* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0 - hanan-salah
Human-Computer Interaction Institute wikipedia , lookup
Artificial intelligence in video games wikipedia , lookup
Wizard of Oz experiment wikipedia , lookup
Computer Go wikipedia , lookup
Technological singularity wikipedia , lookup
Kevin Warwick wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
List of Doctor Who robots wikipedia , lookup
Self-reconfiguring modular robot wikipedia , lookup
Index of robotics articles wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
History of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
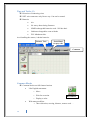
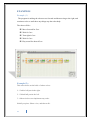
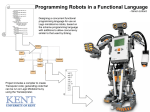
Basic Education College Department of Computer Teacher “LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT 2.0” PREPARED BY Afaf mejbel AL-Ajmi Hanan bahjat salah Noura Al-asmar Ohood motlg owaimer SUPERVISOR Dr : Abeer Al-ameeri 2013 1 Acknowledgement We are thankful to all who contributed in the output of this research is to take effect, to all those who were the cause of our education and guide us and help us. Special thanks for Abeer Al-ameeri parameter on the efforts made by the substance (ARTIFICAL INTELLIGENCE). 2 Table of Contents 6 ........................... ................................ What is the definition of Artificial Intelligence ? 7 .................... ................................ ................................ history of artificial intelligence 8 .............................. ................................ The Advantages for Artificial Intelligence (AI) 8 .......................... ................................ The Disadvantages for Artificial Intelligence (AI) 9 ....................................... ................................ Applications of artificial intelligence : 9 .............. ................................ ................................ ................................ Finance 10 ...................... ................................ ................................ Hospitals and medicine 10 .................................. ................................ ................................ Heavy industry 11 ................................ ................................ Online and telephone customer service 11 ...................................... ................................ ................................ Transportation 11 .......................... ................................ ................................ Telecommunications 12 ................................ ................................ ................................ Toys and games 12 .............. ................................ ................................ ................................ Music 14 ............... ................................ ................................ News, Publishing & Writing 15 ............... ................................ ................................ ................................ Other 15 .................. ................................ Thing that comes to mind when you think of a robot ? 16 ......................................... ................................ Type of robots working for us today : 16 ................................... ................................ ................................ So what is a robot? 17 ...................................... ................................ ................................ Types of robot 17 .................................. ................................ ................................ Robots in society 18 ........................... ................................ ................................ Future development 18 ................................... ................................ ................................ Robotics sets : 19 .................................... ................................ ................................ WHAT IS LEGO? 20 ........................... ................................ ................................ LEGO MINDSTORMS: 21 ............................. ................................ ................................ WHAT IS THE RCX? 22 ............ ................................ ................................ LEGO MINDSTORM VIRSIONS: 22 ...................................... ................................ ................................ 1-Cybermaster 24 ......................................... ................................ ................................ 2- Codepilot 24 ............... ................................ ................................ ................................ 3- Scout 25 ..................................... ................................ ................................ 4- Micro Scout 25 ......................................... ................................ ................................ 5- Spybotics 25 ...................... ................................ ................................ 6- Lego Mindstorms NXT 25 ............... ................................ 7- LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT Educational Version 3 26 ................ ................................ ................................ 8- Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0 26 ........................ ................................ ................................ 9- Lego Mindstorm EV3 26 .............................. ................................ WHAT IS LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT 2.0? 26 ............. ................................ ................................ ................................ Kit features: 27 ......................... ................................ ................................ -NXT Intelligent Brick: 28 ................................... ................................ ................................ -ACTUATORS: 28 ........... ................................ ................................ ................................ Programming 29 ............ ................................ ................................ ................................ 1-NXT-G: 29 ............................. ................................ ................................ 2-LabVIEW Toolkit: 29 ...................................... ................................ ................................ 3-Lego::NXT: 29 ................. ................................ ................................ ................................ 4-Ada: 29 ...................................... ................................ 5-Next Byte Codes & Not eXactly C: 30 ........................................ ................................ ................................ 6-ROBOTC: 30 ........................................ ................................ ................................ 7-RoboMind: 30 ........................................ ................................ ................................ 8-NXTGCC: 30 .............. ................................ ................................ ................................ 9-URBI: 30 ..................................... ................................ ................................ 10-leJOS NXJ: 30 ....................................... ................................ ................................ 11-NxtOSEK: 30 .................. ................................ ................................ 12-MATLAB and Simulink: 31 ................ ................................ ................................ ................................ 13-Lua: 31 ...................... ................................ ................................ 14-FLL NXT Navigation: 31 ......................................... ................................ ................................ 15-ruby-nxt: 31 ............................... ................................ ................................ 16-Robotics. NXT: 32 ........................................ ................................ Lego mindstorms NXT disadvantages: 33 ...................................... ................................ LEGO MINDSTORMS ADVANTAGES: 33 ........................... ................................ ................................ Lego Mindstorms NXT:34 ..................... ................................ Why choose LEGO MINDSTORMS Education NXT? 35 ................................... ................................ ................................ Communications 35 ............... ................................ ................................ ................................ Memory 35 ................................ ................................ ................................ Tips and Tricks (1) 36 ................................ ................................ ................................ Tips and Tricks (2) 36 ................................... ................................ ................................ Common Blocks 39 ................ ................................ ................................ ................................ sound : 40 ................. ................................ ................................ ................................ move : 4 41 ......................... ................................ ................................ EXAMPLES Example (1) 41 ........................................ ................................ ................................ Example(2) : 43 .............. ................................ ................................ ................................ References: 5 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE: What is the definition of Artificial Intelligence? Artificial intelligence (AI) is an area of computer science that emphasizes the creation of intelligent machines that work and react like humans. Some of the activities computers with artificial intelligence are designed for include speech recognition, learning, planning and problem solving. Artificial intelligence (AI) is technology and a branch of computer science that studies and develops intelligent machines and software. Major AI researchers and textbooks define the field as "the study and design of intelligent agents where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its chances of success , " It is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines especially intelligent computer program. It is related to the similar task of using computers to understand human intelligence." Artificial Intelligence is based on the that it is possible to describe and simulate human intelligence in IT systems and devices. Therefore, it is also defined as the study and design of systems or devices depicting the surrounding environment so that behaved as a mimic human behavior.Knowledge engineering is a core part of AI research. Machines can often act and react like humans only if they have abundant information relating to the world. Artificial intelligence must have access to objects, categories, properties and relations between all of them to implement knowledge engineering. Initiating common sense, reasoning and problem-solving power in machines is a difficult and tedious approach. 6 History of artificial intelligence The history of artificial intelligence began in antiquity, with myths, stories and rumors of artificial beings endowed with intelligence or consciousness by master craftsmen; as Pamela McCorduck writes The seeds of modern AI were planted by classical philosophers who attempted to describe the process of human , thinking as the mechanical manipulation of symbols. This work culminated in the invention of the programmable digital computer in the 1940s, a machine based on the abstract essence of mathematical reasoning. This device and the ideas behind it inspired a handful of scientists to begin seriously discussing the possibility of building an electronic brain. The field of artificial intelligence research was founded at a conference on the campus of Dartmouth College in the summer of 1956. Those who attended would become the leaders of AI research for decades. Many of them predicted that a machine as intelligent as a human being would exist in no more than a generation and they were given millions of dollars to make this vision come true. Eventually it became obvious that they had grossly underestimated the difficulty of the project. In 1973, in response to the criticism of Sir James Lighthill and ongoing pressure from congress, the U.S. and British Governments stopped funding undirected research into artificial intelligence. Seven years later, a visionary initiative by the Japanese Government inspired governments and industry to provide AI with billions of dollars, but by the late 80s the investors became disillusioned and withdrew funding again. This cycle of boom and bust, of "AI winters" and summers, continues to haunt the field. Undaunted, there are those who make extraordinary predictions even now. The term artificial intelligence was first coined by John McCarthy in 1956 when he held the first academic conference on the subject. But the journey to understand if machines can truly think began much before that. In Vannevar Bush’s seminal work As We May Think [Bush45] he proposed a system which amplifies people’s own knowledge and understanding. Five years later Alan Turing wrote a paper on the notion of machines being able to simulate human beings and the ability to do intelligent things, such as play Chess [Turing50]. 7 The Advantages for Artificial Intelligence (AI) Jobs - depending on the level and type of intelligence these machines receive in the future, it will obviously have an effect on the type of work they can do, and how well they can do it (they can become more efficient). As the level of AI increases so will their competency to deal with difficult, complex even dangerous tasks that are currently done by humans, a form of applied artificial intelligence. They don't stop - as they are machines there is no need for sleep, they don't get ill , there is no need for breaks or Facebook, they are able to go, go, go! There obviously may be the need for them to be charged or refueled, however the point is, they are definitely going to get a lot more work done than we can. Take the Finance industry for example, there are constant stories arising of artificial intelligence in finance and that stock traders are soon to be a thing of the past. No risk of harm - when we are exploring new undiscovered land or even planets, when a machine gets broken or dies, there is no harm done as they don't feel, they don't have emotions. Where as going on the same type of expeditions a machine does, may simply not be possible or they are exposing themselves to high risk situations. Act as aids - they can act as 24/7 aids to children with disabilities or the elderly, they could even act as a source for learning and teaching. They could even be part of security alerting you to possible fires that you are in threat of, or fending off crime. Their function is almost limitless - as the machines will be able to do everything (but just better) essentially their use, pretty much doesn't have any boundaries. They will make fewer mistakes, they are emotionless, they are more efficient, they are basically giving us more free time to do as we please. The Disadvantages for Artificial Intelligence (AI) 8 Over reliance on AI - as you may have seen in many films such as The Matrix, iRobot or even kids films such as WALL.E, if we rely on machines to do almost everything for us we become very dependent, so much so they have the potential to ruin our lives if something were to go wrong. Although the films are essentially just fiction, it wouldn't be too smart not to have some sort of back up plan to potential issues on our part. Human Feel - as they are machines they obviously can't provide you with that 'human touch and quality', the feeling of a togetherness and emotional understanding, that machines will lack the ability to sympathise and empathise with your situations, and may act irrationally as a consequence. Inferior - as machines will be able to perform almost every task better than us in practically all respects, they will take up many of our jobs, which will then result in masses of people who are then jobless and as a result feel essentially useless. This could then lead us to issues of mental illness and obesity problems etc. Misuse - there is no doubt that this level of technology in the wrong hands can cause mass destruction, where robot armies could be formed, or they could perhaps malfunction or be corrupted which then we could be facing a similar scene to that of terminator ( hey, you never know). Ethically Wrong? - People say that the gift of intuition and intelligence was God's gift to mankind, and so to replicate that would be then to kind of 'play God'. Therefore not right to even attempt to clone our intelligence. Applications of artificial intelligence : Finance Banks use artificial intelligence systems to organize operations, invest in stocks, and manage properties. In August 2001, robots beat humans in a simulated financial trading competition 9 . Financial institutions have long used artificial neural network systems to detect charges or claims outside of the norm, flagging these for human investigation. has deployed artificial intelligence customer support systems, or automated online assistants, at E*TRADE, HSBC, Intuit and Lloyds Banking Group, to assist financial services customers with services such as checking an account balance, signing up for a new credit card or retrieving a forgotten password. Hospitals and medicine A medical clinic can use artificial intelligence systems to organize bed schedules, make a staff rotation, and provide medical information. Artificial neural networks are used as clinical decision support systems for medical diagnosis, such as in Concept Processing technology in EMR software. Other tasks in medicine that can potentially be performed by artificial intelligence include: Computer - aided interpretation of medical images. Such systems help scan digital images, e.g. from computed tomography, for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases. A typical application is the detection of a tumor. Heart sound analysis. Heavy industry Robots have become common in many industries. They are often given jobs that are considered dangerous to humans. Robots have proven effective in jobs that are very repetitive which may lead to mistakes or accidents due to a lapse in concentration and other jobs which humans may find degrading. Japan is the leader in using and producing robots in the world. In 1999, 1,700,000 robots were in use worldwide. 10 Online and telephone customer service An automated online assistant providing customer service on a web page. Artificial intelligence is implemented in automated online assistants that can be seen as avatars on web pages. It can avail for enterprises to reduce their operation and training cost. A major underlying technology to such systems is natural language processing. Similar techniques may be used in answering machines of call centres, such as speech recognition software to allow computers to handle first level of customer support, text mining and natural language processing to allow better customer handling, agent training by automatic mining of best practices from past interactions, support automation and many other technologies to improve agent productivity and customer satisfaction. Transportation Fuzzy logic controllers have been developed for automatic gearboxes in automobiles (the 2006 Audi TT, VW Toureg and VW Caravell feature the DSP transmission which utilizes Fuzzy Logic, a number of Škoda variants (Škoda Fabia) also currently include a Fuzzy Logic based controller). Telecommunications Many telecommunications companies make use of heuristic search in the management of their workforces, for example BT Group has deployed heuristic search in a scheduling application that provides the work schedules of 20,000 engineers. Current robotic and prosthetic hands receive far less tactile information than the human hand. Recent research has developed a tactile sensor array that mimics the mechanical properties and touch receptors of human fingertips. The sensor array is constructed as a rigid core surrounded by conductive fluid contained by an elastomeric skin. Electrodes are mounted on the surface of the rigid core and are 11 connected to an impedance-measuring device within the core. When the artificial skin touches an object the fluid path around the electrodes is deformed, producing impedance changes that map the forces received from the object. The researchers expect that an important function of such artificial fingertips will be adjusting robotic grip on held objects. Scientists from several European countries and Israel developed a prosthetic hand in 2009, called Smart Hand, which functions like a real one—allowing patients to write with it, type on a keyboard, play piano and perform other fine movements. The prosthesis has sensors which enable the patient to sense real feeling in its fingertips. Toys and games The 1990s saw some of the first attempts to mass-produce domestically aimed types of basic Artificial Intelligence for education, or leisure. This prospered greatly with the Digital Revolution, and helped introduce people, especially children, to a life of dealing with various types of Artificial Intelligence, specifically in the form of Tamagotchis and Giga Pets, iPod Touch, the Internet (example: basic search engine interfaces are one simple form), and the first widely released robot, Furby. A mere year later an improved type of domestic robot was released in the form of Aibo, a robotic dog with intelligent features and autonomy. AI has also been applied to video games. Music The evolution of music has always been affected by technology. With AI, scientists are trying to make the computer emulate the activities of the skillful musician. Composition, performance, music theory, sound processing are some of the major areas on which research in Music and Artificial Intelligence are focusing. Aviation The Air Operations Division AOD, uses AI for the rule based expert systems. The AOD has use for artificial intelligence for surrogate operators for combat and 12 training simulators, mission management aids, support systems for tactical decision making, and post processing of the simulator data into symbolic summaries. The use of artificial intelligence in simulators is proving to be very useful for the AOD. Airplane simulators are using artificial intelligence in order to process the data taken from simulated flights. Other than simulated flying, there is also simulated aircraft warfare. The computers are able to come up with the best success scenarios in these situations. The computers can also create strategies based on the placement, size, speed, and strength of the forces and counter forces. Pilots may be given assistance in the air during combat by computers. The artificial intelligent programs can sort the information and provide the pilot with the best possible maneuvers, not to mention getting rid of certain maneuvers that would be impossible for a human being to perform. Multiple aircraft are needed to get good approximations for some calculations so computer simulated pilots are used to gather data. These computer simulated pilots are also used to train future eair traffic controllers. The system used by the AOD in order to measure performance was the Interactive Fault Diagnosis and Isolation System, or IFDIS. It is a rule based expert system put together by collecting information from TF-30 documents and the expert advice from mechanics that work on the TF-30. This system was designed to be used for the development of the TF-30 for the RAAF F-111C. The performance system was also used to replace specialized workers. The system allowed the regular workers to communicate with the system and avoid mistakes, miscalculations, or having to speak to one of the specialized workers. The AOD also uses artificial intelligence in speech recognition software. The air traffic controllers are giving directions to the artificial pilots and the AOD wants to the pilots to respond to the ATC’s with simple responses. The programs that incorporate the speech software must be trained, which means they use neural networks. The program used, the Verbex 7000, is still a very early program that has plenty of room for improvement. The improvements are imperative because ATCs use very specific dialog and the software needs to be able to communicate correctly and promptly every time. 13 The Artificial Intelligence supported Design of Aircraft, or AIDA, is used to help designers in the process of creating conceptual designs of aircraft. This program allows the designers to focus more on the design itself and less on the design process. The software also allows the user to focus less on the software tools. The AIDA uses rule based systems to compute its data. This is a diagram of the arrangement of the AIDA modules. Although simple, the program is proving effective. In 2003, NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center, and many other companies, created software that could enable a damaged aircraft to continue flight until a safe landing zone can be reached. The software compensates for all the damaged components by relying on the undamaged components. The neural network used in the software proved to be effective and marked a triumph for artificial intelligence. The Integrated Vehicle Health Management system, also used by NASA, on board an aircraft must process and interpret data taken from the various sensors on the aircraft. The system needs to be able to determine the structural integrity of the aircraft. The system also needs to implement protocols in case of any damage taken the vehicle. News, Publishing & Writing The company Narrative Science makes computer generated news and reports commercially available, including summarizing team sporting events based on statistical data from the game. It also creates financial reports and real estate analyses. Another company, called Yseop, uses artificial intelligence to turn structured data into intelligent comments and recommendations in natural language. Yseop is able to write financial reports, executive summaries, personalized sales or marketing documents and more at a speed of thousands of pages per second and in multiple languages including English, Spanish, French & German. 14 Other Various tools of artificial intelligence are also being widely deployed in homeland security, speech and text recognition, data mining, and e-mail spam filtering. Applications are also being developed for gesture recognition (understanding of sign language by machines), individual voice recognition, global voice recognition (from a variety of people in a noisy room), facial expression recognition for interpretation of emotion and non verbal cues. Other applications are robot navigation, obstacle avoidance, and What is the first object recognition. Thing that comes to mind when you think of a robot? For many people it is a machine that imitates a human—like the androids in Star Wars, Terminator and Star Trek: The Next Generation. However much these robots capture our imagination, such robots still only inhabit Science Fiction. People still haven't been able to give a robot enough 'common sense' to reliably interact with a dynamic world. However , Rodney Brooks and his team at MIT Artificial Intelligence Lab are working on creating such humanoid robots. The type of robots that you will encounter most frequently are robots that do work 15 that is too dangerous, boring, onerous, or just plain nasty. Most of the robots in the world are of this type. They can be found in auto, medical, manufacturing and space industries. In fact, there are over a million of these . Type of robots working for us today : Some robots like the Mars Rover Sojourner and the upcoming Mars Exploration Rover, or the underwater robot Caribou help us learn about places that are too dangerous for us to go. While other types of robots are just plain fun for kids of all ages. Popular toys such as Teckno, Polly or AIBO ERS-220 seem to hit the store shelves every year around Christmas time. And as much fun as robots are to play with, robots are even much more fun to build. In Being Digital, Nicholas Negroponte tells a wonderful story about an eight year old, pressed during a televised premier of MITMedia Lab's LEGO/Logo work at Hennigan School. A zealous anchor, looking for a cute sound bite, kept asking the child if he was having fun playing with LEGO/Logo. Clearly exasperated, but not wishing to offend, the child first tried to put her off. After her third attempt to get him to talk about fun, the child, sweating under the hot television lights, plaintively looked into the camera and answered, "Yes it is fun, but it's hard fun." So what is a robot? A robot is a mechanical or virtual agent, usually an electro-mechanical machine that is guided by a computer program or electronic circuitry. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous and range from humanoids such as Honda's Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility (ASIMO) and Tosy's TOSY Ping Pong Playing Robot (TOPIO) to industrial robots, collectively programmed 'swarm' robots, and even microscopic nano robots. By mimicking a lifelike appearance or automating movements, a robot may convey a sense of intelligence or thought of its own. Well it is a system 16 that contains sensors, control systems, manipulators, power supplies and software all working together to perform a task. Designing, building, programming and testing a robots is a combination of physics, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, structural engineering, mathematics and computing. In some cases biology, medicine, chemistry might also be involved. A study of robotics means that students are actively engaged with all of these disciplines in a deeply problem-posing problem-solving environment. Types of robot Types of robots come in all shapes and sizes. The purpose of each robot type is engineered to perform and carry out its given responsibility. The different types of robots are designed to operate in a fashion that helps our everyday lives. They’re built with us in mind and have really improved our overall environment. Below is a list of the primary types of robots in the world today. Rescue Robot Mobile Robot Domestic Bots Military Bots Medical Bots School Bots Reading Robot Robots in society TOPIO, a humanoid robot, played ping pong at Tokyo International Robot Exhibition (IREX) 2009. Roughly half of all the robots in the world are in Asia, 32% in Europe, and 16% in North America, 1% in Australasia and 1% in Africa. 40% of all the robots in the world are in Japan,[52] making Japan the country with the highest number of robots. In Japan and other Asian countries, ideas of future robots have been mainly positive, and the start of the pro-robotic society there is thought to be possibly due to the 17 famous 'Astro Boy'. Asian societies such as Japan, and more recently in South Korea and China, believe robots to be more equal to humans, having them care for old people, play with or teach children, or replace pets etc. The general view in Asian cultures is that the more robots advance, the better. Future development Japan hopes to have full-scale commercialization of service robots by 2025. Much technological research in Japan is led by Japanese government agencies, particularly the Trade Ministry. As robots become more advanced, eventually there may be a standard computer operating system designed mainly for robots. Robot Operating System is an opensource set of programs being developed at Stanford University, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the Technical University of Munich, Germany, among others. ROS provides ways to program a robot's navigation and limbs regardless of the specific hardware involved. It also provides high-level commands for items like image recognition and even opening doors. When ROS boots up on a robot's computer, it would obtain data on attributes such as the length and movement of robots' limbs. It would relay this data to higher-level algorithms. Microsoft is also developing a "Windows for robots" system with its Robotics Developer Studio, which has been available since 2007 . Robotics sets : Main articles: Lego Mindstorms, Lego Mindstorms NXT, and Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0 , Lego initiated a robotics line of toys called 'Mindstorms' in 1998, and has continued to expand and update this range ever since. and the name is taken from a paper by Seymour Papert, a computer scientist and educator who developed the educational theory of constructionism, and whose research was at times funded by the Lego Group. 18 WHAT IS LEGO? Lego is a popular line of construction toys manufactured by The Lego Group, a privately held company based in Billund, Denmark. The company's flagship product, Lego, consists of colourful interlocking plastic bricks and an accompanying array of gears, minifigures and various other parts. Lego bricks can be assembled and connected in many ways, to construct such objects as vehicles, buildings, and even working robots. Anything constructed can then be taken apart again, and the pieces used to make other objects. Lego began manufacturing interlocking toy bricks in 1949. Since then a global Lego subculture has developed, supporting movies, games, competitions, and six themed amusement parks.Lego initiated a robotics line of toys called 'Mindstorms' in 1998, and has continued to expand and update this range ever since. The roots of the product originate from a programmable brick developed at the MIT Media Lab, and the name is taken from a paper by Seymour Papert, a computer scientist and educator who developed the educational theory of constructionism, and whose research was at times funded by the Lego Group.The programmable Lego brick which is at the heart of these robotics sets has undergone several updates and redesigned, with the latest being called the 'NXT' brick, being sold under the brand name of Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0. The set includes sensors that detect touch, light, sound and ultrasonic waves, with several others being sold separately, including an RFID reader. The intelligent brick can be programmed using official software available for Windows and Mac computers, and is downloaded onto the brick via Bluetooth or a USB cable. There are also several unofficial programs and compatible programming languages that have been made to work with the brick, and many books have been written to support this community. There are several robotics competitions which use the Lego robotics sets. 19 The earliest is Botball, a national U.S. middle- and high-school competition stemming from the MIT 6.270 Lego robotics tournament. Other Lego robotics competitions include Junior FIRST LEGO League (Jr.FLL) for students ages 6–9, FIRST Lego League (FLL) for students ages 9–14, and FIRST Tech Challenge (FTC) for high school students. Jr.FLL FLL, and FTC offer real-world engineering challenges to participants. FLL uses Lego-based robots to complete tasks. Jr.FLL participants build models out of Lego elements. FTC uses the NXT Intelligent brick and its pieces along with another building platform called TETRIX. In its 2010 season, there were 16,070 FLL teams in over 55 countries. In its 2010 season, there were 2,147 Jr.FLL teams with 12,882 total student participants in the United States and Canada[24] The international RoboCup Junior football competition involves extensive use of Lego Mindstorms equipment which is often pushed to its extreme limits. LEGO MINDSTORMS: The LEGO Mindstorm series of kits contain software and hardware to create small, customizable and programmable robots. They include a programmable brick computer that controls the system, a set of modular sensors and motors, and LEGO parts from the Technics line to create the mechanical systems. The hardware and software roots of the Mindstorms Robotics Invention System kit go back to the programmable brick created at the MIT Media Lab. This brick was programmed in Brick Logo. The first visual programming environment was called LEGO sheets,[1] since it was created by the University of Colorado in 1994 based on Agent Sheets. The original Mindstorms Robotics Invention System kit contained two motors, two touch sensors, and one light sensor. The NXT version has three servo motors and one light, sound, and distance as well as 1 touch sensor. The NXT 2.0 has 2 touch sensors as well as a light and distance sensor, and support for 4 without using a sensor multiplexer. LEGO Mindstorms may be used to build a model of an embedded system with computer-controlled electromechanical parts. Many kinds of 20 real-life embedded systems, from elevator controllers to industrial robots, may be modelled using Mindstorms. Mindstorms kits are also sold and used as an educational tool, originally through a partnership between Lego and the MIT Media Laboratory. The educational version of the products is called Lego Mindstorms for Schools, and comes with the ROBOLAB GUI-based programming software, developed at Tufts University using the National Instruments Lab VIEW as an engine. In addition, the shipped software can be replaced with third party firmware and/or programming languages, including some of the most popular ones used by professionals in the embedded systems industry, like Java and C. The only difference between the educational series, known as the "Challenge Set", and the consumer series, known as the "Inventor Set", is that it includes another touch sensor and several more gearing options. WHAT IS THE RCX? The first generation of Lego Mindstorms was built around a brick known as the RCX (Robotic Command eXplorers). It contains an 8-bit Renesas (Then a part of Hitachi) H8/300 microcontroller as its internal CPU. It also contains 32K of RAM that stores the firmware and user programs. The brick is programmed by uploading a program (written in one of several available programming languages) from a Windows or Mac computer to the brick's RAM via a special infrared (IR) interface. After the user starts a program, an RCX-enabled Mindstorms creation may function totally on its own, acting on internal and external stimuli according to the programmed instructions. Also, two or several more RCX bricks can communicate with each other through the IR interface, enabling inter-brick cooperation or competition. In addition to the IR port, there are three sensor input ports and three motor output ports (also usable for lamps, etc.). There is also an LCD that can display the battery level, the status of the input/output ports, which program is selected or running, and other information. 21 Version 1.0 RCX bricks feature a power adapter jack to allow continuous operation instead of the limited operation time when using batteries. In version 2.0 (as well as later 1.0s included in the RIS 1.5), the power adapter jack was removed. Power adapter equipped RCX bricks are popular for stationary robotics projects (such as robot arms) or for controlling Lego model trains. In the latter context, the RCX needs to be programmed with Digital Command Control (DCC) software to operate multiple wired trains. The IR interface on the RCX is able to communicate with Spybots, Scout Bricks, Lego Train, and the NXT (using a third-party infrared link sensor.) The RCX 1.0 IR receiver carrier frequency is 38.5 kHz, while the RCX 2.0 IR carrier frequency is 76 kHz. Both versions can transmit on either frequency.[6] The carrier signal is generated by one of the RCX's internal timers. The RCX communicates with a computer using a Serial or USB IR tower. The tower is supported by Windows 98, Me, and XP (32-bit). A patch is available for hyper-threading/multi-core CPUs. There is no formal support for Windows Vista (32-bit), but there are reports of correct functionality. The USB tower does not work on a 64-bit OS unless a 32-bit OS is used in conjunction with a virtual machine. The serial tower works normally under 64-bit Windows 7 using a third-party USB-to-serial adapter. All versions of the RCX have a unique number printed on it, necessary for technical support and used as the ID number of the RCX for your Lego Mindstorms account on the now-defunct Lego Mindstorms RCX website. The first RCX produced is marked "000001" and was on display at the Mindstorms 10th Anniversary event. LEGO MINDSTORM VIRSIONS: 1-Cybermaster Cybermaster was mainly sold in Europe and Australia/New Zealand, but was available for a short time in the United States via the Lego Club magazines. It was 22 aimed at a younger audience as an early attempt of merging computer gaming with robotics and Lego. The Pbrick shares many, especially software, features with the RCX but differs in appearance and technical specifications: 1 output (plus 2 built-in) and 3 sensors. It uses RF (27 MHz R/C band) instead of IR for communication. It has two built-in motors with integrated tachometers and speedometers. It is limited to passive sensors (a simple A/D with internal pull-up resistors). The sensors shipped with it are color-coded and have internal resistors in their open state (allowing the Pbrick to sense which sensor is attached to which port). It has a fixed firmware (so it cannot be upgraded or replaced). It has limited RAM for programs (395 bytes) and only one program slot. Despite its obvious limitations it has a number of advantages over its 'big brother', the RCX. The RF link has greater range and is omnidirectional. The built-in tachometer and speedometer sensors on the internal motors provides the same function as the external rotation sensor to the RCX, but without using up sensor ports. This makes it very useful for various mobile platforms and performing basic motion/positioning tasks. It talks the same protocol as the RCX but cannot communicate directly to it (due to IR vs RF) but with a repeater (a computer with 2 serial ports and a simple program) they can be integrated. 23 2- Codepilot Sold as part of the Barcode Truck kit. This unit was the first programmable brick (or Pbrick). It features a single motor, a single touch sensor and a light sensor. It is programmed by setting it to 'learn' and using the light sensor to feed barcoded commands. The command set is very limited. Since barcode is just a series of variances in light, this form of command entry was dubbed VLL (Visual Light Link) and has been used in several later Lego models. 3- Scout Lego also released a blue computer called the Scout, which has 2 sensor ports, 2 motor ports (plus one extra if linked with a Micro Scout using a fiber optic cable), and a built in light sensor, but no PC interface. It comes with the Robotics Discovery Set. The Scout can be programmed from a collection of built-in program combinations. In order to program the Scout, a user must enable "power mode" on it. The Scout can store one program. The Scout is based on a Toshiba microcontroller with 32KB of ROM and 1KB of RAM, where about 400 bytes are available for user-programs. Due to the extremely limited amount of RAM, many predefined subroutines were provided in ROM. The Scout only supports passive external sensors, which means that only touch, temperature and other unpowered sensors can be used. The Analog-to-Digital Converters used in the Scout does only have a resolution of 8 bits in contrast to the 10-bit converters of the RCX. There was a plan for Lego to create a booster set that allows you to program the Scout from a computer with a software such as RCX code. However, due to the complexity of this project, it was abandoned. The RCX can control the Scout brick using the "Send IR Message" program block. The RCX does all of the controlling, and therefore can be programmed with the PC, while the Scout accepts commands. The Scout brick must have all of its options set to "off". 24 4- Micro Scout The Micro Scout was added as an entry level to Lego robotics. It is a very limited Pbrick with a single built-in light sensor and a single built-in motor. It has seven built-in programs and can be controlled by a Scout, Spybotics or RCX unit using VLL. Like the Scout, the Micro Scout is also based on a microcontroller from Toshiba. The unit was sold as part of the Droid Developer Kit (featuring R2D2) and later the Darkside Developer Kit (featuring an AT-AT Imperial Walker). 5- Spybotics Spybotics is a robotics package. It consists of four colour-coded robots called Spybots, a programming language with which to control the Spybots, and ten simulated missions. 6- Lego Mindstorms NXT Lego Mindstorms NXT is a programmable robotics kit released by Lego in July 2006, replacing the first-generation LEGO Mindstorms kit. The kit consists of 577 pieces, including: 3 servo motors, 4 sensors (ultrasonic, sound, touch, and light), 7 connection cables, a USB interface cable, and the NXT Intelligent Brick. The Intelligent Brick is the "brain" of a Mindstorms machine. It lets the robot autonomously perform different operations. The kit also includes NXT-G , a graphical programming environment that enables the creation and downloading of programs to the NXT. The software also has instructions for 4 robots; Alpha-Rex (a humanoid), Tri-Bot (a car), Robo-Arm T-56 (a robotic arm), and Spike (a scorpion) 7- LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT Educational Version This is the educational version of the NXT set from LEGO Education, which is made for school use. Software is sold separately, and the Education Resource Set for the best use. It includes a light sensor, an ultrasonic sensor, a sound sensor, three lamps and a pair of touch sensors. The first set consists of about 400 pieces, and the extra set consists of about 600 pieces. The Education Version is most suited for those who 25 have older versions of MINDSTORMS sets around, mostly thanks to its 3 converter cables. It costs about US$410.00 with the Bluetooth Dongle 8- Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0 The Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0 was launched on 5 August 2009. It contains 619 pieces (includes sensors and motors), two Touch Sensors, an Ultrasonic Sensor, and introduced a new Color Sensor. The NXT 2.0 uses Floating Point operations whereas earlier versions use Integer operation.[10] The kit costs around USD 280. 9- Lego Mindstorm EV3 Lego announced the third generation Mindstorm platform called EV3. EV3 is a further development of the NXT.[11] The system will be available fall 2013. The LEGO MINDSTORMS EV3 set will include motors, sensors, the programmable brick, 550+ LEGO Technic elements and a remote control. One of the new features of the EV3 would be that it would be possible to not only use direct commands or the programs to control the programmable brick as was possible before, but also through an app via a smart device. WHAT IS LEGO MINDSTORMS NXT 2.0? It is the second set from LEGO's Lego Mindstorms series, launched on August 5, 2009 at the Lego Shop in the U.S. The set contains 619 pieces, including a new sensor that can detect colors. It is priced at approximately US$280, C$350, £230 or A$500. Kit features: Includes a sound editor, which may record any sound and then program the NXT Brick to play it. With the image editor you can upload a picture to the NXT Brick to appear on the screen. 26 Includes 619 pieces (including the NXT Brick) -NXT Intelligent Brick: 32-bit Atmel AT91SAM7S256 main microcontroller (256 KB flash memory, 64 KB RAM) 8-bit Atmel ATmega48 microcontroller @ 4 MHz (4 KB flash memory, 512 Bytes RAM) 100x64 pixel LCD Screen four 6-pin input ports (ports 1-4) three 6-pin output ports (ports A-C) USB Port Bluetooth Class II V2.0 Loudspeaker - 8 kHz sound quality, 8-bit resolution, 2–16 kHz sample rate Four Push Buttons Orange button: On/Enter Light grey arrows: moving left and right in the NXT menu Dark grey button: Clear/Go back Powered by six AA batteries or the NXT Rechargeable DC Battery -SENSORS: Parts can be ordered separately. In the original kit, the sensors included are the Color, 2 Touch, and an Ultrasonic. Color Sensor (9694), for detecting 6 different colors: blue, green, red, yellow, white, black Light Sensor (9844), for detecting levels of light. (Included in first version, but in 2.0, replaced by Color Sensor.) Touch Sensor (9843), a simple button that senses if something collided with it. Ultrasonic Sensor (9846), for measuring distances using inaudible sound waves. 27 Sound Sensor (9845), for basic "hearing". Capable of measuring volume, but cannot record actual sounds. Compass Sensor (MS1034), for detecting direction. Has a built-in calibrator to reduce interference from other magnetic items. (Not included in basic kit, for advanced users.) Accelerometer Sensor (MS1040), for sensing which general direction it's moving in. Also can measure G-force. (Not included in basic kit, for advanced users.) RF-ID Sensor, for communication between multiple robots. (Not included in basic kit, for VERY advanced users.) Rotation Sensor (Built into Servo Motors), for measuring how far it has turned. This is unique, because it measures based on the turn of the gears inside, rather than the motor itself. Useful for robots that will coast and act based on distance rolled. Bluetooth communication (Built into "Intelligent brick"), for communication with other devices. Can be used mid-program, or for downloading new programs and data -ACTUATORS: Servo Motor (9842) The color sensor can shine light in red, green, or blue. (Normally it senses color by using the lamp in a setting and reading the reflected light levels. It uses the same lamp here for other uses.) Programming Very simple programs can be created using the NXT Intelligent Brick itself. In order to create larger, more complex programs, programming software on a PC is required. The standard programming software is NXT-G, which is included in the package. Third-party programming software is also available, some of which is listed below: 28 1-NXT-G: NXT-G is the programming software included in the standard base kit. It is based on LabVIEW graphical programming. It features an interactive drag-and-drop environment. 2-LabVIEW Toolkit: NXT-G is powered by LabVIEW, an industry standard in programming. Created by National Instruments, LabVIEW uses data flow programming to create a virtual instrument. To allow for more advanced programming, in the graphical sense, National Instruments released a Toolkit for the NXT. Version 1.0 came out in December 2006. Since its release, several bugs have been found and new sensors have been created. While the toolkit does allow for the creation of new sensors, National Instruments has yet to formally release an update. 3-Lego::NXT: Lego::NXT provides an API between Perl and NXT. 4-Ada: A port of GNAT is available for the NXT. It requires nxtOSEK to run. The port includes Ada bindings to the NXT hardware and nxtOSEK. 5-Next Byte Codes & Not eXactly C: Next Byte Codes (NBC) is a simple open-source language with an assembly language syntax that can be used to program the NXT brick. Not eXactly C (NXC) is a high level open-source language, similar to C, built on top of the NBC compiler. It can also be used to program the NXT brick. NXC is basically NQC for the NXT.[2] It is the most widely used third-party programming language. 29 6-ROBOTC: ROBOTC is an Integrated development environment targeted towards students that is used to program and control LEGO NXT, VEX, RCX, and Arduino robots using a programming language based on the C programming language. 7-RoboMind: RoboMind is an educational programming environment that offers a concise scripting language for programming a simulated robot. These internationalized scripts can, however, also directly be exported to Lego Mindstorms robots. It does not requires custom firmware in order to run. 8-NXTGCC: NXTGCC is a GCC toolchain for programming the NXT firmware in C. 9-URBI: URBI is a parallel and event-driven language, with interfaces to C++/Java and Matlab. It also has a component architecture (UObject) for distributed computation. Urbi is compatible with many robots, including Nao (cf Robocup), Bioloid or Aibo. 10-leJOS NXJ: leJOS NXJ is a high level open source language based on Java that uses custom firmware developed by the leJOS team. 11-NxtOSEK: To be able to write in C (programming language)/C++, nxtOSEK can be used, but that requires custom firmware too. 12-MATLAB and Simulink: MATLAB is a high-level programming language for numerical computing, data acquisition and analysis. It can be used to control LEGO NXT robots over a Bluetooth serial port (serial port communication is part of the base 30 functionality of MATLAB) or via a USB connection; for example using the RWTH - Mindstorms NXT Toolbox (free & open-source). Simulink is a MATLAB-based environment for modeling and simulating dynamic systems. Using Simulink, a user can design control algorithms, automatically generate C code for those algorithms, and download the compiled code onto the LEGO NXT. MATLAB and Simulink code for NXT programming is freely available. 13-Lua: pbLua is an implementation of the Lua programming language, a general purpose scripting language, for Lego Mindstorms. 14-FLL NXT Navigation: FLL Nxt Navigation An open source program to help navigation on the FLL competition table. Uses NXT-G and .txt files to write programs. 15-ruby-nxt: ruby-nxt is a library to program the NXT for the Ruby programming language. Unlike the other languages for the NXT the code isn't compiled to a binary file. Instead the code is directly transmitted to the NXT via a bluetooth connection. This method of execution is significantly slower than executing compiled code directly. 16- Robotics. NXT: Robotics.NXT is a Haskell interface to NXT over Bluetooth. It supports direct commands, messages and many sensors (also unofficial). It has also support for a simple message-based control of a NXT brick via remotely executed program (basic NXC code included). 31 Lego mindstorms NXT disadvantages: Incompatible cable connectors that need to be purchased from LEGO and are costly, without any good reason (except, perhaps, avoiding the risk of American citizens plugging in a phone cable, if it was compatible). Messed-up bluetooth communication - they have invented an unreliable communication protocol on top of a reliable one - very stupid... (http://www.tau.ac.il/~stoledo/lego/btperformance.html) rechargeable battery module is too large, rendering many projects that are created for brick powered by AA cells useless, because the parts cannot be mounted when the battery module is obstructing the space under the brick early versions of firmware had a flaw in the firmware upgrade process, which was very impractical, fortunately, this has been fixed in later versions the software had many serious bugs (and still has some) making the work sometimes difficult, it is also not localized to many languages, making it difficult for kids who do not read English fluently to work with it The NXT-G software is not open-source!!! And you cannot build your own blocks without expensive commercial Lab View licence :-( Flash memory too small, 256KB is nothing. You can buy 4GB low cost flash disk, but they put 256 KB as the memory storage in a product released in 2006??? Wtf? The original RCX touch sensor was an analogue sensor, the NXT touch sensor is a 0/1 switch. The support for user blocks in the software is poor: the blocks are saved into separate directory, and they are not copied when you save your project to a different disk or folder - this results in a lot of disappointment when you learn that you did not copy your user blocks. big blunder: the program created in NXT-G does not have a textual representation, which would be easy to view, understand, debug, etc. (this is implied by the choice for using Lab View kernel, which was a huge mistake) very little support for creating interactive projects that communicate with PC while the project runs. 32 LEGO MINDSTORMS ADVANTAGES: the start up time for working with NXT is very short the assembly of the robot is very intuitive and no electrical wiring is necessary no workshop are needed . very familiar to the student. Lego Mindstorms NXT:Lego Mindstorms NXT is a programmable robotics kit released by Lego in late July 2006. The NXT is the brain of a Mindstorms robot. It's an intelligent, computer Controlled Lego brick that lets a Mindstorms robot come alive and perform different operations. Fig. 1. The Lego Mindstorms NXT. In the center, the NXT brick 1. Above, the three servo motors 6. Below, the four sensors: touch 2, sound 3, light 4 and ultrasonic 5. The NXT has three output ports for attaching motors – Ports A, B and C and four input ports for attaching sensors – Ports 1, 2, 3 and 4. It’s possible to connect a USB cable to the USB port and download programs from a computer to the NXT (or upload data from the robot to the computer). As an alternative the wireless Bluetooth connection can be used for uploading and downloading. In the specific case of our project we simply needed two motors (connected at ports A and C), but we used all the input ports for sensors (Ultrasonic Sensor – port 1, HiTechnic [20] Compass Sensor – port 2, HiTechnic Color Sensor – port 3, Sound Sensor – port 4). 33 Why choose LEGO MINDSTORMS Education NXT? LEGO MINDSTORMS Education (LME) is designed specifically for teachers and other adults working with groups of children aged 8 and up, combining a versatile LEGO building set, user-friendly software and progressive educational activities. LME provides a cost effective, motivating and highly enjoyable solution to cover local curriculum areas in science, engineering, control, design and technology. The software used is based on industry standard programming language that is effective to learn due to its icon based origins. By building and programming smart robots in a natural, step-by-step learning process, students put their knowledge into practice – and are challenged to come up with new ideas themselves. Explain Tools program Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0 34 Communications When connected by USB cable or Bluetooth Give your NXT a new name Check Battery voltage View available memory (in KiloBytes) Firmware version . Memory Select, then delete Programs, Sounds, Graphics, and Unused files. Can free up to 130Kb of Free Storage on the NXT. Tips and Tricks (1) The NXT has memory to store many programs NXT automatically powers down. Bluetooth Communications The NXT has bluetooth communications. If enabled, PCs, NXTs and other bluetooth devices can talk to each other. 35 Disable bluetooth during competition Tips and Tricks (2) Direction of connecting wires NXT wire connectors only fit one way. Can not be rotated. Batteries AA No worry about losing firmware. NiMH rechargeable batteries work. NiCads don't. Lithium rechargeables come with the FLL Mindstorm kits. Avoid stalling the motors, it drains batteries. Pointer Tool Grab Hand to move the display Comment Common Blocks Common blocks are full featured actions Like English statements o Move o Wait for an action Move Block o Display a value With many modifiers o Move direction, steering, distance, motors used . . . 36 Wait for light sensor, light threshold, sensor port, . . . MoveBlock Settings o Move Sound Display Switch (Touch) 37 38 The big open area (the graph paper) is your Work Area. Notice that right now there are only two items in the program steps -- the left one signifies the Start of your program and the right one is a placeholder for the first block or statement in your program . Along the left side of the window is the Programming Palette containing action blocks you select and place into your program. Each block does something different, you will learn about many of them in future projects. Think of them as “verbs”, these are the commands that tell your NXT Brick what to do and when. At the bottom of the Programming Palette are Palette Selector tabs where you can select other palettes of blocks. Along the top of the window are the Menu and Tool Bars. In the Menu bar you see the usual Windows menus, such as “File”, “Edit” and so on. Below that is the Tool bar, with quick-access commands that can speed up many common operations. As you hover your mouse above them you see a brief description (a “tooltip”) that tells you what that button does. In the lower right corner are the Map and Help tabs, these let you scroll around in a big program and get help for each type of block. The Configuration Panel in the lower left allows you to make selections and adjustments for any action block. sound : Sound block inserted after the Start Program Block as shown. Look at the bottom left of the window, the Configuration Panel should be displayed. This is where you make settings for that Sound block : 39 If not already selected, click on the Help tab (?) as shown and hover your mouse over the Sound block. You should then see information about the Sound block. For more detailed help you can click on “More Help >>” and additional info, samples and other links will appear: The Configuration panel for the Sound block allows you to select several kinds of sounds . Depending on the “Action” you select, your robot will play a sound from a Sound File (which you select) or a Tone, which you pick with a small piano-style keyboard. Your NXT Brick can play complex sounds (like voice and music) but it’s a small speaker, so it’s not very loud. move : a Move block. In the Programming Palette it looks like two meshing gears. Here are two screen shots – selecting a Move block, and the Move block in place in your program: Immediately after inserting the Move block the configuration panel allows you to make quite a few settings. It seems to be pretty dense with information, let’s review the parts that we’ll use in this activity: Port: Which motors to control? Which motor is on RIGHT? 40 Direction: Forward, Reverse or Stop? Turn: Go Left , Right or Straight? Which motor is on the LEFT? turn? What to do the after turning? EXAMPLES Example (1) The program is making the robot moves forward and then moving to the right, and continues to do so until there any things stop the robot body. The robot will do: Move forward for 5sec. Wait for 3sec. Turn right in 3sec. Wait for 3sec. Play sound for about 0.5sec Example(2) : This robot works on the balls of where colors : 1 - if white ball putt in the right . 2 - if black ball putt in the left . 3 - Otherwise does not implement any order . Initially requires: Show voice, and then walk . 41 Upon completion of the work: Stops for three seconds and then moving for four seconds and then stand and thus completed what is required. 42 References: 1- Brooks, R. A., “Intelligence without Reason”, In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 569-595. Sydney, Australia, 1991 2- Currie, Adam (1999). "The History of Robotics". Retrieved 2007-09-10. 3- Forster, Dion (2006). "Self validating consciousness in strong artificial intelligence: An African theological contribution". Pretoria: University of South Africa. 4- Crevier, Daniel (1993), AI: The Tumultuous Search for Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY: BasicBooks, ISBN 0-465-02997-3 5- Juan Antonio Breña Moral, “Develop leJOS Programs Step by Step”, Version 0.4, July 2008 6- McCorduck, Pamela (2004), Machines Who Think (2nd ed.), Natick, MA: A. K. Peters, Ltd., ISBN 1-56881-205-1 7- Neil Rosenberg , " Workshop – NXT Programming For Beginners " , Summer, 2012 , 10 June, 2013 . http://www.rocwnc.org/Beginning_NXT_Programming_Workshop.pdf 8- http://www.hightechkids.org/sites/default/files/CoachingLibrary/fll_prog ramming_101_nxt_g.pdf 9- ^ Not eXactly C 10- ^ NBC/NXC - NeXT Byte Codes and Not eXactly C 11- ^ RoboMind's Lego Mindstorms NXT support 12- ^ URBI NXT Page 13- ^ LeJOS, Java for Lego Mindstorms 14- ^ http://lejos-osek.sourceforge.net/index.php 43