* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
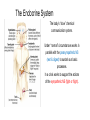
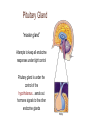
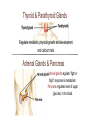
The Endocrine System The body’s “slow” chemical communication system. Under “normal” circumstances works in parallel with the parasympathetic NS (rest & digest) to sustain our basic processes. In a crisis works to support the actions of the sympathetic NS (fight or flight). Example...While walking down the street, you see a giant bear! the hormone epinephrine (adrenalin) released into the bloodstream, sustaining the body’s defensive reaction (“fight or flight” response) the endocrine system finishes what your sympathetic NS started, keeping your heart pounding and muscles tense, ready for action Hormones Hormones are chemicals synthesized (made) by the various endocrine glands and secreted (released) in the bloodstream…have similar structure/function as many neurotransmitters DIFFERENCES BETWEEN… Hormones Neurotransmitters Speed of transmission Slow (minutes) Fast (seconds) Length of influence Last longer (wks) Brief duration Method of transmission Bloodstream Neurons *they are the same thing, just manufactured and located in different parts of the body Neurotransmitters- made in neurons, in the nervous system Hormones- made by gland, in the body and bloodstream Pituitary Gland “master gland” Attempts to keep all endocrine responses under tight control Pituitary gland is under the control of the hypothalamus…sends out hormone signals to the other endocrine glands Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands Regulate metabolic, physical growth and development and calcium rate. Adrenal Glands & Pancreas Adrenal glands regulate “fight or flight” response & metabolism. Pancreas regulates level of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Gonads Regulate bodily development (secondary sex characteristics) and maintain reproductive organs in adults (produce sperm/eggs). produces testosterone produces estrogen & progesterone