* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit1CellsVocabulary
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
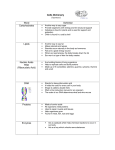
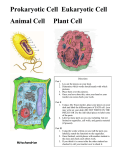
Unit 1 Lesson 1 Characteristics of Cells Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. Cell: smallest functional and structural unit of all living things Organism: any living thing Cell Theory – idea that all organisms are made of one or more cells, cells are the basic unit of all organisms and cells only come from existing cells 4. Unicellular organisms: made of just one cell 5. Multicellular organisms: made of more than one cell 6. Cell membrane: protective layer that covers a cell’s surface, controls what enters and exits 7. Cytoplasm: fluid inside a cell, is where everything is in the cell, like a factory floor 8. Organelles: structures in cells that perform specific functions 9. DNA: short for deoxyribonucleic acid. Contains instructions for all cell processes 10. Nucleus: organelle in eukaryotic cells that contain the cell’s DNA, acts as the boss of the cell 11. Prokaryotes: organisms without a nucleus 12. Eukaryote: organism with a nucleus Unit 1 Lesson 1 Characteristics of Cells Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. Cell: smallest functional and structural unit of all living things Organism: any living thing Cell Theory – idea that all organisms are made of one or more cells, cells are the basic unit of all organisms and cells only come from existing cells 4. Unicellular organisms: made of just one cell 5. Multicellular organisms: made of more than one cell 6. Cell membrane: protective layer that covers a cell’s surface, controls what enters and exits 7. Cytoplasm: fluid inside a cell, is where everything is in the cell, like a factory floor 8. Organelles: structures in cells that perform specific functions 9. DNA: short for deoxyribonucleic acid. Contains instructions for all cell processes 10. Nucleus: organelle in eukaryotic cells that contain the cell’s DNA, acts as the boss of the cell 11. Prokaryotes: organisms without a nucleus 12. Eukaryote: organism with a nucleus Unit 1 Lesson 1 Characteristics of Cells Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. Cell: smallest functional and structural unit of all living things Organism: any living thing Cell Theory – idea that all organisms are made of one or more cells, cells are the basic unit of all organisms and cells only come from existing cells 4. Unicellular organisms: made of just one cell 5. Multicellular organisms: made of more than one cell 6. Cell membrane: protective layer that covers a cell’s surface, controls what enters and exits 7. Cytoplasm: fluid inside a cell, is where everything is in the cell, like a factory floor 8. Organelles: structures in cells that perform specific functions 9. DNA: short for deoxyribonucleic acid. Contains instructions for all cell processes 10. Nucleus: organelle in eukaryotic cells that contain the cell’s DNA, acts as the boss of the cell 11. Prokaryotes: organisms without a nucleus 12. Eukaryote: organism with a nucleus Unit One Lesson Two Chemistry of Life 1. 2. 3. 4. Atoms: basic building blocks of matter Molecule: two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds Compounds: molecules made of two of more different atoms Lipid: chains of fatty acids which are made of hydrogen, carbon and oxygen. Mostly used for energy or storing energy. Also included in some structures and steroids 5. Protein: large molecule made of chains of amino acids. Used to build and repair body structures and regulate body processes 6. Amino acids: molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen atoms. Used to create proteins 7. Enzyme: special proteins used to help chemical processes 8. Carbohydrates: molecules made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Mostly used as an energy source 9. Nucleic acid: made of nucleotides. Carries instructions for making proteins 10. Nucleotides: used to make nucleic acids. Their order tells the order of amino acids needed to make a protein Unit One Lesson Two Chemistry of Life 1. 2. 3. 4. Atoms: basic building blocks of matter Molecule: two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds Compounds: molecules made of two of more different atoms Lipid: chains of fatty acids which are made of hydrogen, carbon and oxygen. Mostly used for energy or storing energy. Also included in some structures and steroids 5. Protein: large molecule made of chains of amino acids. Used to build and repair body structures and regulate body processes 6. Amino acids: molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen atoms. Used to create proteins 7. Enzyme: special proteins used to help chemical processes 8. Carbohydrates: molecules made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Mostly used as an energy source 9. Nucleic acid: made of nucleotides. Carries instructions for making proteins 10. Nucleotides: used to make nucleic acids. Their order tells the order of amino acids needed to make a protein Unit One Lesson Two Chemistry of Life 1. 2. 3. 4. Atoms: basic building blocks of matter Molecule: two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds Compounds: molecules made of two of more different atoms Lipid: chains of fatty acids which are made of hydrogen, carbon and oxygen. Mostly used for energy or storing energy. Also included in some structures and steroids 5. Protein: large molecule made of chains of amino acids. Used to build and repair body structures and regulate body processes 6. Amino acids: molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen atoms. Used to create proteins 7. Enzyme: special proteins used to help chemical processes 8. Carbohydrates: molecules made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Mostly used as an energy source 9. Nucleic acid: made of nucleotides. Carries instructions for making proteins 10. Nucleotides: used to make nucleic acids. Their order tells the order of amino acids needed to make a protein Unit One Lesson Three Cell Structure and Function Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. Cytoskeleton: network of protein filaments that give shape and support to cells Mitochondria: organelle where cellular respiration occurs. Powerhouse of the cell. Ribosome: organelle that uses the DNA’s instructions to make proteins by putting together chains of amino acids. Like a worker in a factory. 4. Endoplasmic Reticulum: system of membranes that helps production, processing and transport of proteins and lipids. Like an assembly line and assembly line workers. 5. Golgi Complex: organelle that processes, packages and distributes material. Like a packaging department. 6. Cell Wall: rigid structure around the cell membrane. Provides support and protection. Part of Security Department 7. Vesicle: bubble-like structures used for storing material. Like storage tanks. 8. Vacuole: vesicle that may contain enzymes, nutrients, water or wastes. Like a large storage tank. 9. Chloroplast: organelle where photosynthesis occurs. Contains chlorophyll. Like solar panels. 10. Lysosomes: organelles containing enzymes which can break down worn out/damaged organelles, waste materials and foreign invaders. Clean up crew. Unit One Lesson Three Cell Structure and Function Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. Cytoskeleton: network of protein filaments that give shape and support to cells Mitochondria: organelle where cellular respiration occurs. Powerhouse of the cell. Ribosome: organelle that uses the DNA’s instructions to make proteins by putting together chains of amino acids. Like a worker in a factory. 4. Endoplasmic Reticulum: system of membranes that helps production, processing and transport of proteins and lipids. Like an assembly line and assembly line workers. 5. Golgi Complex: organelle that processes, packages and distributes material. Like a packaging department. 6. Cell Wall: rigid structure around the cell membrane. Provides support and protection. Part of Security Department 7. Vesicle: bubble-like structures used for storing material. Like storage tanks. 8. Vacuole: vesicle that may contain enzymes, nutrients, water or wastes. Like a large storage tank. 9. Chloroplast: organelle where photosynthesis occurs. Contains chlorophyll. Like solar panels. 10. Lysosomes: organelles containing enzymes which can break down worn out/damaged organelles, waste materials and foreign invaders. Clean up crew Unit One Lesson Three Cell Structure and Function Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. Cytoskeleton: network of protein filaments that give shape and support to cells Mitochondria: organelle where cellular respiration occurs. Powerhouse of the cell. Ribosome: organelle that uses the DNA’s instructions to make proteins by putting together chains of amino acids. Like a worker in a factory. 4. Endoplasmic Reticulum: system of membranes that helps production, processing and transport of proteins and lipids. Like an assembly line and assembly line workers. 5. Golgi Complex: organelle that processes, packages and distributes material. Like a packaging department. 6. Cell Wall: rigid structure around the cell membrane. Provides support and protection. Part of Security Department 7. Vesicle: bubble-like structures used for storing material. Like storage tanks. 8. Vacuole: vesicle that may contain enzymes, nutrients, water or wastes. Like a large storage tank. 9. Chloroplast: organelle where photosynthesis occurs. Contains chlorophyll. Like solar panels. 10. Lysosomes: organelles containing enzymes which can break down worn out/damaged organelles, waste materials and foreign invaders. Clean up crew