* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry of Nitrogen-containing Organic
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
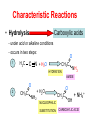
Chemistry of Nitrogen-containing Organic Compounds FSF = Full Structural Formula Key Areas • Functional group – name and structure • Characteristic chemical reactions - type - reactants - products - conditions - mechanism Nitrogen-containing Functional Groups NITRILES AMINES AMIDES AMINO ACIDS POLYAMIDES NITRILES R C N • Not to be confused with cyanides (CN- ) • First member is ethanenitrile. Draw the full structural formula. • Name the fourth member of the family. • C N very polar • Will the C-atom be a nucleophile or electrophile? Producing nitriles • Halagenoalkanes - heating under reflux with NaCN or KCN in ethanol - draw the FSF for 1-bromobutane and then for the nitrile produced on reaction with KCN - what type of reaction is this? - what is significant about the length of the carbon chain? Reaction mechanism H + CH3 C H CN- I - H CH3 C CN H propanenitrile I - Characteristic Reactions • Hydrolysis Carboxylic acids - under acid or alkaline conditions - occurs in two steps: 1 H3C O CH3C C N + H2O HYDRATION NH2 AMIDE O 2 CH3C + H2O NH2 NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION O CH3C OH + NH4+ CARBOXYLIC ACID Characteristic Reactions • Reduction Amines - Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate(III) - in dry ether H3C C N + 4[H] CH3-CH2-NH2 REDUCTION AMINE Draw the FSF for the compound produced when butanenitrile is reduced. AMINES NH2 AMINO GROUP • Relatives of NH3, where H’s have been replaced by a hydrocarbon chain • Naming: CH3-NH2 METHYLAMINE AMINOMETHANE METHYL AMINE or….. AMINES NH2 AMINO GROUP • Draw the full structural formula for 2propylamine and give its alternative name. • What types of INTERMOLECULAR FORCES exist in amines? AMINE STRUCTURE NH2 AMINO GROUP • Amines can be classed as primary, secondary or tertiary H H C N C H C N C SECONDARY PRIMARY C N C TERTIARY Producing amines 1 • Halogenoalkanes - heat with ammonia in ethanol 1 2 Overall, what type of reaction is this? Producing amines 2 • Nitriles (What is a nitrile?) -C≡N - reduction - using LiAlH4 (in dry ether + water) • Draw the simplified strucural formula for the amine produced by reducing butanenitrile. Reactions of amines H H N H • As bases Primary amines, although weak bases, are stronger than ammonia Explained by the inductive effect Inductive Effect H CH3 N H H+ Alkyl groups are electron donating (INDUCTIVE EFFECT) More Alkyl groups = GREATER INDUCTIVE EFFECT MORE BASIC Reactions of amines 2 H H • N H As nucleophiles - with acid chlorides (acyl chlorides) 1. Find out what an acyl chloride is and draw the general structure. 2. Draw a reaction mechanism for an acyl chloride with 3 carbon atoms reacting with ethylamine. 3. What is this type of reaction called? 4. What type of organic compound is the product? AMIDES O R-C NH2 • Are white crystalline solids at room temperature (expect methanamide) • Are important in polymer chemistry • How can amides be made in the lab? Reactions of amides • HYDROLYSIS O CH3C + NH2 H3O+ NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION O CH3C OH + NH4+ CARBOXYLIC ACID Using acid or alkali This is the same as the second step as when nitriles are hydrolysed Using the notation as above, use FSF to draw the hydrolysis carried out under alkaline conditions Reactions of amides 2 • DEHYDRATION Heating an amide with phosphorus(V) oxide dehydrates the compund. Using FSF, construct an equation for the dehydration of an amide with 4 carbon atoms. Name the amide. What type of organic compound is produced? AMINO ACIDS H H R N C H • • • • O C OH Are the building blocks of proteins About 20 in total Draw the FSF for a chiral amino acid Draw the FSF of an amino acid when it is in: Water Zwitterion Acid Alkali Reactions of amino acids • Amino acids join together to form peptides • This is a condensation reaction H N R O C H OH R 1 R H O N C R1 amide An AMIDE group Draw the FSF of a peptide consisting of alanine, cysteine and serine POLYAMIDES O O C HO • • • • R C OH H H H N R N Formed from a diamine and a diacid Nylon is a polyamide Kevlar is an aramid Used to make bullet-proof vests H