* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Cells
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
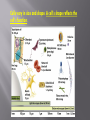
Do Now: Think-Pair-Share What do we have in common with bacteria living in our body ? Microscope observations of organisms led to the discovery of cells. • 1665 – Robert Hook used the first microscope to discover structures he called ‘cells’ • Ten years later , Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a more powerful microscope to observe living organisms in pond water. • It took 150 years of improving the microscopes and compiling the observations made by different scientists to come up with • Cell Theory : • All living things are made of one or more cells • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living organisms • All cells arise from existing cells Contributors to the Cell Theory – Theodor Schwann, Rudolph Virchow, and Matthias Schleiden Cells vary in size and shape. A cell’s shape reflects the cell’s function. Cells in Human Body Cell size is limited by a cell’s surface area-to –volume ratio. Cells with greater surface area – to – volume ratio (smaller cells) can exchange substances more efficiently. All cells share the following features : • Cell membrane • Cytoplasm • Ribosomes All cells are divided into Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells • Very simple in their organization • Have cell walls (some have capsule surrounding the cell wall) • Small in size 1-15 µm • Believed to appear 3.5 billion years ago • Do not have nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Examples all bacterial cells Eukaryotic cells • Complex organization • Can carry out more functions • First appeared 1.5 billion years ago • Have nucleus • Have many different membrane-bound organelles