* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CP-Chapter7-Discovery of cells
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
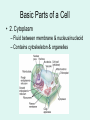
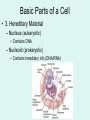
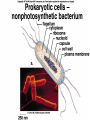
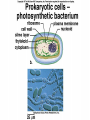
Study the image… DO NOW: • 1. Do you think the structure of the onion cells determines the overall size and shape of the plant? Explain your answer. • 2. If one cell of the onion were changed or damaged, how might it affect the overall structure or function of the plant? • 3. If one cell is not important to the survival of the plant, why is it still worthwhile to study plants at the cellular level? The Discovery of Cells • Cell – smallest unit that can perform all life processes The Cell Theory • 1. all living things are composed of one or more cells (Hooke) • 2. cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism (Schleiden & Schwann) • 3. cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells (Virchow) Hooke (1665) • Used early light microscope • Observed cork cells from a dead oak tree • Called the cells “little boxes” Leeuwenhoek (1678) • First person to observe living cells • Saw bacteria • Saw protists in pond water – Spirogyra Schleiden (1839) • Viewed plant cells • Organisms composed of cells, the basic units of life Schwann (1839) • Viewed animal cells • Organisms composed of cells, the basic units of life Virchow (1855) • “every cell originates from a pre-existing cell” Do Now: 1. Study the cell at your lab table. 1. When you are finished, switch with the lab table next to you. 1. Write down the FOUR things you think ALL CELLS HAVE! Cell Shape & Size • Diversity in shape reflects function • Shape can be simple or complex Four (4) Things all cells have • • • • 1. Plasma (cell) membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Hereditary material 4. Ribosomes Basic Parts of a Cell • 1. Plasma (cell) membrane – Selectively permeable – Covers surface – Acts as barrier Basic Parts of a Cell • 2. Cytoplasm – Fluid between membrane & nucleus/nucleoid – Contains cytoskeleton & organelles Basic Parts of a Cell • 3. Hereditary Material – Nucleus (eukaryotic) • Contains DNA – Nucleoid (prokaryotic) • Contains hereditary info (DNA/RNA) Basic Parts of a cell • 4. Ribosomes – In cytoplasm – Where protein synthesis (making proteins) occurs Types of Cells • Prokaryotic Cells • Eukaryotic Cells