* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SEBI (Venture Capital Funds) Regulations, 1996
Foreign direct investment in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Startup company wikipedia , lookup
Investor-state dispute settlement wikipedia , lookup
International investment agreement wikipedia , lookup
Stock trader wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
Investment banking wikipedia , lookup
Environmental, social and corporate governance wikipedia , lookup
History of investment banking in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Venture capital financing wikipedia , lookup
Special-purpose acquisition company wikipedia , lookup
Fund governance wikipedia , lookup
Money market fund wikipedia , lookup
Venture capital wikipedia , lookup
Mutual fund wikipedia , lookup
Socially responsible investing wikipedia , lookup
Corporate venture capital wikipedia , lookup
History of private equity and venture capital wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Leveraged buyout wikipedia , lookup
Private equity wikipedia , lookup
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Private money investing wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 2000s wikipedia , lookup
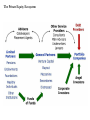
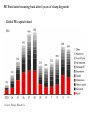
Workshop on Investment Banking and Project Finance Private Equity Strictly Private & Confidential The Private Equity Ecosystem The first Venture Capital investment in financial history ARDC credited with the first major venture capital success story when its 1957 investment of $70,000 in Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) would be valued at over $355 million after the company's IPO in 1968 ARDC made an annualized return of 101% on the transaction Arguably the first noted Private Equity Buyout in financial history J. Pierpon Morgan’s 1901 acquisition of Carnegie Steel Company from Andrew Carnegie and Henry Phipps for $480 Mn represents the first true major Private Equity buyout The real PE boom came in 1980s in USA …. • For the first time, the public became aware of the ability of private equity to affect mainstream companies and "corporate raiders" and "hostile takeovers" entered the public consciousness • The decade would see one of the largest booms in private equity culminating in the 1989 leveraged buyout of RJR Nabisco • In 1980s PE industry raised $2.4 bn of annual investor commitment and by end of 1989 the figure stood at $21bn Private Equity industry is a $1.2 Tn industry today Exits Global Buyout Exit value $500Bn Source: Dealogic Fund Raising Buyout Capital Raised $300Bn Investments Buyout Deal Value $300Bn Some of the largest PE funds globally include …. Goldman Sachs $20.3 Bn TPG Buyout $ 18.9 Bn Apollo Global Mgmt $ 18.4 Bn CVC Partners $ 18.2 Bn KKR $17.6 Bn Blackstone $ 16.3 Bn TPG Growth $ 15.4 Bn Apax Partners $ 11.2 Bn Source: Forbes PE Fund raise bouncing back after 4 years of sharp degrowth Global PE capital raised $Bn Source: Preqin, Bain & Co. PE constitute 54% of total FDI in India % of total FDI flow in India 160 funds out of 325 registered & active funds made investments in 2013 Source: Bloomberg, CEIC Top sectors attracting PE investments … Source: Dealogic, ET Early & Growth Stage deals comprise more than 70% Source: Bain & Co. Opinion – which sectors are likely to attract most PE/VC investments in next 2 years Source: Bain & Co. Issues faced by PE investors … survey of major LP concerns Source: IVCA Limited Partners Survey, 2014 Structure of PE funds • Domestic Fund Trust, Company or LLP Trust structure mostly prevalent Provisions of Companies Act restricts fund raising • Difficulty in redemption of securities, buyback restriction to 25% of paid up capital • Difficulty in distributing profit/dividend (e.g. compulsory transfer to general reserve for dividends in excess of 10% of PV of shares) • Lengthy wind up procedures • Offshore Fund LLC or LLP outside India • Unified Fund LLC or LLP outside India with a Trust registered in India for domestic investors Unified vs. Co-Investment Structures Regulatory framework • Both Domestic & Offshore funds regulated by SEBI SEBI (Venture Capital Funds) Regulations, 1996 SEBI (Foreign Venture Capital Investors) Regulations, 2000 (FVCI Regulations) SEBI (Alternate Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012 • SEBI (Venture Capital Funds) Regulations, 1996 VCFs not permitted to invest in securities of foreign countries Negative list for VCFs: real esate, gold trading, NBFC etc. MOA/Trust Deed prohibited to make an invitation for IPO • The SEBI (Foreign Venture Capital Investor) Regulations, 2000 Covering Investors incorporated outside India No min capital or corpus or individual contribution Mandatory to appoint domestic custodian Regulatory framework (cont’d) • SEBI (Alternate Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012 All VCFs/FVCFs registered as AIF AIF shall have a minimum corpus of Rs 20 crore The fund or any of its scheme shall not have more than 1,000 investors AIF shall not accept investment of value less than Rs. 1 cr from an investor Not to invest more than 25% of funds in one investee company AIFs shall not invest in associate companies Funds to give investors financial information of portfolio companies Units of AIF may be listed on stock exchanges subject to a minimum tradable lot of Rs. 1 cr Funds enjoying certain incentives from SEBI or the Central Govt. will fall under Category I AIF (venture capital funds, SME funds, social venture funds and infrastructure funds) Note: AIFs categorized under PE funds, RE funds and MFs