* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - scome911
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
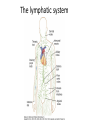
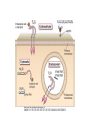
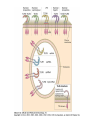
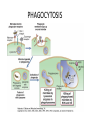
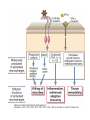
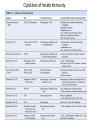
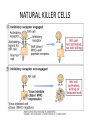
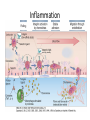
Ahfad University for Women School of Medicine Basic and Applied Immunology Course Dr Rayan Gamal Goda 2nd Year Registrar Soba University Hospital Clinical Immunology and Allergy MD Programme Sudan Medical Specialization Board Member of Sudanese society for clinical immunology and allergy Member of sudanese Association of Rheumatology Course Objectives • Offer a quick revision of basic immunology, and covers important topics in clinical immunology. • Emphasize the role of immunology in current medical practice • Walk you through important, difficult topics. • More importantly to help you understand immunology and simplify this very interesting subject. This course will be... • • • • Key point guided, interactive tutorials All is encouraged to participate If no one participates; ..... ?? Hello!!! Write down a list of all topics you want to be covered. • SLE, RA, Primary immunodeficiency...etc • Basically: a tailored course to your needs. • This course is for you; please... – Ask and don’t be afraid to know – Participate actively. – Help me help you. Basic Immunology What do we know? Where do we stand? ...etc. What is ... • • • • • • • • • Immunology Immune Response Components of the immune system Innate immunity Adaptive immunity Tolerance and autoimmunity Tumour Immunology Transplantation Clinical immunology Immune Response • The reaction that occurs in response to the introduction of foreign substances. • Most of medicine and medical practice revolves around this point. • Foreign substances; microbes, cancer cells, chemical substances, ...etc. The Immune Response • Innate/ natural or native immunity • Components: – Skin – Mucosal Epithelia – Chemical Barriers: e.g. Defensins. – Others: plasma proteins; complement, cytokines, acute phase reactants. – Cells: DCs, phagocytes, NK cells, T& B cells, Mast cells. • Adaptive immunity – Cell mediated immunity – Humoral immunity • Components: – Lymphocytes – Antibodies Immune Response Organs of the Immune System • What are the organs of the immune system? – Bone Marrow – Liver – Spleen – Thymus – Lymph nodes – Lymphatic vessels The lymphatic system INNATE IMMUNE RESPONSE • Receptors: e.g. Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Death Associated Molecular Patterns, ... NOD Like receptors, RIG like receptors, ...etc • Cellular components: Epithelial barriers, Phagocytes, Dendritic Cells, Natural killer cells (NK Cells), B and T lymphocytes with limited specificity, and Mast Cells. Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs) • Soluble components: Natural antibodies, acute phase reactants, complement. • Natural Antibodies: e.g. IgM. • Acute Phase Reactants: e.g. IL-8. • Defensins and Cathelicidins. • Soluble Receptors: complement, Pentraxins, , Collectins, and Ficolins. Death Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) • They play a role in the natural homeostasis of the immune system. • They recognize endogenous molecules that are produced from damaged or dying cells. • Can be: stress induced proteins Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs) • Crystals: Monosodium urate • Nuclear Proteins: HMGB1. Mechanisms • Physical barriers • Chemical barriers • Cellular mechanisms: – PHAGOCYTOSIS ( MACROPHAGES, DCs, B CELLS,...ETC) – NK CELLS: including Natural Killer T cells. – T & B CELLS including ᵞᵟ T cells – MAST CELLS < < WHY? - Eosinophils, and basophils. CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM • Phagocytes: – Dendritic cells – Monocytes /Macrophages – Neutrophils – Mast cells – Eosinophils – Basophils Dendritic cells • These are the guru cells, everything in immunology begins with the dendritic cells. Also known as the best Antigen Presenting Cells. PHAGOCYTOSIS Cytokines of Innate Immunity Complement • It is a group of plasma proteins, work to opsonize microbes, promote the recuitment of phagocytes to the site of infection, and sometimes directly kill the microbe. • It is composed of 3 different pathways: – Classical , alternative and Mannose- binding Lectin pathways. – All these pathways meet at C3, to form c5,c6,c7,c8,c9 ... Membrane Attack Complex (MAC). • It can also help to activate B cells, in adaptive immunity. NATURAL KILLER CELLS Inflammation Case study • In reflection to what we discussed: how did these problem occur? • How was the immune system involved? • Questions..?? THANK YOU!! • If you have a questions, problems, feel free to contact me at any time: • Email: [email protected] • Maybe a group google hangout?!!