* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Constructive Interference
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Electron-beam lithography wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
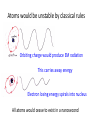
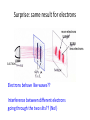
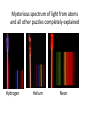
Quantum Superposition Mark Van Raamsdonk The Quantum World All matter made of elementary particles Modern physics: understand in detail how nature works at distances 100,000,000,000,000 times smaller than we can see! Classical physics fails at these distance scales Atoms would be unstable by classical rules Orbiting charge would produce EM radiation This carries away energy Electron losing energy spirals into nucleus All atoms would cease to exist in a nanosecond The double slit experiment Bright line appears directly between the slits, with other bright lines to the sides Explain via wave interference Recall: light is a wave of oscillating electric and magnetic fields Oscillating electric field Oscillating magnetic field James Clerk Maxwell 1864 Light waves from two slits add up to make bright central line Constructive Interference In this direction, light from two slits is “out of phase” and cancels Destructive Interference CRUCIAL POINT: Pattern on screen results from combination of light waves from the two different slits. Surprise: same result for electrons more electrons XXXX XXXX less electrons XXXX ELECTRON Electrons behave like waves?? Interference between different electrons going through the two slits?? (No!) Bigger surprise: same pattern when we send in one at a time! Each electron can “see” both slits! Explanation: quantum superposition electrons can be in two places at once! Electron at a definite location Single electron at a superposition of two locations Single electron at a superposition of many locations Electron in superposition has no definite location until we measure it The wavefunction Mathematically, we describe a quantum superposition by a function Y(x) Y largest here Y zero here Y is larger/smaller in magnitude in places where we are more/less likely to find electron Schrodinger’s Equation Determines how wavefunctions will evolve with time Correctly explains double slit experiment in terms of single electrons A model of atoms Schrodinger’s equation shows that electrons can exist in stable configurations around nuclei Wavefunctions and energies for these configurations determine most properties of matter Mysterious spectrum of light from atoms and all other puzzles completely explained Hydrogen Helium Neon Key idea: quantum superposition For any two allowed states of any quantum system, the system can exist in a state which is the