* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
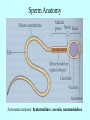
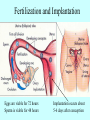
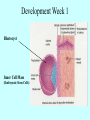
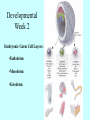
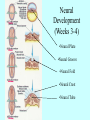
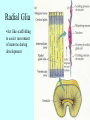
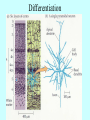
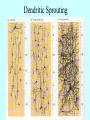
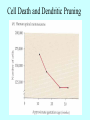
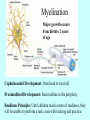
It Takes Teamwork Sperm Anatomy Acrosome enzymes: hyaluronidase, acrosin, neuraminidase Fertilization and Implantation Eggs are viable for 72 hours Sperm is viable for 48 hours Implantation occurs about 5-6 days after conception Development Week 1 Blastocyst Inner Cell Mass (Embryonic Stem Cells) Developmental Week 2 Embryonic Germ Cell Layers: •Endoderm •Mesoderm •Ectoderm Neural Development (Weeks 3-4) •Neural Plate •Neural Groove •Neural Fold •Neural Crest •Neural Tube Neural Tube Defects Anencephaly: Failed closure of the Anterior Neuropore Spina Bifida: Failed closure of the Posterior Neuropore Steps in Neural Development •Mitosis •Migration •Differentiation •Dendritic Sprouting and Bulb Growth •Synaptogenesis •Cell Death •Dendritic Pruning •Myelination Mitosis Migration •Growth Cones form and use: •Radial Glia •Contact Inhibition •Contact Adhesion •Fasciculation •Guide Posts •Chemotropism Growth Cones Growth Cone Radial Glia •Act like scaffolding to assist movement of neurons during development Contact Inhibition/Adhesion The growth cones of migrating cells can be attracted to other cell surfaces by contact adhesion molecules on those cells. Likewise, growth cones of migrating cells can be repelled from other cell surfaces by contact inhibition molecules on those cells. Fasciculation Adhesion molecules allow the bonding of same type axons to form a nerve bundle. Guide Posts Intermediate targets that help guide or direct the growth cone of the migrating cell in the proper direction Chemotropism Target Cell or Tissue Target tissues or cells can release chemicals that will attract the specific growth cones of migrating cells. Differentiation Dendritic Sprouting Synaptogenesis Cell Death and Dendritic Pruning Myelination Major growth occurs from birthto 2 years of age Cephalocaudal Development: from head to toe (tail) Proximodistal Development: from midline to the periphery Readiness Principle: Until children reach a state of readiness, they will be unable to perform a task, even with training and practice.