* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DCC-promoted peptide coupling
Survey
Document related concepts
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
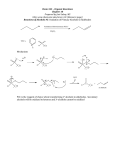
5221 Central Avenue, Suite 8A Richmond, CA 94804 Phone: Email: 510-528-8396 [email protected] DCC N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide A reagent for coupling and for dehydration ProductInformation CAT No Grade Application Storage C1395 BioXtra, ≥99.0% (GC) coupling and for dehydration Room temperature Product Name: N,N’-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide CAS Number: 538-75-0 Formula: C6H11N=C=NC6H11 Molecular weight: 206.33 Melting point: 34-35 °C(lit.) Boiling point 122-124 °C Synonym: Carbodicyclohexylimide;Carbodiimide, dicyclohexyl-; Dicyclimide; dicyclohexyl-carbodiimid; n,n’-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide,1msol.inn-methylpyrrolidone,peptidesynthesisgrade; n,n’-methan- etetraylbis -cyclohexaamin; n,n’-methanetetraylbis-cyclohexanamin; N,N’-methanetetraylbis- Cyclohexanamine Suitability N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide is an organic compound with the chemical formula C13H22N2 whose primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. Under standard conditions, it exists in the form of white crystals with a heavy, sweet odor. The low melting point of this material allows it to be melted for easy handling. It is highly soluble in dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile and dimethylformamide, but insoluble in water. The compound is often abbreviated DCC. DCC is a dehydrating agent for the preparation of amides, ketones, nitriles. In these reactions, DCC hydrates to form dicyclohexylurea (DCU), a compound that is insoluble in most organic solvents and in water and hence is readily removed by filtration. DCC can also be used to invert secondary alcohols. Moffatt oxidation A solution of DCC and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) effects the so-called Pfitzner-Moffatt oxidation. This procedure is used for the oxidation of alcohols toaldehydes and ketones. Unlike metal-mediated oxidations, the reaction conditions are sufficiently mild to avoid over-oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids. Generally, three equivalents of DCC and 0.5 equivalent of proton source in DMSO are allowed to react overnight at room temperature. The reaction is quenched with acid. Dehydration Alcohols can also be dehydrated using DCC. This reaction proceeds by first giving the O-acylurea intermediate which is then hydrogenolyzed to produce the corresponding alkene: RCHOHCH2R' + (C6H11N)2C → RCH=CHR' + (C6H11NH)2CO Inversion of secondary alcohols Secondary alcohols can be stereochemically inverted by formation of a formyl ester followed by saponification. The secondary alcohol is mixed directly with DCC, formic acid, and a strong base such as sodium methoxide. 1 Esterification A range of alcohols, including even some tertiary alcohols, can be esterified using a carboxylic acid in the presence of DCC and a catalytic amount of DMAP. DCC-promoted peptide coupling During protein synthesis (such as Fmoc solid-state synthesizers), the N-terminus is often used as the attachment site on which the amino acid monomers are added. To enhance the electrophilicity of carboxylate group, the negatively charged oxygen must first be "activated" into a better leaving group. DCC is used for this purpose. The negatively charged oxygen will act as a nucleophile, attacking the central carbon in DCC. DCC is temporarily attached to the former carboxylate group forming a highly electrophilic intermediate, making nucleophilic attack by the terminal amino group on the growing peptide more efficient. Safety DCC is a potent allergen and a sensitizer, often causing skin rashes. Application: A reagent for coupling and for dehydration It is also used to modifie bovine heart mitochondrial transhydrogenase, and a inhibitor of F1F0-ATPase and other proton-translocating enzymes. Specification Grade Purity (GC) Appearance (Color) Appearance (Form) Infrared Spectrum Proton NMR Spectrum BioXtra 99.0 % White Powder or Solid or Crystals or Crystalline Chunk(s)or Chunk(s) Conforms to Structure or Proton NMR Spectrum Conforms to Structure or Infrared Spectrum 2









![Group Activity 3 [10 PTS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010780770_1-3445600a9b56e890a0f283c789afe8fb-150x150.png)

