* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab Sporks and Beans Natural Selection AP Bio 2010
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
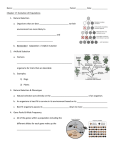
1 NAME: ______________________________________________ DATE: ______________ BLOCK: ___________ responsible for the spoon-like appearance of both the spoon and fork while the UF (caused by a genetic mutation) is responsible for the fork-like appearance of the spork. These two alleles show incomplete dominance. The genotype US US yields the phenotype of a spoon and the US UF has a phenotype of a spork. PART I: Spoon v. Spork Predict: 1. Which phenotype (spoon or spork) will be the better predator and why do you think this? Data: Person # of prey for spoon # of prey for spork 1 2 Average Conclusion: 2. Which phenotype (spoon or spork) was the better predator? 3. Think of a dolphin, tuna, and shark. What traits do they have in common that are useful in an aquatic environment? PART II: Population Competition Predict: 4. In a population that contains 75% spoons and 25% sporks, which phenotype will eat more prey and why do you think this? 2 Data: Record the top six predators and the number of prey eaten. Predator # or prey eaten phenotype 1 2 3 4 5 6 Conclusion: 5. Which phenotype was more successful in the population and why? PART THREE: Natural Selection Predict: 6. If survivors are allowed to reproduce, what do you think will happen to spoons and sporks over several generations? Data: # Generation spoons 1 2 3 4 5 6 # sporks # US alleles # UF alleles Freq. of # US allele Freq. of # UF allele 3 Conclusion: 7. Explain what happened to the allele frequencies and why. PART FOUR: Natural Selection Again Predict: 8. What if the food source goes extinct and the only prey left changes to a harder, drier food? What do you think will happen to the allele frequencies and why? Data: # Generation spoons # sporks # US alleles # UF alleles Freq. of # US allele Freq. of # UF allele 1 2 3 4 5 6 Conclusion: 9. What actually happened to the allele frequencies when the food source changed? 4 DO YOU REALLY GET IT? For each pair of statements, circle the letter of the statement that is true. a. Mutations are detrimental to fitness. b. A mutation may result in a more adaptive trait under certain environmental conditions. c. New traits can appear in a population that are unnecessary and when there is already an existing trait that is successful. d. New traits appear as a result of need/use/disuse. e. Acquired characteristics are heritable. f. Acquired characteristics are not heritable. g. Genetic variation is very important and relevant to evolution and natural selection. h. Genetic variation is not important and irrelevant to evolution and natural selection. i. Environmental conditions are not considered important in causing selective pressures. j. Environmental conditions are considered important in causing selective pressures. k. Survival is all that is needed to affect natural selection. l. Survival is important, but reproductive success is also needed for natural selection. m. Evolutionary change is based on the changing proportion of individuals with particular alleles. n. Evolutionary change is based on gradual modifications in traits, not the changing proportion of individuals with particular alleles. o. Evolution is deterministic and works toward a future goal. p. Evolution is the result of organisms interacting with current environmental conditions, and is not goal oriented.