* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution PowerPoint
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
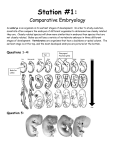
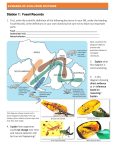
Theory of Evolution What is Evolution? Evolution is a process of change through time. A change in species over time. Theories of evolution provide an explanation for the differences and similarities in structure, function, and behavior among life forms. Existing life forms have evolved from earlier ones, by gradual changes in Supporting Observations 1. Geologic Records – contains fossils that indicate that simple organisms evolved into increasingly complex multicellular organisms. a.The earth is 4.5 – 5 billion years old (determined by radioactive dating of rocks) b.Fossils are direct or indirect remains of organisms preserved in tar, amber, rock, etc. c.Fossils have been found indicating that organisms existed over 3 billion years ago. Fossils Fossil Evidence The fossil sequence shows that the upper layers (strata) contain fossils of younger organisms, whereas the lower layers (strata) contain fossils of older organisms. The fossils in the upper strata resemble some of the fossils in the lower strata. This suggests links between older and younger organisms. Supporting Observations 2. Comparative Anatomy - Shows similarities in anatomical features of seemingly different organisms. Includes Homologous Structures Homologous Structures • Anatomical parts that are similar in structure and origin, although they may currently have different functions. Analogous Structures • Anatomical Structures that look different but have the same function. Ex: whale and shark flipper (whale skeleton is made of bone and shark skeleton is cartilage) Analogous Structures Supporting Observations 3. Comparative Embryology Comparison of early embryonic development among groups of organisms reveal similarities which suggest common ancestry Supporting Observations 4. Comparative Biochemistry The closer the evolutionary relationship between organisms, the more alike the base sequences are on the DNA molecule. As a result, the more alike the amino acid sequences are that make up the proteins in the organisms. Comparative Biochemistry Baboon Chimp Lemur Gorilla Human ASN SER ALA SER SER THR THR THR THR THR THR ALA SER ALA ALA GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY ASP ASP GLU ASP ASP GLU GLU LYS GLU GLU VAL VAL VAL VAL VAL ASP GLU GLU GLU GLU ASP ASP ASP ASP ASP SER THR SER THR THR PRO PRO PRO PRO PRO GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY GLY SER GLY GLY ASN ALA HIS ALA ALA ASN ASN ASN ASN ASN Differences between Humans Baboon Chimp 5 0 Lemur 7 Gorilla 0 Theories of Evolution • • Attempts to explain the diversities among species. Adaptations are a major component of these theories. Adaptation – any characteristic that allows an organism to survive in its environment. Lamarck's Main Ideas 1. Use and Disuse - new organs or structures arise according to the needs of an organism. The size is determine by the degree to which they are used. 2. Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics – useful characteristics acquired by an organism during its lifetime can be transmitted to its offspring. These result in the species being better suited to their environment. Lamarck's Giraffes Was Lamarck correct? • • Tested by scientists who cut off mouse tails. The tailless mice were then bred. The result.....baby mice WITH tails. This challenged Lamarck's two main ideas. The mice survived without tails, but did not pass on the “tailless” characteristic to their offspring. Charles Darwin • • • 1809 – 1892 Naturalist who traveled on the HMS Beagle documenting organisms. Developed the Theory of Natural Selection Theory of Natural Selection • • Nature selects the organisms that are better adapted to survive and reproduce in a particular environment. There are 6 parts to the theory: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Overproduction Competition Variation Survival of the Fittest Transmission of favorable variations Evolution of Species (Speciation) Theory of Natural Selection 1. Overproduction More offspring are produced than can actually survive. Theory of Natural Selection 2. Competition – Due to overproduction, organisms compete for resources (materials needed to survive. Ex: food, water, shelter) Theory of Natural Selection 3. Variation – Individuals within a species can vary and have different traits. Theory of Natural Selection Survival of the Fittest During competition, individuals with favorable traits (adaptations) will survive. Those without favorable traits will die. Theory of Natural Selection 5. Transmission of Favorable Traits Individuals with favorable traits survive and REPRODUCE, passing on their traits to another generation. - High adaptive value traits get passed on. - Low adaptive value traits die out. Theory of Natural Selection 6. Speciation - Over many generations, favorable adaptations accumulate and many changes lead to the emergence of a new species. Modern Theory of Evolution Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection is the presently accepted theory of evolution. However, Darwin's theory did not explain sources of genetic variation Variations within a species increase the chance of survival when conditions change. Sources of Genetic Variation in a Population 1. Mutations – changes in base sequences in a gene that may cause variation and new characteristics. Only mutations in gametes can become the basis for evolutionary change. 2. Sexual Reproduction - Genes are randomly combined, creating variation in offspring. 3. Isolation Adaptive Value of Traits • • Adaptive Value – some variations give individuals advantages over others in their struggle for survival. They have a high adaptive value. In a changing OR unchanging environment: – traits with a high adaptive value increase the chance of survival and reproduction. They increase in frequency. – Traits with low adaptive value will decrease in frequency. Sources of Genetic Variation in a Population 3. Isolation – Genetic variation may increase if populations (groups of one type of organism) are separated. Geographic – Separated by a physical barrier Reproductive – Individuals reproduce at different times (spring vs. fall) Result of Isolation The gene pools of isolated populations may become different as a result of isolation. The populations may change so much that they lose the ability to successfully interbreed and are now considered different species. Ex: Galapagos Finches Rate of Evolutionary Change • • Not all populations evolve at the same rate. Slow Evolution (Gradualism) – some populations change very little over millions of years, indicating that they are well adapted (suited) to their environment. Ex: Horseshoe Crabs Rate of Evolutionary Change • Rapid Evolution (Punctuated Evolution) - some populations of organisms change a lot over millions of years, indicating periods of stability with rapid periods of change and evolution. Ex: Horses Punctuated Evolution of Horses Phylogenetic Tree • • Phylogenetic trees show evolutionary pathways, and are used to show how closely related organisms are. They are used to show/reveal: 1. All organisms come from a common ancestor 2. The relationship between different species 3. What species are extinct and still living 4. Evolution involves a gradual change Phylogenetic Tree • Which organism is most closely related to the Hagfish? Why? Phylogenetic Tree