected cells (e.g. CMV) • In response to CMV infection the Vγ4:Vδ5 population is expanded. • Also respond to tumor cells mainly in the early phase of tumor development. VγVδ1 T-cell receptors recognize lipid antigens presented by CD1d Sulfatide is a glycolipid made by human cells and is abundant in the intestinal epithelium. The upper panel shows sulfatide being bound by CD1d in the endoplasmic reticulum and then transported to the cell surface. There the sulfatide is recognized by the antigen receptor of a Vγ:Vδ T cell. the chemical structure of sulfatide. • IFN gamma (CD27+) • IL17 (CD27-) The role of γδ Tcells in tumor development • Both pro- and anti-tumor effects possible • Anti-tumor effect was usually dependent on stress-induced sugnals • Antitumor effect: mediated via IFNγ, TNF, Th1 and CTL • Pro-tumor effect: IL17, recruitment of Tregs, MDSC and mactophages which produce IL1β, IL23…. Induction of more IL17….. Receptor–ligand interactions mediating tumour cell recognition by human γδ T cells. Innate lymphocytes with αβ TCR iNKT cells Activation of NKT cells requires two signals, one from the T-cell receptor and the other from a cytokine receptor. • αβTCR, but with very limites specificity and usage of TCR gene segments (Vα24-Jα18: Vβ11 ). Glycolipid, phospholipid recognition (αgalactosyl ceramide, α-Gal-Cer) • Develop in the thymus • Master regulator transcription factor is (PLZF) promyeloytic leukemia zincfinger protein • Selected on double-positive cells in the thymus • Lipid antigens are presened by CD1d • CD1d is constrantly recycling between the membrane and the endosomal vesicles • Saponins allow removal of self-lypids and loading of foreign lipids • NK-cell activation requires at least two signals. In responding to changes in self and microbial lipid antigens, NKT cells orchestrate an immune response through interactions with several different types of cells of innate and adaptive immunity. The NKT cell can have conjugate interactions withvarious cell types. • NK cells, • Dendritic cells, • Macrophages, and neutrophils of innate immunity and also the B cells of adaptive immunity. • Cytokine secretion, NKT cells can also influence the T cells of adaptive immunity (may produce IFNγ or IL4 among others.). NKT cell immunoregulatory axis. • Anti-tumor effect • NKT-deficient mice exhibited significantly increased susceptibility to ethylcholanthrene(MCA-) induced sarcomas and B16F10 melanoma tumors • effect reversed by the administration of liverderived iNKT cells during the early stages of tumor growth • iNKT, IFNγ and CD8-dependent process. • May indirectly have anti-tumor effect by killing tumor—associated macrophages (TAMs) • Solid tumors do not express CD1d • Selective R H Wiltrout Immunotherapy (2011) 3(10), 1167–1184 Manipulating iNKT Cells for Cancer Treatment Mucosa-associated invariant T (MAIT) • MAIT cells αβ comprose 1-10% of T-cells in blood, and 2040% in the liver. • MAIT cells recognize by-products of riboflavine synthesis called pterins (humans aquire it from diet of microbiota. • αβTCR, but with very limites specificity and VαJα usage (Vα7.2Jα33).Lipid presentation via MR1, an unconventional MHC class I molecules. • Highly conserved receptor and lipid presentation suggwst coevolution of the receptor and the pathogen. MAIT cells recognize by-products of the synthesis of riboflavin called pterins. Other MHC class Ib proteins encoded outside the MHC region MR1 – molecules are expressed on various cell types (MHC Related-1) They have polar antigen binding site They present microbial riboflavin (vitamin B2) metabolic products and byproducts to mucosa associated invariant T cells (MAIT) Corbet AJ et al.: Nature, 2014 vol509, 361- Many vitamin biosynthetic pathways are unique to bacteria and yeast. Mammals can only acquire riboflavin, so MAIT cells use these metabolites to detect microbial infection. MAIT cell numbers and maturation are dependent on the microbiota. 1-10% of T-cells in the blood 20-40% in liver Thank you