* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chem 231 Exam #1 Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogenation wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
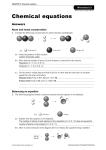
Chem 231 Exam #2 Study Guide * Please be aware that this is only a guide for studying. Don’t rely solely on this sheet! The exam will take place in Oly204 from 6-7pm on Monday, November 6th. The exam will be worth 50 pts and you will be given 1 hour. You will not be allowed to use any materials for the exam. The exam will cover materials from Chapters 3-4. I will provide you with a copy of Table 3.1 (Relative Strengths of Acids and Bases). The exam will consist of a mixture of multiple choice and short answer questions. Questions will be similar to the suggested homework problems from the book and in-class activities. In General: Be able to write conjugate acid and base pairs Be able to write curved arrow notation for an acid-base reaction Know the relationship of Ka and pKa Be able to predict the outcome of an acid-base reaction Know the bond strength effect and the electronegativity effect for acids and bases Know how enthalpy, entropy, free energy and the equilibrium constant are related (Can you predict acidity from free energy values?) Be able to explain acidity based on resonance effects and inductive effects Be able to predict order of acidity and bascity Know how to name (systematic IUPAC system only) alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alkyl halides and alcohols Given a name, be able to draw the structure Know how to draw (without models) different conformations of ethane and butane (eclipsed, staggered) and predict their energies Know how to draw Newman projections as well as wedge and dash drawings Know how to draw (without models) different conformations of cyclohexane Be able to distinguish between axial and equatorial positions on cyclohexane Be able to fill in missing reactants, products or catalysts for hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes. Look at the general reaction. Be able to fill in missing reactants, products or catalysts for the reduction of alkyl halides. Look at the general reaction. Be able to fill in missing reactants, products or catalysts for the alkylation of terminal alkynes. Look at the general reaction. Know the definition and meaning of the following terms: Substitution Addition Elimination Rearrangement Reaction mechanism Bronsted-Lowry theory Conjugate base/conjugate acid Lewis acid-base theory Spectator ion Carbocation Carbanion Nucleophile Electrophile Ka/pKa Inductive effect Electron withdrawing group Potential energy Kinetic energy Enthalpy (∆H) Entropy (∆S) Free Energy (∆G) Conformations Conformational Analysis Newman projection Staggered conformation Eclipsed conformation Heat of Combustion Ring strain Steric hindrance Equatorial position Axial position 1,3-diaxial interaction Hydrogenation Reduction Alkylation * You do not need to know how to name bicyclic molecules (4.4B) or Retrosynthetic Analysis (4.19A).