* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous detection device wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
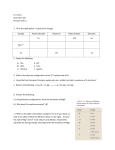
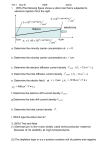
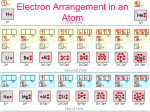
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 1. Fill in the table below. Include ionic charges Isotope Atomic Number Neutrons Mass Number Electrons 𝟏𝟐𝟐 𝟑− 𝟓𝟏𝑺𝒃 51 71 122 54 𝟒𝟖 𝟒+ 𝟐𝟐𝑻𝒊 22 26 48 18 𝟏𝟗𝟓 𝟒+ 𝟕𝟖𝑷𝒕 78 117 195 74 2. Name the following a) SO3 b) WO3 c) Pt(CO3)2 Sulfur trioxide Tungsten (VI) oxide Platinum (IV) carbonate d. HCl e. TeH2 f. Hg2SO3 Hydrochloric acid Tellerium dihydride Mercury (I) sulfite 3. What is the electron configuration of the 2nd excited state of S? [Ne] 3s2 3p3 3d1 4. Using the Pauli Exclusion Principle, explain why an s-orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons? There is only one s-orbital in each shell. Adding a third electron would mean that two of the three would have the same set of four quantum numbers. 5. Balance the following: C6H14 (l) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + H2O (g) 2, 19, 12, 14 6. Answer the following. a.) Using electron configurations, show the formation of BeO. See slides 7 and 10 of lecture 7. b.) Why does this reaction proceed? (3) So that each ion can reach a noble gas configuration. c.) Refer to the table of ionization energies in Ch 4 of your book, as well as the table of electron affinities shown on the right. Assume the radii of Be2+ and O2- to be 60 pm and 200 pm, respectively. Calculate the energy change associated with the formation of BeO . REVIEW SLIDES 17-20 in lecture 7. EI = 1.49 aJ + 2.92 aJ = 4.41 aJ EEA = -0.234 aJ + 1.30 aJ = 1.07 aJ Ec =[ (231 aJ pm) (+2)(-2)]/(260 pm) = -3.55 aJ Etotal = EI + EEA + Ec =1.93 aJ 7. Which ion has the largest radius? a) Pt4+ b) Ir6+ c) O2d) Sn2+ 8. The number of protons in an atom determines its: a) reactivity b) chemical identity c) solubility d) phase 9. Which of the following sets of quantum numbers does NOT represent a possible ground state electron of Zr: a) 5, 0, 0, ½ b) 5, 1, 1, ½ c) 4, 0, 0, - ½ d) 2, 1, -1, - ½ e) 3, 2, -2, ½ 10. Explain how and why atoms emit light. Conservation of energy. When electrons relax, they release their excess energy as radiation. 11. Why does the Bohr model fail for atoms with more than one electron? It violates the uncertainty principle 12. A certain element, X, has 3 isotopes (49X, 50X, and 51X). The isotope masses are 49.122 amu, 50.456 amu, and 51.246 amu. Analysis confirms that 3.00% of all X is 51X. Given that the average mass of X is 50.000, determine the percent abundances of the other isotopes. 49 X= 35.9%, 50 X = 61.1% and 51X=3.00% 13. A sphere of gold has a radius of 1.5 inches. The volume of a sphere is 4.19r3. Given that the mass of this sphere is 4469 g, calculate the density of gold in g/cm3 to the correct number of significant figures. V = 4.19(1.5 in)3 =113.13 in3 x (2.54 cm/ in)3 = 231.73 cm3 ρ = 4469 g/ 231.73 cm3 = 19.2 g/cm3 19 g/cm3 14. A laser emits 200mJ of energy per hour. Given that the wavelength of the photons in the beam is 300 nm, and assuming that the emission rate is constant, how many photons are emitted per minute? E= nhc/λ; where E is the energy per minute and n is the number of photons per minute n= E λ/(hc); n =[ (.200J/60)*(300 x 10-9m)]/[(6.626 x 10-34J s)(3.0 x 108 ms-1)] = 5.0 x 1015 15. A photon with some energy Ep strikes a metal surface. An electron is ejected with a velocity of 5.00 Mm/s. The threshold frequency of the metal is 6.30 x 1013 s-1. What is the wavelength of the photon, in nm? Significant figures count. 17 nm 16. What is an orbital? A probability map of the places an electron is likely to be found. 17. Why do atoms exhibit discontinuous (line) spectra when they emit light? Why can’t an atom emit any wavelength of light? Energy is quantized. Emission is due to specific transitions between ground and excited states. 18. Refer to the activity series in chapter 10. For the single replacement reactions below, write the half reactions. Label the reducing and oxidizing agents. Show the net ionic equation. If no reaction occurs, write “no reaction”. REVIEW LECTURE 8 a.) Titanium (IV) perchlorate (aq) +Lithium (s) Products are lithium perchlorate and titanium metal. Ti4+ gets reduced, Li(s) gets oxidized. There are 4 electrons transferred. b.) Magnesium (s) + Sulfuric acid (aq) Products are magnesium sulfate and hydrogen gas. Mg(s) is oxidized, H+ is reduced. 2 electrons are transferred. c.) Aluminum nitrate (aq) + Potassium (s) Products are potassium nitrate and aluminum. Three electrons are transferred. Potassium is oxidized to K+. Al3+ is reduced to Al(s). 19. Provide an acceptable set of quantum numbers for a valence electron on a Boron atom. n=2; allowed values of L are 0 and 1; if L= 0, mL must be 0 if L =1, mL can be -1, 0, or 1 ms = +1/2, -1/2 examples: 2,0,0, ½; 2, 1, -1, ½; etc. There are 8 possibilities 20. If you have not done so, answer the BONUS question on your last quiz. Equations 𝐸𝑛 = 𝑛ℎ𝑣 𝑣𝜆 = 𝑐 𝜌 = 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠/𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝐸𝑘 = 𝐸𝑝ℎ𝑜𝑡𝑜𝑛 − 𝐸𝑡ℎ𝑟𝑒𝑠ℎ𝑜𝑙𝑑 = ℎ𝑣𝑝 − ℎ𝑣𝑇 𝐹𝑜𝑟 𝑎𝑛 𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑛 𝑖𝑛 𝑚𝑜𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛: 𝐸𝑘 = ̅̅̅2̅ 𝑚𝑒 𝑉 2 h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js c = 3 x 108 ms-1 me = 9.109 x 10-31 kg Volume of a sphere = 𝐸𝑐 = 𝑘 𝑄1 𝑄2 𝑑 4 𝜋𝑟 3 3 where r is the radius where k = 231 aJ•pm, d = nuclear separation distance, Q = charge 1 in = 2.54 cm