* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carnitine Overview
Personalized medicine wikipedia , lookup
Metabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
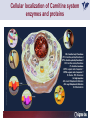
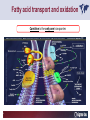
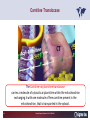
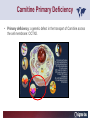
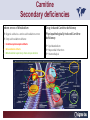
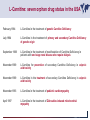
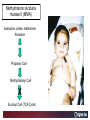
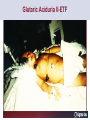
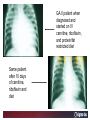
Carnitine Overview 1 Carnitine: historical overview 1905 Carnitine is isolated from muscle tissue 1927 Identification of L-Carnitine chemical structure CH3 H3C N+ CH3 H CH2 C OH CH2 _ COO Background Stimulation of fatty acid oxidation Congenital carnitine metabolism disorders are discovered L-Carnitine first launched in Italy Carnitine’s role in acyl-group transfer is recognised US FDA Orphan Drug designation: 1952 1973 1977 1978 1982 Sigma-Tau synthesizes the biologically active L-carnitine and its derivative Acetyl-L-Carnitine 1985 1995 • • • 1984 *primary deficiency 1992 secondary deficiency 1999 dialysis deficiency Sigma-Tau is the first inventor of L-Carnitine industrial production process (Italian Patent no.1156852) *second Orphan Drug Designation awarded by US FDA 3 Carnitine • Carnitine is an endogenous quaternary compound that is synthesised from amino acids lysine and methionine, reaction catalyzed by γ-butyrobetaine hydroxylase. 4 Carnitine sources 25% of free L-carnitine is synthesized in liver and kidney where enzyme γ-butyrobetaine hydroxylase is highly expressed. 75% of free L-carnitine, is absorbed from dietary intake. 5 Carnitine/Acetyl-L-Carnitine ratio in fluid Plasma concentration of free carnitine is in dynamic balance with acylcarnitines with the acyl to free Carnitine ratio of ≤ 0.4 being considered normal. 6 Carnitine System Overview - PB – 29.03.2013 Cellular localization of Carnitine system enzymes and proteins 7 The essential role of Carnitine • Fatty acid transport and oxidation • Detoxification of toxic metabolites • Regulation of the mitochondrial acyl-CoA/CoA ratio • Stabilization of cell membranes • Balance glucose & fatty acid oxidation 8 Fatty acid transport and oxidation Carnitine is the only one transporter. 9 Acyl-CoA-Synthetase Long-chain fatty acids (>12 C) are extracted from triglycerides by an intracellular lipase. Fatty acids are then activated by Acyl-CoA Synthetase, located in the outer mitochondrial membrane. 10 Carnitine Palmitoyl-Transferase I Carnitine The Carnitine Palmitoyl - Transferase I catalyzes the transfer of acyl groups from activated fatty acid (acyl-CoA) to carnitine, forming acylcarnitine and releasing CoA in cytoplasm Acyl-CoA CPT I CoA + Acyl-L-carnitine Acyl CoA + L-carnitine 11 Carnitine System Overview - PB – 29.03.2013 Carnitine Translocase The Carnitine–acylcarnitine translocase carries a molecule of cytosolic acylcarnitine within the mitochondrion exchanging it with one molecule of free carnitine present in the mitochondrion, that is transported in the cytosol. 12 Carnitine System Overview - PB – 29.03.2013 Carnitine Palmitoyl-Transferase II The Carnitine Palmitoyl - Transferase II is located on the inner side of mitochondrial matrix. It converts acylcarnitine in acyl-CoA and L-Carnitine. Acyl-carnitine + CoA 13 CPT II Acyl-CoA + L-carnitine Energy production Finally the acyl-CoA is conveyed to the beta-oxidation and fragmented in chains containing two Carbons (acetyl-CoA), which subsequently enter in the Krebs cycle, the Electron Transport Chain, with the final result of energy production (ATP). 14 Carnitine System Overview - PB – 29.03.2013 L-Carnitine: Mechanism of Action 15 Detoxification of toxic metabolites Long chain fatty acids then accumulate and become cytotoxic by degrading cellular membranes and inhibiying enzymes. 16 Regulation of the mitochondrial Acyl-CoA/ CoA ratio • Free CoA is an essential element in the cell’s metabolic pathsways, cell membranes are impermeable to CoA. • Carnitine controls intracellular/intramitochondrial concentrations of acyl-CoA and free CoA. Acyl CoA + L-carnitine CoA + Acyl-L-carnitine Free CoA regulates mitochondrial key-enzymes (pyruvate dehydrogenase and beta-oxidation dehydrogenases), which control lipid and glucose metabolism. 17 Stabilization of cell membranes Carnitine has a stabilizing effect on cell membranes, regulates the turnover of damaged fatty acids within the phospholipid membranes (ie, after oxidative stress insult). 18 Mitochondrial carnitine pathway interplay between lipid and glucose metabolism Indications for L-Carnitine Cardiovascular disease Sport Renal insufficiency Pregnancy/ Delivery Immunedeficits Inborn metabolic errors L-Carnitine Fatigue/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Muscle diseases Cancer Nutritional deficits Diabetes Infertility Carnitine Primary Deficiency • Primary deficiency: a genetic defect in the transport of Carnitine across the cell membrane: OCTN2. Carnitine Secondary deficiencies Inborn errors of Metabolism Drug-induced Carnitine deficiency Organic acidurias –amino acid oxidation errors Physiopathologically-induced Carnitine deficiency: Fatty acid oxidation defects: Carnitine system enzyme defects Beta oxidation defects Mitochondrial respiratory chain enzyme defects Dys-Metabolism Myocardial Infarction Haemodialysis FDA approval based on the Clinical Cases of Prof Susan Winter L-Carnitine: seven orphan drug status in the USA February 1984 L-Carnitine in the treatment of genetic Carnitine Deficiency July 1984 L-Carnitine in the treatment of primary and secondary Carnitine Deficiency of genetic origin September 1988 L-Carnitine in the treatment of manifestation of Carnitine Deficiency in patients with end stage renal disease who require dialysis November 1989 L-Carnitine for prevention of secondary Carnitine Deficiency in valproic acid toxicity November 1989 L-Carnitine in the treatment of secondary Carnitine Deficiency in valproic acid toxicity November 1993 L-Carnitine in the treatment of pediatric cardiomyopathy April 1997 L-Carnitine in the treatment of Zidovudine-induced mitochondrial myopathy Methylmalonic Aciduria mutase 0 (MMA) Isoleucine ,valine, methionine threonine Propionyl CoA Methylmalonyl CoA X Succinyl CoA (TCA Cycle) Initial Patient Experience • 1982- MMA mut0-neonatal onset – Results in increased excretion of propionyl carnitine (not understood in 1982) – Only treatment in 1982 was dietary and supportive – Long term prognosis fatal • Rousson T, Guibaud P. Long term outcome of organic acidurias:survey of 105 French cases (1967-1983) J Inherit Metab Dis 1984;7 Suppl 1:10-2 – 1983/1984-Carnitine treatment • Roe CR, Hoppel CL, Stacey TE, Chalmers RA, Tracey BM, Millington DS. Metabolic response to carnitine in methylmalonic aciduria. An effective strategy for elimination of propionyl groups. Arch Dis Child 1983 Nov;58(11):916-20 • Chalmers RA, Stacey TE, Tracey BM, de Sousa C, Roe CR, Millington DS, Hoppel,C. L-Carnitine insufficiency in disorders of organic acid metabolism: response to L-carnitine by patients with methylmalonic aciduria and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric aciduria.J Inherit Metab Dis. 1984;7 Suppl 2:109-10 Carnitine Values Plasma Micromoles/liter Total - 17.4 Normal (30-70) Free - 7.9 Normal (25-65) Ester - 9.5 Normal (0-10) Urine Micromoles/liter 53.1 Normal (300-360) 7.5 Normal (140-200) 45.6 Normal (140-200) Metabolic Analysis Laboratory. Austin Shug, PhD Weight gain First 36 Cases of Carnitine Deficiency (1965-1987) • Encephalopathy (77%) • Progressive Muscle Weakness (77%) • Lipid Excess in Muscle (100%) • Cardiomyopathy (23%) • Low Serum Carnitine (89%) • Low Muscle Carnitine (100%) Plasma Carnitine Deficiency 51 Cases • Hypotonia/ gross motor delay (85%) • Recurrent infections with metabolic decompensations (85%) • Failure to thrive (75%) • Mental retardation (40%) • Cardiomyopathy (30%) • Encephalopathy (5%) Winter SC et al. Am J Dis Child 1987;141:660. Medium Chain Fatty Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (MCAD) FDA approval of Carnitine for Inborn Errors of Metabolism • 1985- oral carnitine approved by FDA for treatment of primary carnitine deficiency • 1992-NDA for treatment for secondary carnitine deficiency due to IEM based on retrospective data Limited to disorders where Acyl CoA metabolites accumulate Summary of Data • Significant drop in hospitalization frequency for all groups • Significant increase in survival • Significant improvement in failure to thrive • Significant change in biochemical parameters – Improved ketosis-restoration of beta oxidation – Increased excretion of accumulating acyl groups – Positive effect on Acyl CoA/Free CoA ratio RB – Age 10 Years MMA Mut 0 RB – Effect of Carnitine PO and IV on Plasma Carnitine Metabolites Carnitine intake (mg/kg/day) Plasma carnitine (mmol/L) Date Oral IV Total Free Ester 6/13 400 0 87.6 7.2 80.4 6/16 0 200 170.0 63.4 106.6 6/21 400 300 396.7 304.0 92.7 6/26 666 300 523.5 338.8 134.7 6/30 666 0 186.5 94.6 91.9 10 years on IV carnitine therapy 6 months on IV carnitine therapy Glutaric Aciduria II-ETF GA II patient when diagnosed and started on IV carnitine, riboflavin, and protein/fat restricted diet Same patient after 10 days of carnitine, riboflavin and diet Patient at Age 14 Remaining well on L-Carnitine treatment Valproic Acid, Hepatic Failure and Carnitine Deficiency Drug induced Carnitine Deficiency: Valproate Survival (%) The survival of patients with VPA hepatotoxicity gets worse the longer the valproate is continued: comparison of L-carnitine–treated patients with untreated patients 100 L-Carnitine treated 80 Untreated controls 60 40 20 0 Hepatotoxic episode duration before valproate stopped Reproduced with permission from Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. Bohan TP. Neurology. 2001;56:1405-1409. The essential role of Carnitine • Life-saving • Key role in healthy metabolism 46 谢谢 Thank You L-Carnitine