* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit FOur
Intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Personality psychology wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Vladimir J. Konečni wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
James M. Honeycutt wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
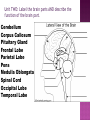
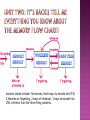
Final Exam Review Define psychology—what is the most credible association dedicated to psychology? Why is psychology called a soft science? What is the difference between hard and soft sciences? What are schools of psychology? Briefly summarize the ideas behind the following schools: Humanistic, Psychodynamic, Structuralism, Functionalism, Biological , Gestalt, Behaviorism, Cognitive, Behavioral 1. Clinical A. 2. Community B. 3. Counseling 4. Developmental C. D. E. 5. Experimental 6. Industrial/Organizational 7. Educational F. G. H. 8. School 9. Social I. works to overcome educational difficulties studies the maturation process works with diagnosis and treatment of disorders studies any mental psychological issue develops and presents programs to help maintain mental health studies how society influences the individual works with psychological issues relating to business works with people who exhibit trouble coping with everyday problems studies issues related to how people learn Define the following: Independent Variable Dependent Variable Hypothesis Experimental Group Control Group Try this sample: “Mrs. Muller wanted to test the effects of caffeine on human behavior test scores. She believes that if caffeine is given to a person, their test scores will be higher.” How will she set up and run her experiment? What type of research study is this? Clues: “Yippee! I can’t wait to try it!” Define and give an example of the following: a. Halo Effect b. Hawthorne Effect c. John Henry Effect d. Novelty Effect Nature v Nurture Briefly define the debate and explain why it is controversial. How did we learn about this debate throughout the entire semester? Pull examples from specific units! Milgram’s experiment: What were the details of this experiment? Why was it controversial? What did it change in psychology? Define the research type: Experimental Descriptive Correlational Historical Causal-Comparative Describe a specific experiment design that fits into each of the four areas. What is the difference between natural observation and a typical experiment? Unit TWO: Label the brain parts AND describe the function of the brain part. Cerebellum Corpus Callosum Pituitary Gland Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Pons Medulla Oblongata Spinal Cord Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe Explain all of the theories of intelligence we discussed in class. Be sure to include the name of the theorist, the aspects of intelligence, and whether or not you agree with this perspective. Options: Describe the lower extreme of intelligence in regards to the four types of mental retardation. What are the four categories and what defines each in regards to IQ levels and functioning abilities? What three criteria must be met for one to be diagnosed with mental retardation? Spearman Sternberg R.B. Cattell Thurstone Guilford Gardner Name each of the seven “sins” of memory to define. After you define the “sins” be sure to use an example of how it affects memory. (finish quickly—try them all!) Define and give examples: State-Dependent Memory Effect Context-Dependent Memory Effect Clues— here are the names of the sins: Persistence, Blocking, Transience, Absentmindedness, Bias, Misattribution, Suggestibility Defend and discuss this statement: Discuss the following: What is thinking? What are the three types of thinking we discussed in class? As per our discussion on Daniel Pink’s novel A Whole New Mind, it was concluded that Left brain functioning is important but no longer sufficient to compete in our challenging and changing world. What is the difference between right and left brain capabilities? Name examples of the characteristics of each side. Who was Phineas Gage and what did his study conclude about frontal lobe brain study? Why is this study important? What real-life examples did we discuss? What are reliability and validity in regards to: Running an experiment? Intelligence testing? Answers should include: five senses, three ways to encode into STM, 2 theories on forgetting, 2 ways of rehearsal, 3 ways to encode into LTM, retrieval from the three filing cabinets. Describe Operant Conditioning including: Reinforcer Positive Reinforcer Negative Reinforcer Punishment Describe classical conditioning including: US UR CS CR Use the Pavlov’s Dogs experiment to put it all together! “Whenever you lie in your bed, you normally fall asleep very quickly, more quickly than you would on the couch. One week, you experience a lot of stress, and instead of falling asleep, you lie awake several nights in a row. Now, although the stress is gone, you have difficulty sleeping in your bed.” Define the following in regards to the example scenario. US: UR: CS: CR: Phases Define the following specifically in terms of classical conditioning learning—what is happening at each stage? of Learning Acquisition Phase Extinction Phase Spontaneous Recovery Reconditioning Can you draw the phases of learning chart? Define the following: Stimulus Generalization Stimulus Discrimination Taste Aversion (Garcia Effect) Phobias How could you describe the difference between generalization and discrimination in this case? CS: Large Black Dog CR: Fear 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. For each of the following explain if it is positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement or a punishment and WHY! Police pulling drivers over and giving prizes for buckling up. Suspending a baseball player for hitting a ref after a bad call. An inmate is allowed extra TV time after completing all of his assigned duties well. Teacher holds a student during lunch until they complete their homework. A cat presses a lever to open a door to get out of the puzzle box. A mother smiles when their child utters “MAMA”. Taking cough medicine to stop a cough. A child is put into “time out” for talking back. A driver is given a ticket for running a red light. You get a zero for cheating. You get an A on your final!! Examples: Define the following schedules of reinforcement: Fixed ratio Variable ratio Fixed interval Variable interval What is the difference between a ratio and an interval? Which schedule of reinforcement is described below? 1. Getting a pay check every other week. 2. Pop quizzes 3. Slot machines at gambling casinos 4. A worker receives $1 for every 100 envelopes stuffed What Review Piaget’s theory of child development. Do you remember the stages listed below? Sensorimotor Preoperational Concrete Operational Formal operations is temperament? The difference between: Easy and difficult infants? Secure and insecure attachments? What Review Birth Order and Personality (reading from packet) How does this tie into the nature v nurture debate? Permissive are the three types of parenting styles (on the spectrum) and what are the positives and negatives of each? Authoritative Authoritarian Trait Recall the major theories of personality listed to the right. Do you remember the basics of each one? Theory Social-Cognitive Theory Humanistic Theory Psychodynamic Theory What are the positives and negatives to Gordon Allport’s Trait Theory and OCEAN test? What is the difference between: Cardinal Trait Central Trait Secondary Trait Give an example of a historical figure who lived his/her life by a cardinal trait. Other examples? What are the foundations of Freud’s theory of personality? Focus on three main beliefs of Freud and his followers! What is the significance of this iceberg? What is “free association?” How does it relate to psychoanalysis? How do the following terms relate to the iceberg theory? Morality Principle Pleasure Principle Reality Principle What are the psychosexual stages and how do they connect to psychoanalysis? What are the defense mechanisms and how do they relate to psychoanalysis? Does it seem like I am really reviewing Freud and Psychoanalysis? Good observation. Maybe there is a reason… Who are the NeoFreudians and how do they differ from Freud? Compare and contrast Freud’s psychosexual stages with Erikson’s psychosocial stages What’s the Humanistic Theory all about? Don’t forget about Carl Rodgers and Abraham Maslow Describe What are the major differences between normal and abnormal behavior? Specific criteria we discussed in class! Look in your abnormal psych mini-packet if you forget. the changes in treatment of the mentally ill from the 1800s to present day. Don’t forget about good old Nelly Bly! What What is the purpose of the DSM and who approves of the published updates? similarities did we find in the diagnosis of mental disorders? Think of the types of criteria found within the DSM of multiple disorders… HINT: one possible answer could be: evidence of social and occupational dysfunction. What is sociology? What are the possible careers for a person interested in sociology? How does sociology differ from psychology? What other “soft science” field is similar to sociology? (it studies specific cultures) What is culture? Difference between culture and society? Material v Nonmaterial culture Identify and give examples of the following: Norms Folkways Mores Laws Cultural Universals Ethnocentrism What is cultural anthropology? Describe Margaret Mead’s case study of the Arapesh and Mundugamor peoples… How does this study relate to the nature v nurture debate? Describe What are the 5 agents of socialization? Define: Socialization Resocialization Total Institution the case of “Genie the Wild Child” and how it relates to both socialization AND the nature vs. nurture debate. What is collective behavior and list the collectivities we discussed in class. Why is collective behavior hard to study? are social movements different than collective behavior? Your task: Take each of the social movements below and describe which type of social movement it is/was: How Women’s Movement Revolutionary War 1960s Peace Movement The Religious Right (Roe v. Wade – A women’s right to privacy) Do you know your theories? What is deviance? What two things must occur for an action to be labeled as deviance? CulturalTransmission Structural Strain Control Conflict Labeling What social functions come from deviance? What are the characteristics of cults as discussed in class? How does a cult differ from a religion? What tactics do cults often use to “suck people in?” Work on essay questions 6 and 7. Jeopardy review sheets to complete with a partner…