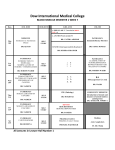
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Adaptation to Injury
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Histology of Chronic Inflammation Robbins’ Basic Pathology 2-20 7th Ed. Maturation of Monocytes into Macrophages Robbins’ Basic Pathology 2-21 Macrophage/Lymphocyte Stimulation Adapted from Robbins’ Basic Pathology 2-22 Responses to Injury Adapted from Robbins’ Basic Pathology 3-16 7th Ed Phases of Wound Healing Robbins’ Basic Pathology 3-14 Cellular Adaptation to Injury • • • • Atrophy Hypertrophy Hyperplasia Metaplasia Atrophy Robbins’ Basic Pathology 1-4 Hypertrophy (increase in cell size) • Uterus during pregnancy Robbins’ Basic Pathology 1-3 Hyperplasia (increase in cell number) • Thyroid Adenoma Robbins’ Pathologic Basis for Disease 8-6 Reversible vs. Irreversible Cell Injury • Reversible – Loss of ATP= cell swelling – glycolysis=lactic acid= decreased pH – decreased protein production • Irreversible – plasma membrane damage – Damaged mitochondria – damage lysosomes Robbins’ Basic Pathology 1-19 7th Ed. Transition from Reversible to Irreversible Robbins’ Basic Pathology 1-6 7th Ed. Necrosis vs. Apoptosis Necrosis Chromatin clumping Organelle swelling Membrane Damage Robbins’ Basic Pathology 1-6 Necrosis vs. Apoptosis Apoptosis Chromatin condensation and fragmentation. Cytoplasmic budding. Phagocytosis of extruded apoptotic bodies. Robbins’ Basic Pathology 1-12 Apoptosis 1. Stimulus of apoptosis. (Death ligands, lack of growth factors or hormones, Injury). 2. Regulatory cytoplasmic proteins. (BCL-2 family) (Some promote some inhibit apoptosis) 3. Execution caspases. (Activate endonucleases and proteinases). 4. Formation of Apoptotic Bodies. (contain organelles and cytosolic components). Robbins’ Basic Pathology 1-23 A Adapted from Robbins’ Basic Pathology 1-25 7th Ed. N Next Time • Introduction to the immune system • Readings: Abbas & Lichtman, Chapter 1 Objectives 1. Describe the pathophysiology of acute inflammation. 1. Chronology, vascular changes, cellular events, histology, resolution. 2. Differences from chronic inflammation 2. Describe the response and the cellular adaptations to injury. 1. Phases of wound healing 2. Atrophy, Hypertrophy, Hyperplasia, Metaplasia 3. Describe the differences between reversible and irreversible injury. 4. Describe the differences between apoptosis and necrosis.