* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 12: Bioenergetics
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
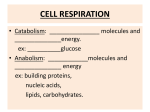
Chemistry 506 Dr. Hunter’s Class Chapter 20. 1 Chemistry 506: Allied Health Chemistry 2 Chapter 20: Bioenergetics Energy Generation in the Cell Introduction to General, Organic & Biochemistry, 5th Edition by Bettelheim and March: Chapter 20, Pages 641-664 Outline Notes by Dr. Allen D. Hunter, YSU Department of Chemistry, 2000. Outline 1A SECTION(S) 20.1/2 INTRODUCTION & MITOCHONDRIA .......................................................................................... 2 1B SECTION(S) 20.3 COMMON CATABOLIC MOLECULES ............................................................................................ 6 1C SECTION(S) 20.4 CITRIC ACID CYCLE ........................................................................................................................ 12 1D SECTION(S) 20.5/6/7 ATP SYNTHESIS ........................................................................................................................... 14 1E SECTION(S) 20.8 USES OF ENERGY IN CELLS ........................................................................................................... 15 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 1A Section(s) 20.1/2 Chapter 20. 2 Introduction & Mitochondria Metabolism All of the chemical reactions in a cell Catabolism The chemical reactions in the cell that break complex molecules down Anabolism The chemical reaction in the cell that build complex molecules Complexity Thousands of interrelated compounds, reactions, and enzymes All under detailed feedback and control Ultimately governed by the DNA and the cell’s responses to the environment 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 Chapter 20. Energy Generation in the Cell General Process Overall Catabolic Pathway Figure 20.1 on page 643 CO2 multiple pathways citric acid cycle C2 & C4 NADH FADH2 membrane pumps ATP generation H+ returns ATPase 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University high [H+] intermembrane 3 Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 Chapter 20. Structure of Mitochondrion Figures 20.2 and 20.3 on pages 644 and 645 Outer Membrane Inner Membrane High [H+] Low [H+] H+ Pumps ATPase Inter-membrane region Folds called Crista Central region 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University 4 Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 Chapter 20. 5 Summary of Process Multiple “food” molecules get converted into a small number of common C2 and C4 molecules These C2/C4 molecules enter the center of the mitochondria where they are “processed” by the citric acid pathway The citric acid pathway gives H+ and e- which are used to generate NADH and FADH2 These are e-, H+, and energy carrier molecules These are used by proteins on the inner mitochondrial membrane to pump H+ ions from the center to the intermembrane region This gives a proton gradient This proton gradient drives protein reactions on the inner membrane which allow them back into the center of the mitochondrion which simultaneously using their energy to generate ATP from ADP 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 1B Section(s) 20.3 Chapter 20. Common Catabolic Molecules Pi-AMP-ADP-ATP Path Inorganic Phosphate, Pi, H2PO4- (charge depends on pH) Adenosine Monophosphate, AMP Adenosine Diphosphate, ADP Adenosine Triphosphate, ATP ATP is the highest energy 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University 6 Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 Chapter 20. Structure of ATP Molecule Page 646 of the text Adenine, Ribose, Adenosine, and Phosphate moieties ADP and AMP structures Adenosine NH 2 N N - N O O O P O O P O - O P - O O CH 2 OH Adenine O H H H OH Phosphate groups N OH Ribose 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University 7 Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 Chapter 20. Phosphate Bonds ATP is “energy currency” of the cell “high energy bonds” vs. convertible energy Adenine - O O O P O O P O- O P O- O CH 2 O- Ribose Hydrolysis Hydrolysis of ATP ATP + H2O ADP + Pi + Energy Hydrolysis of ADP ADP + H2O AMP + Pi + Energy Normally ADP not hydrolyzed by cells 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University 8 Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 Chapter 20. 9 Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, NAD Figure 20.6 on page 648 Often Referred to as NAD+ to reflect the charge on the Nicotinamide base Is a Coenzyme Contains ADP, Ribose, and a Nicotinamide Base O C NH 2 N O ADP CH 2 H O Nicotinamide H H H OH OH Ribose NAD+ + H+ + 2e- NADH Thus NADH carries 2e-, a proton, and energy to where it is needed 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 Chapter 20. 10 Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide, FAD Figure 20.6 on page 648 Is a Coenzyme Contains ADP, Ribitol (a straight chain sugar), and Flavin The latter two groups making up Riboflavin (the vitamin) O ADP OH CH C H2 N CH CH CH 2 Flavin OH OH Ribitol Riboflavin FAD + 2H+ + 2e- FADH2 Thus FADH2 carries 2e-, two protons, and energy to where it is needed 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 Chapter 20. 11 Acetyl CoA Figure 20.7 on page 649 Transports C2 units (acyl groups) Often written as CH3-CO-S-CoA or Acyl-CoA O CoA S C CH 3 O N H O Phosphorylated ADP Pantothenic Acid H2C H2 C Mercaptoethylamine S C CH 3 Acyl Group CoEnzyme A Notice the overall similarity in the structures of ATP, NADH, FADH2, and Acetyl CoA 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 1C Section(s) 20.4 Chapter 20. 12 Citric Acid Cycle Also known as Krebs Cycle and Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Figure 20.8 on page 650 Overall Molecular Flow 8 different chemicals 8 different sets of enzymes Takes place in the center of the mitochondrion C2 fragments enter the cycle as Acetyl CoA C2 (Acetyl CoA) NADH C4 C6 NAD+ C6 NAD+ C4 NADH + CO2 C4 C5 FADH2 C4 NAD+ C4 FAD GTP NADH + CO2 GDP 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 Chapter 20. 13 Overall Energy Flow Produces two CO2, three NADH, one FADH2, and one GTP per cycle GTP is Guanidine Triphosphate (ATP like) 3 NADH 9 ATP 1 FADH2 2 ATP 1 GTP 1 ATP Thus: Acetyl CoA 12 ATP 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 1D Section(s) 20.5/6/7 Chapter 20. 14 ATP Synthesis Proton Pumps Flavo Protein, FeS Protein, Quinone Enzyme Complex Sited on the inner mitochondrial membrane Use NADH and FADH2 to pump H+ into the inter-membrane space This generates the proton gradient ATPase An enzyme on the inner mitochondrial membrane Allows H+ to flow back into the central membrane cavity H+ flow mechanically coupled to ATP generation ADP + Pi (ATPase) ATP Net Results Each NADH 3 ATP Each FADH2 2 ATP 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Dr. Hunter’s Class Chemistry 506 1E Section(s) 20.8 Uses of Energy in Cells Molecular Synthesis Anabolic Pathways To Generate Gradients via Active Pumps H+, K+, etc. Mechanical Energy Muscles Molecular motors Heat Problems: 20.1 to 20.49 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Chapter 20. 15 Chemistry 506 Dr. Hunter’s Class Chapter 20. 16 Index of Topics and Vocabulary A Acetyl Co .......................................................................... 13 Acetyl CoA ................................................................. 11, 12 acyl groups........................................................................ 11 Acyl-CoA.......................................................................... 11 Adenine............................................................................... 7 Adenosine ........................................................................... 7 Adenosine Diphosphate ...................................................... 6 Adenosine Monophosphate ................................................. 6 Adenosine Triphosphate ..................................................... 6 ADP ............................................................ 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 14 AMP ............................................................................... 6, 7 Anabolic Pathways ........................................................... 15 Anabolism........................................................................... 2 ATP ................................................................ 5, 6, 8, 11, 14 ATP like............................................................................ 13 ATP Synthesis .................................................................. 14 ATPase ............................................................................. 14 B break complex molecules down .......................................... 2 build complex molecules .................................................... 2 C C2 fragments..................................................................... 12 C2 units............................................................................. 11 Catabolic Pathway .............................................................. 3 Catabolism .......................................................................... 2 central membrane cavity ................................................... 14 CH3-CO-S-CoA ................................................................ 11 chemical reactions in a cell ................................................. 2 Citric Acid Cycle .............................................................. 12 CO2 ................................................................................... 13 Coenzyme ..................................................................... 9, 10 Common Catabolic Molecules ............................................ 6 Complexity ......................................................................... 2 convertible energy .............................................................. 8 Flavin ............................................................................... 10 Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide............................................ 10 Flavo Protein .................................................................... 14 food molecules ................................................................... 5 G Gradients via Active Pumps ............................................. 15 GTP .................................................................................. 13 Guanidine Triphosphate ................................................... 13 H H+ .......................................................................... 5, 14, 15 H2PO4- ................................................................................ 6 Heat .................................................................................. 15 high energy bonds .............................................................. 8 Hydrolysis .......................................................................... 8 Hydrolysis of ADP ............................................................. 8 Hydrolysis of ATP ............................................................. 8 I inner membrane .................................................................. 5 inner mitochondrial membrane..................................... 5, 14 Inorganic Phosphate ........................................................... 6 inter-membrane region ....................................................... 5 inter-membrane space ...................................................... 14 Introduction & Mitochondria ............................................. 2 K K+ .................................................................................... 15 Krebs Cycle ...................................................................... 12 M DNA ................................................................................... 2 Mechanical Energy........................................................... 15 mechanically coupled to ATP generation ......................... 14 Metabolism......................................................................... 2 mitochondrion .................................................................. 12 Mitochondrion .................................................................... 4 Molecular Flow ................................................................ 12 Molecular motors ............................................................. 15 Molecular Synthesis ......................................................... 15 Muscles ............................................................................ 15 E N e- NAD ................................................................................... 9 NAD+ ................................................................................. 9 NADH .............................................................. 5, 11, 13, 14 Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide .................................. 9 Nicotinamide base .............................................................. 9 Nicotinamide Base ............................................................. 9 D ............................................................................. 5, 9, 10 energy ........................................................................... 9, 10 Energy................................................................................. 8 energy carrier molecules ..................................................... 5 energy currency .................................................................. 8 Energy Flow ..................................................................... 13 Energy Generation in the Cell............................................. 3 enzyme .............................................................................. 14 enzymes ............................................................................ 12 F P Phosphate ........................................................................... 7 Phosphate Bonds ................................................................ 8 Pi ................................................................................ 6, 14 Problems........................................................................... 15 proton ........................................................................... 9, 10 proton gradient ............................................................. 5, 14 FAD .................................................................................. 10 FADH2 ........................................................ 5, 10, 11, 13, 14 feedback and control ........................................................... 2 FeS Protein ....................................................................... 14 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University Chemistry 506 Dr. Hunter’s Class Proton Pumps .................................................................... 14 pump H+............................................................................ 14 pump H+ ions ...................................................................... 5 Chapter 20. 17 S Q similarity in the structures ................................................ 11 Structure of ATP Molecule ................................................ 7 sugar ................................................................................. 10 Quinone Enzyme Complex ............................................... 14 T R Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle ................................................. 12 Ribitol ............................................................................... 10 Riboflavin ......................................................................... 10 Ribose ............................................................................. 7, 9 U Uses of Energy in Cells .................................................... 15 V vitamin ............................................................................. 10 2000, Dr. Allen D. Hunter, Department of Chemistry, Youngstown State University