* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate System
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
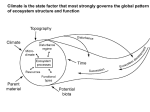
Climate System Sophie Zechmeister-Boltenstern Reference: Chapin F. St., Matson P., Mooney Harold A. 2002 Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology. Springer, Berlin, 490 p. Structure of this lecture • • • • • • The Atmospheric System The Oceans Landform effects on Climate Vegetation Influences on Climate Climate Variability Climate and Ecosystems Climate is the state factor that most strongly governs the global pattern of ecosystem structure and function Climate is a key mechanism by which ecosystems interact with the total Earth System Energy Budget Energy in = energy out Half of solar radiation reaches Earth The atmosphere is transparent to shortwave but absorbs longwave radiation (greenhouse effect) The atmosphere is heated from the bottom by longwave radiation and convection Energy Budget The temperature of a body determines wavelengths of energy emitted Solar radiation has high energy (shortwave) that readily penetrates the atmosphere Earth emits low-energy (longwave) radiation that is absorbed by the atmosphere Atmospheric Structure The atmosphere is heated from the bottom Therefore it is warmest near the and gets colder with increasing elevation Atmospheric Circulation Uneven heating of Earth’s surface causes atmospheric circulation Greater heating at equator than poles 1. sun’s rays hit more directly 2. less atmosphere to penetrate Therefore 1. Net gain of energy at equator 2. Net loss of energy at poles Air rises at equator and subsides at poles (vertical circulation) Circulation cells explain global distribution of rainfall Earth’s rotation determines wind direction (horizontal circulation) (Coriolis force) tropical easterlies temperate westerlies At 30º N & S, air descends more strongly over cold ocean than over land At 60 º N & S, air descends over cold land (high pressure) and rises over warm ocean (low pressure) Pressure gradients create geographic variation in prevailing winds In summer at 60 º N & S, air descends over cold ocean (high pressure) and rises over warm land (low pressure) 1. Cool equator-ward flow of air on W coast of continents 2. Warm poleward flow of air on E coasts of continents Creates planetary waves Uneven heating of Earth’s surface causes atmospheric circulation 60% of heat transport is carried by atmosphere through storms that Move along pressure gradients 40% is carried by ocean currents (conveyor belt) surface (warm) currents move poleward deep (cold) currents move equatorward Ocean Circulation Ocean currents are similar to wind patterns: 1. Driven by Coriolis forces 2. Driven by winds Ocean currents move 40% of “excess heat” from equator to poles Driven by circulation of deep ocean waters Deepwater formation occurs near Greenland and in Antarctic Landform effects on climate • Land-water interactions – Monsoons – Land-sea breezes • Mountain effects – Rain shadow – Effects of aspect – Air drainage (inversion) Vegetation effects on climate Amazonasgebiet How can the atmosphere warm? 1. More solar radiation variation in Earth’s orbit 2. Less reflected shortwave less sulfate aerosols darker surface of Earth (land-cover change) 3. More absorbed longwave more “greenhouse gases” Temporal Variability in Climate 1. Long-Term Changes Changes in solar orbit causes long-term variations in solar input to Earth Climate effects on vegetation Earth’s climate is now warmer than at any time in the last 1000 years 1. increased solar input (small warming effect) 2. Increased sulfate aerosols reflects radiation (small cooling effect) 3. Increased greenhouse gas concentrations (large warming effect) 4. Land-cover change creates a darker surface (large warming effect) Inerannual Climate Variability The Pacific Ocean strongly influences the climate system becauseIt is the largest ocean basin. Normal ocean current and wind direction in central Pacific is easterly Interannual climate variation ENSO events Teleconnections carry these climate effects throughout the globe (e.g., El Niño creates warm winters in AK and Calif) Weltweite Folgen von El Niňo Seasonal and Daily Variations Seasonal variation in climate results from tilt in Earth’s axis Changes sun angle and day length Climate and Ecosystem Distribution and Structure Climate gives rise to predictable types of ecosystems Summary • Climate is a complex system determined by radiation in- and output, atmospheric circulations and oceans • Milankowich cycles induce ice ages • Landforms and landcover affect climate • Interannual variability include ENSO (El Nino) and NAO events • Vegetation depends on climate but it also affects climate