* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nobel Prize of physiology or medicine (1984) (4) Part I The
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Myasthenia gravis wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmune encephalitis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
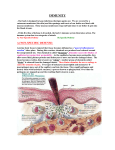
Nobel Prize of physiology or medicine (1984) (4) Part I The specificity in development & control of immune system Niels L. Jerne, Georges J.F. Kohler. & Cesar Mistein were awarded the Noble Prize in physiology or medicine (1984) jointly for theories concerning" the specificity in development & control of immune system" and the discovery of "the principle for production of monoclonal antibodies" Nobel Prize winners in physiology medicine (1984) Niels K.Jerne, Georges J.F. Kohler Milstein & & Cesar Niels K. Jerns is a leading theoretician in immunology. He has been considered by his 3 main theories that he has outlined the development of medical immunology. In the present review, we will present an outline of his work concerning skin diseases. The first theory: (Specificity is predetermined) Instead of the body creates antibodies in response to an antigen, Jerns postulated that immune system has the specific antibodies it needs to fight antigen. (1955) The second theory: (Reactivity against self antigen creates diversity) It was known that the immune system learns to be tolerant to the individual's own self; Jerns postulated that this learning took place in the thymus. (1971) Thymus gland The third theory: (antibodies, anti-antibodies theory) It was known that T cells & B cells communicate with each others. Jerns network theory (1974) postulated that the active sites of antibodies were attracted to both specific antigen (idiotype) & to other antibodies (anti-antibodies) to the same site The antibodies were imbalance until another antigen introduce &binds It will disturb the balance, creating an immune response The network theory has been applied recently to diagnose & treat diseasee. Jerne third theory: Network theory Antibody 1 (AK-1) has a structure in its variable (V) region which can bind to antigen. The V region of (AK-1) contains unique structures which stimulate the production of various anti antibodies (AK2). Some Ak2 express v region structures which mimic the antigen & which therefore can stimulate AK-1 production. • Some examples where the network theory has been applied to experimental & clinical medicine: 1. Infectious diseases 2. Allergy, anti-pollen antibodies 3. Autoimmune disease 4. Transplantation 5. Endocrinology Antigenic shift: how a flu virus transforms &shift Human network theory gives a • picture of infectious disease spread @Autoimmune disease: May be caused by antibodies directed by the body own tissue. For example pemphigus vulgaris, alopecia areata, vitiligo, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma… T cell involvement in the immune pathogenesis of Pemphigus vulgaris J. Clin. Invest. 116:1159, 2OO6 Auto-immune disease Allergy, anti-pollen antibodies @Transplantation: It contributes to immunological tolerance against antigen in the foreign graft. Face transplants in rabbit before moving to humans. @Endocrinology: Antibodies against hormones & hormone receptors may prevent binding of the hormone to the receptor It has been described for insulin & its receptor Diabetes mellitus (Type 1). Immune system destroys beta cells