* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SBI 4UI Review of Biochemistry Name: Learning Goals R Y G
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
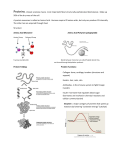
SBI 4UI (1.1) (1.1) (1.1) (1.1) (1.1) (1.1) (1.1) (1.2) (1.2) (1.2) (1.2) Review of Biochemistry Name: ________________________________________ Learning Goals Explain isotopes, radioisotopes Explain how the parent isotope will decay into the daughter isotope using carbon 14 as an example. Include an explanation of a half-life and how it can be used to predict the age of organic compounds. Draw and label a graph of radioactive decay. Explain organic compounds Compare intramolecular forces to intermolecular forces Explain physical bonds like hydrogen bonds Compare hydrophobic and hydrophillic Explain an ion and give examples Identify the 4 groups of organic compounds and their characteristics Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic acids For carbohydrates, you need to; know the monomer structure of glucose (ie: draw it or identify it in a model) know the monomer is a saccharide and these saccharides make polymers. identify functional groups in the glucose. explain what disaccharides and polysaccharides are with examples. explain isomers. know that monomers are held by glycosidic linkages. draw diagrams and explain condensation & hydrolysis reactions to join monomers. For lipids, you need to; know the monomer structure of triglyceride (ie: glycerol + 3 fatty acids) draw the monomer and identify it in a model. know that the monomer cannot form a polymer. know that the lipid has a non-polar fatty acid region and , in the case of a phospholipid, a polar phosphate group in place of one fatty acid chain. know the functional groups on fatty acids and glycerol. compare steroids to lipids. draw diagrams and explain condensation & hydrolysis reactions to join molecules together. For proteins, you need to; know that the monomer is amino acid. know there are 20 different amino acids and the basic structure is an amine group, a carboxyl group and a side “R” group along with a H atom. It is the R group that will determine the type of amino acid. know there are essential and non-essential amino acids. know how these monomers can attach using peptide bonds to form polymers called polypeptides. The polypeptides can fold by attaching the R groups together (ie: the R groups are polar, non-polar, electrically charged, etc.) to form secondary and tertiary structures. You can then attach different polypeptides to form a quaternary structure. R Y G know that the polypeptide is the primary structure. the shape that the protein forms will determine what it will act upon. draw diagrams and explain condensation & hydrolysis reactions to join monomers. (1.3) Explain the following reactions in words & diagrams: neutralization (acid-base, pH, buffers), redox (reduction –oxidation), condensation/hydrolysis (forming or breaking polymers) (1.3) Explain enzymes in terms of; the type of molecule (enzymes vs co-enzymes) its functions ( catalyst, how it affects rate of chemical reactions, activation energy) how it works ( active sites, substrate, enzyme-substrate complex, induced fit model) it conditions of function (temperature, pH, inhibitors, activators, allosteric site) (activity) Explain the purpose, background and conclusions for the activity Nutrients & Indicators (activity)Explain the purpose, background and conclusions for the activity Amylase & Starch (activity) Explain the purpose, background and conclusions for the activity Dialysis Tubing (activity) Explain the purpose, background and conclusions for the activity Half Life of the M&Mium (activity) Explain the purpose, background and conclusions for the activity Beef Liver Enzyme (activity) Explain the purpose, background and conclusions for the activity Effects of Saltwater and Fresh water on Potato Cells (2.1 and the power point), compare prokaryotes to eukaryotes and explain the following cell structures AND be able to identify them in a plant-animal cell diagrams nucleus (DNA, nucleolus) rough & smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus (steps in protein excretion), lysosomes, peroxisomes, vacuoles, vesicles, chloroplasts, mitochondria, cell wall, cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, cell membrane (fluid mosaic model, phospholipids & membrane proteins) (2.2) Explain and compare 3 types of membrane transport; passive transport (diffusion, osmosis & facilitated diffusion), active transport (primary & secondary) membrane assisted transport (endocytosis & exocytosis) (2.2) Explain 3 osmotic conditions (hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic) with examples and 3 factors that affect the rate of diffusion with examples