* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Factors That Affect Climate Change File
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Milankovitch cycles wikipedia , lookup
Factors That Affect Climate
Change
Weather vs. Climate
Climate-
The pattern of temperature, wind,
precipitation, and other conditions within a region,
averaged over a long period of time.
Weather-
The conditions of temperature, wind, precipitation,
air pressure at any given moment.
Which would you most likely look at when
•planning a winter vacation?
•planning a picnic?
Climate Change
Climates on the earth have
changed many times over
billions of years.
Between 20 to 100 thousand
years ago, a good portion of
North America was covered
in a thick sheet of glacial
ice.
Recently, the
Intergovernmental Panel on
Climate Change (IPCC) has
presented evidence that
global climates are once
again changing.
(global warming intro videoclip)
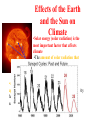
Effects of the Earth
and the Sun on
Climate
•Solar energy (solar radiation) is the
most important factor that affects
climate
•The amount of solar radiation that
reaches the earth varies in a mostly
irregular fashion
•A sunspot cycle has been identified which occurs
approximately every 11 years. Variations in sunspot activity
have been linked to changes in global climate by some
scientists.
The Earth in Space
Because of the earth’s
spherical shape, different
latitudes receive different
intensities due to the
changing angles at which
they strike the surface.
The sun’s rays are less
concentrated here
The sun’s rays are most
concentrated here
{
{
Milankovic Cycles
In the early 1900’s, the Serbian mathematician Milutin
Milankovic showed that the amount and intensity of solar
radiation received by the earth varies due to a series of three
variables. Milankovic’s calculations support the idea that earth’s
climate is expected to change over long periods of time.
The Earth in Space
The seasons that we experience on earth are caused by a
combination of the earth’s tilt on its axis, and its position in orbit
around the sun.
Earth’s axis of rotation
is currently 23.44o.
This angle is slowly
decreasing over
thousands of years.
The intensity of solar
radiation changes for
different parts of the
earth at different times
during its orbital period.
The Earth in Space
Other factors that result in changes in the intensity of solar
radiation received by the earth are;
Changes in the earth’s
orbital eccentricity
result in periods where
the earth will be closer
or farther from the sun.
!
The Earth in Space
Not only does the earth
tilt on its axis, but
because it is not a
perfect sphere, the earth
wobbles as it spins
about this axis.
This wobble affects the
solar energy received by
the different
hemispheres and leads
to smaller or larger
differences between the
seasons in these two
hemispheres.
Click picture
for animation
The Albedo Effect
The presence of ice and snow on the earth’s surface can have
an effect on how much solar radiation gets reflected from the
earth’s surface back out into space.
albedo- a measure of the fraction (or amount) of solar radiation or light
that is reflected by a surface.
Lighter-coloured materials have a high albedo (reflect a lot of
radiation) and darker-coloured materials have a low albedo
(absorb more radiation than they reflect).
Comparing albedo
land < water < ice
Videoclip “Arctic Changes
The Atmosphere
The earth’s atmosphere is a mixture of gases (mostly nitrogen
and oxygen and water vapour), extending from its surface up to
an altitude of about 560 km.
The atmosphere allows solar radiation to strike the earth’s
surface, but then is able to absorb some thermal energy and
reflect it back to earth before it can go out into space. This is
called the greenhouse effect.
Without the greenhouse effect,
the average surface
temperature on the earth
would be about –20oC!
The Atmosphere
Since gases are fluid, the particles are able to move past each
other. Warmer, and therefore less dense, gas will rise above
colder, more dense gas. This creates looping patterns of gas
within the atmosphere. This, combined with the constant
rotation of the earth creates prevailing wind patterns which we
experience on the earth’s surface.
Prevailing winds transfer
thermal energy and
moisture in a predictable
way across the globe.
They also help to create
consistent movements in
water called ocean
currents.
The Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere is made up of all of the water on the earth in all
of its different forms.
The Hydrosphere
Click here and scroll
The Earth’s Major Ocean Currents
down to video on ocean
(link to laptop)
currents
Ocean currents can affect climate since they help to distribute
thermal energy concentrated at the equator towards the poles.
An overall circulatory pattern exists and is called the great
ocean conveyor belt since it distributes thermal energy around
the entire earth.
The Great
Ocean
Conveyor Belt
The Hydrosphere
Above colder water is colder and drier air.
Cold ocean currents bring a drier climate to a coastal region.
Above warmer water is warmer and humid (wetter) air.
Warm ocean currents bring a more humid climate to a coastal
region.
How do ocean currents affect climate? CLICK HERE to find out!
(click on “Keeping Current” link)
Moving Continents
The outer surface of the earth consists of huge pieces of solid
rock know as tectonic plates.
These rock plates (about 12 major ones), move only a few
centimetres each year, but this is enough to change the
distribution of land and water across the surface of the earth
over hundreds of thousands of years.
When major plates collide, huge mountain ranges can
form, creating changing patterns of wind and precipitation in
that area.
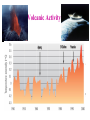
Volcanic Activity
The movement of tectonic plates also leads to the formation of
active volcanoes. As a result of a volcanic eruption, huge
amounts of ash, dust, and gases are spewed into the atmosphere
as aerosols. The presence of these aerosols in the atmosphere can
result in the reflection and scattering of more solar radiation from
the earth, leading to less energy absorbed and cooler global
temperatures.
Some theories suggest that a large meteor which impacted the
earth millions of years ago induced a similar but larger effect and
eventually led to the demise of the dinosaurs.
Human Activities
Since the Human Industrial Revolution which began in the late
1700’s, human beings have been developing and using
technologies which have been linked to the changes in climate
that are being experienced in current times. Climate changes that
can be related to human activities are called anthropogenic
factors.
Anthropogenic climate change factors include:
•pollutants produced from the burning of fossil fuels
•depletion of forests, known as deforestation
• “greenhouse” gases to the atmosphere such as
methane, nitrous oxide, and CFC’s from various
industries (even H2O (water) is a greenhouse gas,
but when it concentrates, it falls as rain)
Homework
Complete p.278 #1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8