* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Kyoto Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
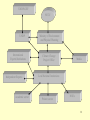
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Energiewende in Germany wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
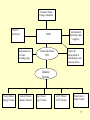
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Views on the Kyoto Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
REReP regional meeting on “Energy and climate” in South Eastern Europe May 22-23rd, 2008 Brussels, Belgium Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Short overview of the climate change and energy status, regional/cross-border projects, reporting 1 Status of National Communication under UNFCCC • In 1998 Republic of Macedonia became a party to the UN Convention on Climate Change • In January 2000, the Climate Change Project Office was set up within the Ministry of Environment and Physical Planning, financially supported by UNDP-GEF • In March 2003, Republic of Macedonia adopted the First National Communication on Climate Change and submitted it to the UNFCCC Secretariat. • In 2004 Republic of Macedonia ratified the Kyoto Protocol to the UNFCCC and became party in 2005 2 Relevant projects FNC: Time frame 2000-2003 SNC: Time frame 2005-2008 -ongoing Top-Ups Project: Time frame 2003-2004 Regional Project on Capacity building for improving the quality of GHG inventories (Europe and CIS Region) Development on National Strategy for the Clean Development Mechanism for the first commitment period under Kyoto Protocol, 20082012 3 Relevant National Strategic Documents • National Strategy for SD (on-going): Energy and Climate Change identified as key contributor towards SD • Second NEAP identified problems and solutions in climate changes • National Strategy for the CDM for the first commitment period 2008-2012 under Kyoto Protocol was adopted in February 2007 • National Strategy on environmental investments (ongoing), carbon financing recognized as potential tool for attracting investments • National strategy for environmental approximation • Strategy on Energy Efficiency 4 Relevant Programs, Projects energy/climate sector •Macedonian Sustainable Energy Program (GEF Program under CC focal area run by the energy Agency including two componenets: Sustainable Energy Financing Facility(SEFF)+Project Development Facility (PDF) • Investment Options in Energy Sector, 2003 •Solar water heaters project, financially supported by ADA •Projects under FP6 Programs and other EU supported projects for research 5 Relevant Documents in energy/climate -EU level• Treaty establishing the Energy Community, Environmental , Chapter III-the acquis on environment • http://www.enchapter.org (In-Depth Review of the Investment Climate and Market Structure in the Energy Sector, Energy Charter Secretariat-Republic of Macedonia 6 Relevant Documents&Laws-national level •Questionnaire prepared for the Commission of Sustainable Development (CSD) •EU Questionnaires, prepared for the purpose of the country’s application for EU candidate status, 2005 •MoUs for collaboration on Kyoto Protocol implementation with Italy, Slovenia, UNDP •National Indicators on environment (including energy and CC indicators) •Progress monitoring project 2007-2008 EC, DG ENV,Supporting the Accession Process of the Candidate Countries 7 Relevant Laws • Law on Environment • Law on energy, May 2006 • Law on Energy Agency establishment 8 Legislative level Law on Environment Climate change issues are incorporated in the Law on Environment, including details on: • preparation of inventories of GHG emissions and removals by sinks • action plan on measures and activities to abate increase of GHG emissions and to mitigate adverse impacts of climate change. • an Article on Clean Development Mechanism is introduced into the amended Law 9 Related institutional framework in the Country (including DNA for CDM) 10 UNDP-GEF NCCC UNDP International Experts/Institutions Independent Experts Academic sector Ministry of Environment and Physical Planning Climate Change Project Office Media Lead National Institutions Private sector NGOs 11 DNA under the MoEPPSingle Model Ministry CDM Executive Board Figure 1 DNA structure in Macedonia Ministry of Environment and Physical Planning DNA Secretariat Department of Sustainable Development Technical Review Ministry of Economy Technical Review Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry & Water Supply Technical Review Ministry of Transport and Communication Written Opinion on Approval Letter Sectoral Ministry (Agric, Econ, or Trans) Ministry of Finance Ministry of Foreign Affairs Technical Review Ministry of Finance Technical Advisory/Working Group Provides written opinion on CDM projects 12 Chapters covered by National Communication • • • • • • • • GHG Inventory Transfer on technologies, including activities relating to the transfer of, and access to, environmentally sound technologies and know-how, the development and enhancement of endogenous capacities, technologies and know-how, and measures relating to enhancing the enabling environment for development and transfer of technologies Research and systematic observation, including information on participation in, and contribution to activities and programmes, as appropriate, of national, regional and global research networks and observing systems, as well as information on research relating to programmes containing measures to mitigate climate change; programmes containing measures to facilitate adequate adaptation to climate change; and the development of emission factors and activity data. Education, training and public awareness Capacity building, including information about the involvement of stakeholders in capacitybuilding, coordination and sustainability of capacity-building activities, and the dissemination and sharing of information on capacity-building activities. Information and networking, including information on participation in and contribution to networks, and access to, and use of, information technologies for information exchange Chapters on Vulnerability and Adaptation including intersectoral action plan GHG Abatement strategy, 13 National GHG Inventory Process The GHG Inventory developed within the FNC • Applied IPCC 1996 Revised Guidelines, for the base year 1994 and series for the period 19901998. • Covers the three main greenhouse gases – CO2, N2O and CH4, for the following sectors: Energy, Industrial Processes, Agriculture, Land-use Change and Forestry, and Waste 14 GHG Inventory within SNC • Base year 2000, according to the Guidelines for the preparation of National Communications (17/CP.8) • Recalculation of the series 1990-1998, taking into account the gaps, uncertainties and recommendations from the stocktaking exercise and improved data from the new studies and assessments on national level • Applying improved emission factors for Energy and Waste sector, which will be developed under the regional project • Calculation of the GHG Inventories for 1999 in order to establish continual series of 10 years • For Energy, Industry and Waste sectors to the extent possible, calculation for the GHG emissions for the years 2001 and 2002 15 Institutional arrangements MOEPP, as a supervisor and coordinator of the whole process; National institution, as a responsible party for the compilation of the Inventory Independent sectoral national experts/consultants for the critical sectors not covered by the National institution. 16 National Climate Change Committee UNFCCC Secretariat Governmental Institutions (data suppliers) MOEPP Representatives of wider working group Experts for improvement of methodologies and emission factors National Institution NITL Database Operator Energy Enterer Energy Checker Industry Enterer Industry Checker Agr. Enterer Agr. Checker LUCF Enterer LUCF Checker Waste Enterer Waste Checker 17 Inventory Cycle for the SNC Responsible parties: NI+NE Revision of the inventory under the FNC (series 1990-1998) Application of Tier 2 methodology to the extent possible Extension of the current GHGs set with non-direct GHGs: HFCs, PFCs and SF6, as well as CO, NOx, SOx and NMVOCs Identification/verification of data sources Entering and documenting the input data (activity data and emission factors) for the upgraded inventory Checking and validating the input data and emission estimates 18 Inventory Cycle for the SNC Integrative tasks (related to the whole inventory) Responsible party: NI Upgrading/Maintaining the GHG Inventory database Calculating the integral GHG emissions Reporting the total GHG emissions Performing Key Sources analyses Undertaking Uncertainty Management to extent possible Preparing GHG Inventory Report + Summary in English and in Macedonian Experts’ and stakeholders’ discussion about the results 19 Further steps needed -approximation• DIRECTIVE 2003/87/EC of the EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 13 October 2003 establishing a scheme for greenhouse gas emission allowance trading within the Community and amending Council Directive 96/61/EC, as amended by Directive 2004/101/EC 20 Further steps needed • Developing and maintaining national capacity for archiving and updating inventory data is critical to the sustainability of the inventory process. Identified institutions for different sectors need to be supplemented by existing infrastructure and technical expertise. • Further, deeper involvement of national institutions obliged for data collection (the Statistical Office) is of crucial importance in order to make adjustments of the data collection methodology, aiming to cover identified GHG related data in the above sectors. 21 Further steps needed • Set of institutional, legislative and technical measures need to be undertaken, which will not only provide more sophisticated GHG inventory in place, but will also contribute towards providing a background for establishment of a national registry system, as a country requirement within its process of EU accession. • As an initial step, amendments to the existing Law on Environment are necessary, in order to create background for creation of Law on greenhouse gas allowance trading, i.e to transpose the Emission Allowance Trading Directive (EATD) into national legislation. • Introduction of a learning-by-doing “pilot phase” for Emissions Trading for a two year period, aiming to strengthen capacities at the local authorities, companies and other stakeholders for the implementation of the system will be very helpful. 22 Thank you for the attention Teodora Obradovik Grncarovska, M.Sc, UNFCCC Focal point for the Republic of Macedonia E-mail: [email protected] 23 For more information see: www.moepp.gov.mk www.unfccc.org.mk 24