* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test #5 Review
Jahn–Teller effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fluorochemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
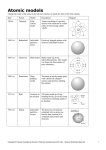
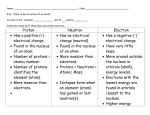
Test #5 Review Significant Figures Define precision. How detailed is your measurement. Define accuracy. How correct is your measurement. Is it possible to be very precise and very inaccurate? Yes. You could, for example, measure your height to be 5.6224 meters. Significant Figures Which is more accurate, 2.3 meters or 2.321 meters? Impossible to say. You don’t know the correct length. How many sig figs in 2.00 grams? three How many sig figs in 1500 liters? two How many sig figs in 200.00 Newtons? five Unit Conversion How many meters in 362 centimeters? 3.62 m How grams in 4.5 kilograms? 4500 g If 22.1 p equals 84 q, how many p are equal to 469 q? 120 p (remember, only two sig figs) What is the melting temperature? 100 degrees C Once melting begins, how much energy is needed to finish? 60 calories Phase Changes Which phase has no definite volume or shape? gas Which has the higher temperature, melting or freezing? It’s the same! Changing from gas to liquid phase is called . . . condensation. Does a liquid absorb or give off energy when freezing? Energy is given off. Atomic History Who discovered the nucleus? Ernest Rutherford Who discovered the electron? J. J. Thomson Who made the first periodic table of the elements? Dmitri Mendeleev What did the “gold foil” experiment discover? the nucleus Atomic Basics What is the mass of the proton? 1 amu Which force holds the nucleus together? the strong force Which force holds the electrons around the nucleus? the electromagnetic force Define mass number. number of protons + number of neutrons Atomic Basics The identity of an element depends on the number of . . . . . . protons How many protons in one atom of iron? 26 How many neutrons in one atom of 19F? 10 How many electrons in a +1 ion of potassium? 18 Atomic Basics How many valence electrons in one atom of sulfur? 6 What is an ion? a charged atom What is the most likely charge on an ion of sulfur? -2 Add two neutrons to calcium-40. What’s the new element? calcium-42 Table Trends Which is more reactive, lithium or potassium? potassium Why? Less force; it’s easier to remove an electron. Which is more reactive, fluorine or bromine? fluorine Why? It attracts electrons with greater force. Table Trends Which is larger, lithium or potassium? potassium Why? more energy levels Which is larger, fluorine or bromine? bromine (For the same reason – more energy levels.) Why do elements in the same family behave the same? They all have the same number of valence electrons. Chemical Formulas Predict the formula for potassium sulfide. K2S Predict the formula for calcium iodide. CaI2 Predict the formula for gallium oxide. Ga2O3 Predict the formula for lithium sulfite. Li2SO3 Chemical Bonds Which bond would form between sodium and oxygen? ionic Which bond would form between nitrogen and oxygen? covalent What is the name of SiO2? silicon dioxide Which would be a better conductor, SiO2 or KCl? Potassium chloride; it’s ionic. Here are some other topics: • • • • • • electron orbitals types of chemical reactions balancing equations energy of chemical reactions reaction rates acids & bases