* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Supplement 2
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
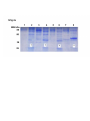
Supplemental materials 2 – Cloning, expression and purification of recombinant TOP1 fragments 1. Materials and Methods 1-1. RT-PCR Total RNA was extracted from MCF-7 cells by using TRIzol reagents in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions (Life Technologies, Rockville, MD, USA). The quality of the total RNA was assessed by using formaldehyde gel electrophoresis. Next, 0.5 µg of the total RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA using a Superscript II Reverse Transcriptase kit (Fermentas Life Sciences, Schwerte, Germany) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Subsequently, cDNA for amino acid sequence 1-765 of Homo sapiens DNA TOP1 (NCBI accession: NP_003277.1) was randomly divided into 4 fragments by PCR with primers containing BamH/HindⅢ restriction sites on both ends. The primer sequences, performing parameters, amplified nucleic acid sequences, and amino acid sizes are listed in Table 1. 1-2. Expression of TOP1 fragments We directionally cloned the PCR products into PQE 30 UA expression vectors (Qiagen, Germany), and examined their DNA sequences before transformation of the cloned plasmids into compete E coli M15 cells (Qiagen). We cultivated the cells at 37°C in Luria Bertani (LB) media containing kanamycin (25 μg/mL) and ampicillin (100 μg/mL), and induced the expression vectors by the addition of 1 mM of IPTG for 3 hours at 37°C after the culture density reached A 600 nm = 0.6. 1-3. SDS-PAGE analysis After induction of the expression vectors, we centrifuged the cells followed by sonicated decellularization. We analyzed the supernatant of the sonification with SDS-PAGE, which was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue and compared to non-induced samples. 1-4. Purification of recombination TOP1 fragments After induction, we harvested the cells by centrifugation, and resuspended the pellet in Tris/HCl buffer (pH 8.0). Next, we broken down the nucleic acids by mild sonification and purified the recombinant proteins with a Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) resin (Qiagen). We analyzed the expression of the recombinant proteins by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblots using anti-SCL-70 autoantibodies and the rabbit antibody against the novel TAA, respectively. 2. Results SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the plasmids expressed corresponding sizes of recombinant proteins (SFig. 2a). SFig. 2b illustrates the amino acid sequences of the 4 recombinant fragments deduced from DNA sequencing after cloning into the vectors. 3. Discussion and Conclusion By successfully cloning and expressing 4 protein fragments of human TOP1, we were able to determine whether the novel TAA was part of TOP1 and whether anti-SCL-70 autoantibodies were different from the autoantibodies against the novel TAA in cancer patients. Table 1. Primer sequences and amplification conditions of PCR for cloning TOP1 fragments TOP1 Fragments Primers PCR conditions Amplified sequences 1 2 3 4 F: 5’-CCGGATCCATGAGTGGGGACCAC-‘3 30 cycle: 94℃ ,30s, 56℃, 247-873 bp R: 5’-AGGGGTACCCTCTTCTTCCCACCAT-‘3 30s, 72℃ ,1 min 30s F: 5’-ATGGATCCAAAAAGAAGCCGAAG-‘3 30 cycle: 94℃ ,30s, 56℃, 820-1491 bp R: 5’-CTCGGTACCGGAAACCAGCCAAGT-‘3 30s, 72℃ , 1 min 30s F: 5’-ATGGATCCGTTACTTGGCTGGTT-‘3 30 cycle: 94℃ ,30s, 56℃, 1474-1920 bp R: 5’-CTCGGTACCCTTGTTCTCCATAAA-‘3 30s, 72℃ ,1 min 20s F: 5’-ACGGATCCCTATTTATGGAGAACAA-‘3 30 cycle: 94℃ ,30s, 56℃, 1921-2544 bp R: 5’-CGCGGTACCCTAAAACTCATAGTC-‘3 30s, 72℃ ,1 min30s The grey highlighted sequences in the primers were designed for subcloning into BamH/HindⅢ sites of the vector PQE30 UA. RNA Corresponding Protein sizes 209 aa 224 aa 149 aa 208 aa 5. Legends SFig. 2a SDS-PAGE analysis of 4 recombinant fragments of TOP1. Lanes 2, 4, 6 and 8 are IPTG induced samples of the fragments 1-4, respectively (as indicated by), while lanes 1, 3, 5 and 7 are corresponding non-induced samples. Molecular mass markers (kDa) are shown on left side. SFig. 2b The amino acid sequences of the 4 recombinant fragments of TOP1. The grey highlighted sequences are overlaps between the fragments when cloned by RT-PCR.