* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Immune System
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
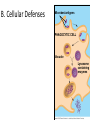
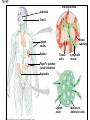
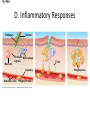
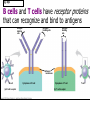
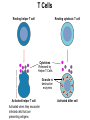
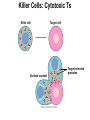
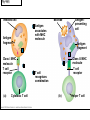
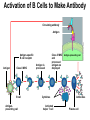
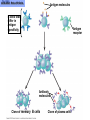
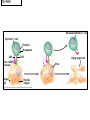
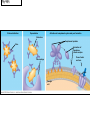
The Immune System 2 Divisions of Immunity in Humans and Other Mammals I. Innate Immunity “Non-Specific” II. Acquired immunity “Specific” A. Barrier Defenses Skin B. Cellular Defenses Microbes/antigens PHAGOCYTIC CELL Vacuole Lysosome containing enzymes There are different types of phagocytic cells: Fig. 43-7 Interstitial fluid Adenoid Adenoid Tonsil Tonsil Blood Blood capillary capillary Lymph Lymph nodes nodes Spleen Spleen Peyer’s patches Peyer’s patches (small intestine) (small intestine) Appendix Appendix Lymphatic vessels Tissue Tissue cells cells Lymph Lymph node node Lymphatic Lymphatic vessel vessel Masses of Masses of defensive cells defensive cells Fig. 43-8-3 D. Inflammatory Responses Pathogen Splinter Chemical Macrophage signals Mast cell Capillary Red blood cells Phagocytic cell Fluid Phagocytosis II. Acquired immunity lymphocyte receptors provide pathogen-specific recognition Fig. 43-9 B cells and T cells have receptor proteins that can recognize and bind to antigens Antigenbinding site Antigenbinding site Antigenbinding site Plasma membrane B cell (a) B cell receptor Cytoplasm of B cell Cytoplasm of T cell (b) T cell receptor T cell B Cells Antigen-specific B cell receptor Class II MHC and processed antigen are displayed Antigen Antibodies (Immunoglobins) B cell Cytokines (Lymphokines) Plasma cell bacteria Activated helper T cell T Cells Resting helper T cell Resting cytotoxic T cell Cytokines Released by Helper T-Cells Granule w/ destructive enzymes Activated helper T cell Activated when they encounter infected cells that are presenting antigens Activated killer cell Killer Cells: Cytotoxic Ts Killer cell Surface contact Target cell Target-oriented granules Fig. 43-12 Infected cell Microbe Antigenpresenting cell 1 Antigen associates with MHC molecule Antigen fragment Antigen fragment 1 1 Class I MHC molecule T cell receptor (a) 2 2 Cytotoxic T cell Class II MHC molecule T cell receptor 2 T cell recognizes combination (b) Helper T cell Activation of B Cells to Make Antibody Circulating antibody Antigen Antigen-specific B cell receptor Antigen Class II MHC B cell Antigenpresenting cell Antigen is processed Class II MHC Antigen-presenting cell and processed antigen are displayed Cytokines Activated helper T cell Antibodies Plasma cell Fig. 43-14 Animation: Role of B Cells Antigen molecules B cells that differ in antigen specificity Antigen receptor Antibody molecules Clone of memory B cells Clone of plasma cells Fig. 43-16 Humoral (antibody-mediated) immune response Cell-mediated immune response Key Antigen (1st exposure) + Engulfed by Gives rise to Antigenpresenting cell + Stimulates + + B cell Helper T cell + Cytotoxic T cell + Memory Helper T cells + + + Antigen (2nd exposure) Plasma cells Memory B cells + Memory Cytotoxic T cells Active Cytotoxic T cells Secreted antibodies Defend against extracellular pathogens by binding to antigens, thereby neutralizing pathogens or making them better targets for phagocytes and complement proteins. Defend against intracellular pathogens and cancer by binding to and lysing the infected cells or cancer cells. Fig. 43-17 Helper T Cells Antigenpresenting cell Peptide antigen Bacterium Class II MHC molecule CD4 TCR (T cell receptor) Helper T cell Humoral immunity (secretion of antibodies by plasma cells) Cytokines + B cell + + + Cytotoxic T cell Cell-mediated immunity (attack on infected cells) Fig. 43-18-3 Released cytotoxic T cell Cytotoxic T cell Perforin Granzymes CD8 TCR Class I MHC molecule Target cell Dying target cell Pore Peptide antigen Fig. 43-19 Antigen-presenting cell Bacterium Peptide antigen Class II MHC molecule TCR CD4 B cell + Cytokines Clone of plasma cells Secreted antibody molecules Endoplasmic reticulum of plasma cell Helper T cell Activated helper T cell Clone of memory B cells 2 µm Fig. 43-21 Viral neutralization Opsonization Activation of complement system and pore formation Bacterium Complement proteins Virus Formation of membrane attack complex Flow of water and ions Macrophage Pore Foreign cell