* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune System
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
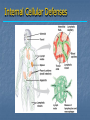
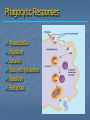
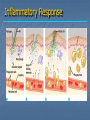
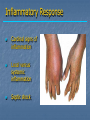
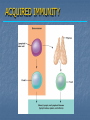
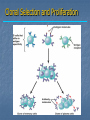
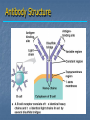
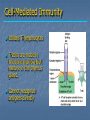
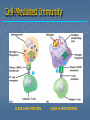
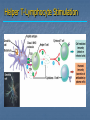
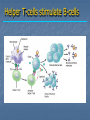
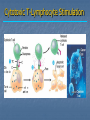
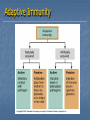
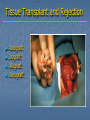
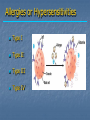
Immune System Chapter 43 Introduction to the Immune System An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders. It must also deal with abnormal body cells, which, in some cases, may develop into cancer. Two major kinds of defense have evolved to counter such threats. Innate Defenses Acquired Defenses Overview of the Immune System External Barriers: Skin Mucous membranes Secretions Internal Cellular Defenses: Phagocytic cells Neutrophils Monocytes Eosinophils Dendritic cells Internal Cellular Defenses Phagocytic Responses Pseudopodia Ingestion Vacuole Fuse with lysosome Digestion Exocytosis Internal Cellular Defenses: Natural Killer Cells Non-specific Perforins Apoptosis Internal Chemical Defenses: Interferons Complement proteins Inflammatory Response Inflammatory Response Cardinal signs of inflammation Local versus systemic inflammation Septic shock ACQUIRED IMMUNITY All cells have cell surface macromolecules Adaptive immunity is sensitive to specific infections Antigens distinguish self versus non-self ACQUIRED IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY Humoral Immunity Also known as antibody-mediated immunity Utilizes B-lymphocytes Recognizes antigen directly Made in the bone marrow Clonal Selection and Proliferation Humoral Immunity Antibody Structure Antibody Classes Antibody Classes Antibody Functions Cell-Mediated Immunity Utilizes T-lymphocytes T-cells are made in the bone marrow but mature in the thymus gland. Cannot recognize antigens directly Cell-Mediated Immunity CLASS I MHC PROTEIN CLASS II MHC PROTEIN Helper T-Lymphocyte Stimulation Helper T-cells stimulate B-cells Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Stimulation Overview of Adaptive Immunity Adaptive Immunity Problems with the Immune System Blood Transfusion Reaction Tissue Rejection Allergies Autoimmune disease Immunodeficiencies Blood Transfusion Reactions Blood Transfusion Reactions Rhesus Factor Blood Type Presence of Type of Receive? D Antigen? Antibody? Rh Positive Yes None + and - No Anti-D - only Rh Negative Tissue Transplant and Rejection Autograft Isograft Allograft Xenograft Allergies or Hypersensitivities Type I Type II Type III Type IV Autoimmune Diseases Multiple sclerosis Rheumatoid arthritis Systemic lupus Grave's disease Type I diabetes mellitus Immunodeficiency Diseases Primary Immunodeficiency a.k.a. “inborn” SCID Secondary Immunodeficiency a.k.a. “acquired” Drugs Stress and Hodgkin’s AIDS