* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nonspecific vs. Specific
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
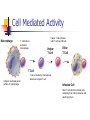
The Immune System Objective 7 Immune System Function: fight infection using cells to destroy invading substances Two types: Nonspecific Specific Nonspecific Nonspecific = doesn’t matter which disease you have First line of defense Second line of defense Interferon First Line of Defense Prevent the enemy from breaching the perimeter Skin, mucus, cilia are tools your body uses to deny the enemy access to your body Second Line of Defense Should the enemy breach the perimeter a second line of defense is necessary Inflammatory response White blood cells move into the damaged area surround and destroy the invaders Fever Chemicals released by the immune system that trigger a rise in body temperature Cooks invaders Raises heart rate Inflammatory Response Skin Wound Phagocytes move into the area and engulf the bacteria and cell debris Bacteria enter the wound Capillary Animations http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cmb WE3jLUgM http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uNG -jZxvhcg Interferon Interferon: proteins that “interfere” with viral reproduction Nonspecific because they are released for all viruses, not specific ones Specific Specific = strategies the body uses to defeat a particular disease Humoral activity Cell-mediated activity Humoral Immunity B cells recognize invaders by their foreign molecules (antigens) B cells divide rapidly into two new cells Plasma cells Memory B cells Make antibodies Remember the invader for next time Antibodies attach to the invaders until they are eaten by macrophages Humoral Activity Cell-Mediated Immunity Cell-mediated immunity kicks in when cells are cancerous or infected Macrophages tell the T cells which cells are infected Killer T cells hunt down and kill the infected cells Cell Mediated Activity Macrophage Helper T cell activates killer T cells and B cells T cell binds to activated macrophage Helper T Cell Killer T Cell T Cell Antigens are displayed on surface of macrophage T cell, activated by macrophage, becomes a helper T cell Infected Cell Killer T cells bind to infected cells, disrupting their cell membranes and destroying them Animations http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1tB OmG0QMbA