* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOLOGY CLASS NOTES UNIT 7_Part 2 Other Patterns of
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
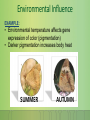
Unit 7: (Part 2) Mendelian Genetics Mrs. Howland Biology 10 Rev. Jan 2016 Exceptions to the Rule… What happens if nature doesn’t follow Mendel’s principles? Multiple alleles Codominance Incomplete dominance Sex-linked dominance Dominance according to Mendel’s Principles One allele masks the other MALE MALE FEMALE Multiple alleles are when a gene can present several different phenotypes, so there are more than 2 possible alleles. MULTIPLE ALLELES Organisms still have ONLY 2 alleles in their genotype Allows for variety among organisms Polygenic Traits POLYGENIC TRAITS: Traits that result from several genes interacting; controlled by 2 or more genes EXAMPLE: Human skin color Codominance Codominance = Neither allele completely masks the other BOTH alleles are dominant Phenotype is some of each trait EXAMPLE: Chicken feather color Examples of CODOMINANCE Examples of CODOMINANCE ABO Blood Type Genotype Phenotype Cat fur color (black/tan) Some flower colors RBC Incomplete Dominance INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE = When alleles are neither recessive nor dominant Phenotype for heterozygous offspring is in between the homozygous phenotypes EXAMPLES: Incomplete Dominance Human hair Remember the DIFFERENCES! Can you define each of these? VIDEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I6hYr yyGXoU Looking at Punnett Squares ~ What is different from what we’ve seen before? Alleles have same letter because they are for the same trait: “C” SUPERSCRIPTS show the different forms of the trait (“R” and “W”) Codominance ~ Punnett Square CODOMINANCE: FB = Black feathers FW = White feathers Heterozygous = Black and white feathers GENOTYPIC RATIO ____ FBFR : ____ : FBFW : ____FWFW PHENOTYPIC RATIO ____ BLACK : ____ : BLACK & WHITE : ____WHITE Incomplete Dominance ~ Punnett Square CODOMINANCE: FR = Red flower FW = White flower Heterozygous = pink GENOTYPIC RATIO ____ FRFR : ____ : FRFW : ____FWFW PHENOTYPIC RATIO ____ RED : ____ : PINK : ____WHITE Environmental Influence Are genes affected by the environment? Genes lay out the ‘plan’ The environment may help determine phenotype Environment may affect the expression of genes EXAMPLE: • Environmental temperature affects gene expression of color (pigmentation) • Darker pigmentation increases body heat SUMMER AUTUMN Environmental Influence EXAMPLE: • Environmental temperature affects gene expression of color (pigmentation) • Darker pigmentation increases body heat SUMMER AUTUMN