* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (ATP). - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
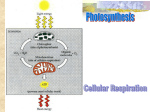
Cellular Energy Biology Vocabulary 34) ATP 35) Phosphorylation 36) Photosynthesis 37) Pigments ATP ENERGY • All cells need __________for life. • Some things we use energy for are: •Moving •Thinking •Sleeping •Breathing •Growing •Reproducing The principal chemical compound used by living things to store energy is: adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Labeled Sketch: Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups Energy Storage/ Energy Release Energy Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) + Phosphate Energy Partially charged battery Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Fully charged battery Energy can be stored by adding a phosphate group to ADP, creating ATP, called phosphorylation. Breaking the phosphate chemical bond in ATP releases energy, changing the ATP back into ADP. ATP: • ATP is used for active transport, movement of cell organelles and other basic functions (mitosis, etc) •Glucose: sugar molecule that stores 90 times more energy than ATP. Glucose is used to regenerate ATP. Why do we use ATP? Why not just get energy from sugar directly? • ATP is small units of energy. Sugar is a very high energy molecule (if you burn it all at once…spontaneous combustion!) Comparison of burning a marshmallow at a campfire vs in your body. When sugar Both have in common burned in fire: (Similarities) When sugar burned in body Energy is -Glucose and oxygen are Energy is released reactants. stored in quickly as -Carbon dioxide and water small ATP heat and light are products. molecules for slow use -Both release energy. Analogy: • Power lines= sugar = tons of energy • Wall socket = ATP = smaller units of energy Photosynthesis • Process by which plants use water, carbon dioxide, and energy from sunlight to produce sugar (and oxygen). Basic Equation 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Photosynthesis Experiments • 1600’s – Van Helmont Determined that mass gained during plant growth does NOT come from the soil. He concluded it must come from the water he added. • 1700’s – Preistly Determined that plants release oxygen • 1700’s – Ingenhousz Building on Preistly’s work, he determined that oxygen was only produced in the presence of light. Photosynthesis Equation in Detail Chemical Equation 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 + ATP + NADPH Glucose continues to be processed into ATP. Oxygen released for use in aerobic reactions ATP utilized as energy for reactions NADPH used in later photosynthesis reactions How do plants USE these raw materials? Light and Pigments -Why are most plants green? -Are there plants / photosynthetic organisms that are other colors? -Why? The answer lies in: 1) Light Spectra 2) Pigments Light and Pigments What is the light spectra? Visible light is just a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum Light and Pigments The longest wavelengths have the lowest energies. (radio) As wavelengths decrease, the energy increases. (gamma) Light and Pigments Different colors correspond to different wavelengths The colors of the rainbow are ROY G BIV: red orange yellow green blue indigo violet. red has the longest wavelength, and the lowest energy violet has the shortest wavelength, and the highest energy Seeing color The color an object appears depends on the colors of light it reflects. For example, a red book only reflects red light: White light Homework Only red light is reflected A pair of purple pants would reflect purple light (and red and blue, as purple is made up of red and blue): Purple light A white hat would reflect all seven colors: Homework White light Using colored light If we look at a colored object in colored light we see something different. Shirt looks red White light Homework Shorts look blue In different colors of light these clothes would look different: Red Shirt looks red light Shorts look black Shirt looks black Blue light Homework Shorts look blue Light and Pigments Plants gather light spectra with light absorbing molecules called PIGMENTS The major pigment used by plants is chlorophyll There are two main chlorophyll types a and b Light and Pigments Chlorophyll a and b absorb light very well in the violet/blue and orange/red parts of the spectrum. But very poorly in the green part of the spectrum. This makes most plants green (remember, to see a color it needs to be reflected) Light and Pigments Other pigments are also present in plants that use other wavelengths These include: -Beta-carotene -Xanthophyll (orange) (Lutein) (yellow) Light and Pigments Autumn Leaves There is so much chlorophyll, it masks other pigment colors. Light regulates chlorophyll production, so shorter days means less chlorophyll is produced, and the green color fades. Anthocynanins, producing red color, are produced during the breakdown of chlorophyll. Photosynthesis And the Calvin Cycle Biology Vocabulary 38) Granum 39) Photophosphorylation 40) Stroma 41) Thylakoid Overview of Reactions 1) The Light Reaction Reactants H2O Light NADP+ ADP + P Products ATP NADPH O2 2) The Calvin Cycle (AKA The Dark Reaction) CO2 Sugar Reactants ATP Products NADP+ NADPH ADP + P Location of Reactions Thylakoid: Sac-like photosynthetic membranes, location of the light reaction Granum: A collection or stack of thylakoids Stroma: Gel-like space outside the thylakoid, location of the Calvin Cycle Location of Reactions Chloroplast Water CO2 Chloroplast NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Thylakoid Sugars Stroma Photophosphorylation Definition: Using light energy to phosphorylate ADP to make ATP A way to hold energy. What is NADPH / NADP+ ? NADPH is a coenzyme that is an electron carrier. It exists in two forms: NADPH has the electron NADP+ lacks the electron Two Sets of Reactions Light dependent reactions: use light to store energy in carrier molecules (ATP, NADPH) Photosynthesis Light Reaction 1) What is water needed for? Water Chloroplast CO2 NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle Animation ATP NADPH O2 Used in the light reaction Chloroplast when sunlight is present Sugars Photosynthesis Light Reaction 2) What product is released at the end of the light reaction? Water CO2 Oxygen Chloroplast Chloroplast NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Sugars Photosynthesis Light Reaction 3) What two high energy molecules are produced by the light reaction Water CO2 ATP Chloroplast Chloroplast & NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Sugars NADPH Two Sets of Reactions Light independent reactions (Calvin Cycle): Uses energy from light dependent reactions to produce sugars Photosynthesis Light Reaction 4) What is carbon dioxide needed for? Water CO2 Provides Carbon to make sugar in the Calvin Cycle Chloroplast Chloroplast NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Sugars Photosynthesis Light Reaction 5) What product is made at the end of the Calvin Cycle? Water CO2 Sugar (Glucose) Chloroplast Chloroplast NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Sugars Photosynthesis Light Reaction 6) What two low energy molecules are produced at the end of the Calvin Cycle? Water CO2 Chloroplast Chloroplast ADP NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions NADP+ Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 +P Sugars Location of Reactions 7) The light reaction takes place in the thylakoid membranes. 8) The Calvin Cycle takes place in the stroma. 9) The light reaction requires energy from the sun 10) Which part of photosynthesis uses ATP to make energy? The Calvin Cycle Water Chloroplast CO2 NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Sugars Chloroplast What kind of energy storage molecule is made using the energy from ATP? Sugar Calvin Cycle Overview Animation 1 Animation 2 Cellular Respiration Biology Chapter 9 Chemical Pathways Vocabulary 42) Aerobic 43) Anaerobic 44) calorie 45) Cellular respiration 46) Fermentation 47) Glycolysis Basic Need for Energy Energy in Food: What is the difference between a: calorie(lower case c) and Calorie (upper case C)? -A calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree C. -A Calorie is a kilocalorie, or 1000 calories For example, 1 gram of glucose releases 3811 calories, on a food label 3.8 Calories Basic Need for Energy Energy in Food: Organisms cannot use glucose directly, it must be broken down into smaller units. This process in living things begins with glycolysis. If oxygen is present, glycolysis is followed by the Krebs Cycle and electron transport chain – This is called Cellular Respiration An Overview: Cellular Respiration • The equation for cellular respiration is exactly the opposite of photosynthesis. • Equation: 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O and energy Breaking Down Energy Slowly: • Glucose needs to be broken down in small steps so that energy is not wasted. First Step: Glycolysis • Definition: The process of breaking the glucose in half to forming 2 molecules of pyruvate, a 3 carbon chain. • Uses 2 ATP to start reaction • Produces 4 ATP and 2 NADH Glycolysis • Does not require oxygen • Very Fast – thousands of ATP produced in milliseconds • Stops when it runs out of NAD+ (electron carrier) • If oxygen is available: Cellular respiration starts • If oxygen is NOT available, to make more NAD+, your body goes through fermentation. • This way ATP can be made even without Oxygen. Why use ATP in Glycolysis if you want ATP? • You have to use a little energy to make even more energy. • Like a bank, you put money in to earn interest. Animation Fermentation • Fermentation is releasing energy in the absence of oxygen. It is an ANAEROBIC process. • Ultimately it allows NADH to be converted to NAD+, allowing glycolysis to continue. • There are two main types of fermentation – Alcoholic Fermentation – Lactic Acid Fermentation Alcoholic Fermentation • Alcoholic fermentation is found in Yeasts, and a few other microorganisms. • The equation is: Pyruvic acid + NADH alcohol + CO2 + NAD+ Note: Carbon Dioxide is also produced, so when yeast conducts fermentation, there is the release of carbon dioxide as well as alcohol. Alcoholic Fermentation • Alcoholic fermentation diagram Lactic Acid Fermentation • Pyruvic acid from glycolysis can be converted to lactic acid. • This conversion regenerates NAD+ for glycolysis to continue • The equation is: Pyruvic acid + NADH lactic acid + NAD+ Lactic acid fermentation is used by muscles when they run out of oxygen, ultimately causing soreness. Lactic acid is also created by unicellular organisms in the production of cheese, pickles, kimchi and other foods. Lactic Acid Fermentation • Lactic Acid fermentation diagram Krebs Cycle • In the Krebs Cycle, pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide. Krebs Cycle • Where does it occur: Mitochondria • It requires oxygen – it is AEROBIC • It is also known as the Citric Acid Cycle Krebs Cycle So far, from 1 glucose Glycolysis produced: 2 NADH and 2 ATP Krebs Cycle produced: 8 NADH and 2 FADH2 and 2 ATP Animation Krebs Cycle What happens to the Krebs cycle products? Carbon Dioxide is released to the atmosphere ATP is used for cellular activities NADH and FADH2 are used in the electron transport chain to produce large amounts of ATP Electron Transport Chain • Uses the high energy electrons from the Krebs cycle to convert ADP into ATP Electron Transport Chain • Where does it occur: Inner membrane of the Mitochondria • It requires oxygen – it is AEROBIC Electron transport chain Cellular Respiration totals So far, from 1 glucose Glycolysis: 2 ATP + Krebs Cycle: 2 ATP + Electron Transport: Totals: 32 ATP 36 ATP from 1 glucose This is 38% efficiency The rest of the energy is released as heat Energy use by humans Cells contains small amounts of ready ATP -About 5 seconds worth After that, your body uses lactic acid formation -This lasts for about 90 seconds -You breathe hard to get rid of the lactic acid buildup For exercise longer than 90 seconds, cellular respiration is used -This is a slow method to generate ATP -Glycogen (a form of carbohydrate) is used for the first 15-20 minutes of cellular respiration -After that other molecules, such as fats, are broken down