* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt - Old Saybrook Public Schools
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
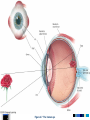
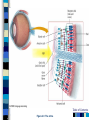
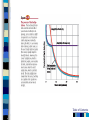
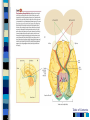
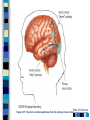
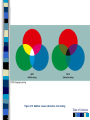
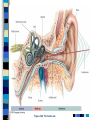
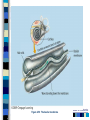
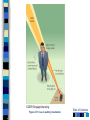
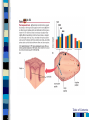
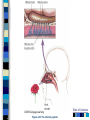
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception – 8th Edition Sensation and Perception: The Distinction Sensation : stimulation of sense organs Perception: selection, organization, and interpretation of sensory input Psychophysics = the study of how physical stimuli are translated into psychological experience Table of Contents Figure 4.1 The distinction between sensation and perception Table of Contents Psychophysics: Basic Concepts Sensation begins with a detectable stimulus – Psychological versus physical Fechner: the concept of the threshold – Absolute threshold: detected 50% of the time. – F 4.2 – Just noticeable difference (JND): smallest difference detectable • Weber’s law: size of JND proportional to size of initial stimulus Table of Contents Table of Contents Psychophysics: Concepts and Issues Signal-Detection Theory: Sensory processes + decision processes – F 4.3 – applications Subliminal Perception: Existence vs. practical effects – 1957 study in a drive in movie – Objective evaluation – critical thinking Sensory Adaptation: Decline in sensitivity Table of Contents Table of Contents Vision: The Stimulus Light = electromagnetic radiation - F 4.5 – Amplitude: perception of brightness – Wavelength: perception of color – purity: mix of wavelengths • perception of saturation, or richness of colors. – F 4.6 Refraction Reflection Absorption Diffraction Table of Contents Table of Contents The Eye: Converting Light into Neural Impulses The eye: housing and channeling Components: – Cornea: where light enters the eye • Anterior chamber – Lens: focuses the light rays on the retina - presbyopia – Iris: colored ring of muscle, constricts or dilates via amount of light – Pupil: regulates amount of light Eye conditions – F 4.8 – Nearsightness – mypoia – Farsightness - hyperopia Table of Contents Table of Contents Figure 4.7 The human eye Table of Contents Figure 4.8 Nearsightedness and farsightedness The Retina: An Extension of the CNS Retina: absorbs light, processes images, and sends information to the brain Optic disk: where the optic nerve leaves the eye/ blind spot Receptor cells: - F 4.8 – Rods: black and white/ low light vision – Cones: color and daylight vision • Adaptation: becoming more or less sensitive to light as needed – F 4.10 Information processing: – Receptive fields – Lateral antagonism Table of Contents Table of Contents Figure 4.9 The retina Table of Contents Hubel and Wiesel: Feature Detectors and the Nobel Prize Early 1960’s: Hubel and Wiesel – Microelectrode recording of axons in primary visual cortex of animals – Discovered feature detectors: neurons that respond selectively to lines, edges, etc. – F 4.14 – Groundbreaking research: Nobel Prize in 1981 Later research: cells specific to faces in the temporal lobes of monkeys and humans Cell specialization – F 4.16 – fusifacial form area (FFA) – Quiroga et al. (2005) - hippocampus cellscommon name? Greebles research – Gauthier et al. (1999) – F 4.17 – Facial recognition cells can be trained to recognize other types of stimuli Table of Contents The Retina and the Brain: Visual Information Processing Light -> rods and cones -> neural signals -> bipolar cells -> ganglion cells -> optic nerve -> optic chiasm > opposite half brain -> Main pathway: lateral geniculate nucleus (thalamus) -> primary visual cortex (occipital lobe) – magnocellular: where – parvocellular: what – Blindsight – Wesiskrantz (1994) Second pathway: superior colliculus ->thalamus -> primary visual cortex Table of Contents Table of Contents Figure 4.15 The what and where pathways from the primary visual cortexTable of Contents Basics of Color Vision Wavelength determines color – Longer = red / shorter = violet Amplitude determines brightness Purity determines saturation Computer generated colors and human color vision: 48 bit color scanners v. humans Table of Contents Figure 4.18 The color solid Table of Contents Figure 4.19 Additive versus subtractive color mixing Table of Contents Theories of Color Vision Trichromatic theory - Young and Helmholtz – Receptors for red, green, blue – color mixing – F 4.21 Opponent Process theory – Hering – 3 pairs of antagonistic colors – negative afterimages – red/green, blue/yellow, black/white Current perspective: both theories necessary Color vision defects Color vision defects: simulations Table of Contents Table of Contents XX4.20 Table of Contents XXX Table of Contents Perception: Perceiving Forms, Patterns, and Objects Reversible figures – F 4.23, F 4.31 Perceptual sets – readiness to perceive a stimulus in a particular way – ambiguous stimuli – F 4.24 – effects of motivational factors Inattentional blindness/change blindness – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nkn3wRyb9Bk&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=38XO7ac9eSs Feature detection theory - bottom-up processing. Form perception - top-down processing Subjective contours Gestalt psychologists: the whole is more than the sum of its parts – Reversible figures and perceptual sets demonstrate that the same visual stimulus can result in very different perceptions Table of Contents XX4.25 Table of Contents XX4.27 XX4.26 Table of Contents Principles of Perception Gestalt principles of form perception: – figure-ground, proximity, similarity, continuity, closure, and simplicity – Point of view effects – F 4.34 Recent research: – Distal (stimuli outside the body) vs. proximal (stimulus energies impinging on sensory receptors) stimuli. – Perceptual hypotheses • Context – Object recognition – object background consistency – F 4.35 Table of Contents XX4.28 Table of Contents XXX4.29 Table of Contents XXX4.30 Table of Contents XXX4.31 Table of Contents XXX4.32 XXX4.33 Table of Contents Depth and Distance Perception Binocular cues – clues from both eyes together – retinal disparity – up to 25 feet – Convergence – Creating 3D effects – stereoscope – after Wheatstone and Viewmasters, random dot stereogram- after Brewester, Redgreen anaglyphs, and autostereograms – Magic Eye – strabismus or "wandering eye" – stereoblindness (5 – 10%), the case of “Stereo Sue” Monocular cues – clues from a single eye – Figure 4.36 – motion parallax – accommodation – pictorial depth cues Table of Contents Wheatstone's original stereoscope Table of Contents Schematic of red-green anaglyphs Table of Contents Random Dot stereograms Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents Emphasis on linear perspective during the Western Renaissance Table of Contents Stability in the Perceptual World: Perceptual Constancies Perceptual constancies – stable perceptions amid changing stimuli – – – – – Size Shape Brightness Hue Location in space Table of Contents Optical Illusions: The Power of Misleading Cues Optical Illusions - discrepancy between visual appearance and physical reality Famous optical illusions: Muller-Lyer Illusion, Ponzo Illusion, Poggendorf Illusion, Upside-Down T Illusion, Zollner Illusion, the Ames Room, and Impossible Figures Cultural differences: Perceptual hypotheses at work http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/ - website with visual illusions and other visual effects Art and Illusion – pages 175 - 179 Table of Contents XXX4.40 Table of Contents XXX4.20 Table of Contents XXX4.41 Table of Contents XXX4.45 Table of Contents Hearing: The Auditory System Stimulus = sound waves (vibrations of molecules traveling in air) – Amplitude (loudness) – Wavelength (pitch) – Purity (timbre) Wavelength described in terms of frequency: measured in cycles per second (Hz) – Frequency increase = pitch increase Sound pressure (SPL) – decibels – F 4.48 Table of Contents XXX 4.47 Table of Contents The Ear: Three Divisions External ear (pinna): collects sound. Middle ear: the ossicles (hammer, anvil, stirrup) Inner ear: the cochlea – a fluid-filled, coiled tunnel – contains the hair cells, the auditory receptors – lined up on the basilar membrane Table of Contents Table of Contents Figure 4.49 The human ear Figure 4.50 The basilar membrane Table of Contents The Auditory Pathway Sound waves vibrate bones of the middle ear Stirrup hits against the oval window of cochlea Sets the fluid inside in motion Hair cells are stimulated with the movement of the basilar membrane Physical stimulation converted into neural impulses Sent through the thalamus to the auditory cortex (temporal lobes) Table of Contents Theories of Hearing: Place or Frequency? Hermann von Helmholtz (1863) – Place theory Other researchers (Rutherford, 1886) – Frequency theory Georg von Bekesy (1947) – Traveling wave theory Table of Contents Auditory Localization: Where Did that Sound Come From? Two cues critical: Intensity (loudness) Timing of sounds arriving at each ear – F 4.51 – Head as “shadow” or partial sound barrier Timing differences as small as 1/100,000 of a second Table of Contents Figure 4.51 Cues in auditory localization Table of Contents The Chemical Senses: Taste Taste (gustation) Physical stimulus: soluble chemical substances – Receptor cells found in taste buds Pathway: taste buds -> neural impulse -> thalamus -> cortex – Four primary tastes: sweet, sour, bitter, and salty – Taste: learned and social processes Culture and taste – F 4.53 Table of Contents XXX 4.52 Table of Contents The Chemical Senses: Smell Smell (Olfaction) Physical stimuli: substances carried in the air – dissolved in fluid, the mucus in the nose – Olfactory receptors = olfactory cilia Pathway: Olfactory cilia -> neural impulse -> olfactory nerve -> olfactory bulb (brain) – Does not go through thalamus Table of Contents Table of Contents Figure 4.54 The olfactory system Skin Senses: Touch Physical stimuli = mechanical, thermal, and chemical energy impinging on the skin. - receptors/detector – F 4.55 Pathway: Sensory receptors -> the spinal column -> brainstem -> cross to opposite side of brain -> thalamus -> somatosensory (parietal lobe) Temperature: free nerve endings in the skin Pain receptors: also free nerve endings – Two pain pathways: fast vs. slow Table of Contents Table of Contents Figure 4.56 Pathways for pain signals Other Senses: Kinesthetic and Vestibular Kinesthesis - knowing the position of the various parts of the body – Receptors in joints/muscles Vestibular - equilibrium/balance – Semicircular canals Synesthesia – “The man who tasted shapes” MIT Synesthesia Project Table of Contents