* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L. Ciasto`s presentation notes: overview - geo.uni
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
Critical Depth wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea fish wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
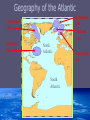
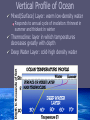
An Introduction to the Ocean Geography of the Atlantic Circulation of the Ocean Wind Driven Currents Thermohaline Circulation Vertical Structure of the Ocean Geography of the Atlantic Greeland Sea Labrador Sea Sargasso Sea Iceland Sea North Atlantic South Atlantic Norwegian Sea Circulation of the Ocean The Surface Currents Circulation of the Ocean Wind Driven Currents Driven by energy transfer from wind to surface(mixed) layers of ocean Carries warm water north along the western boundaries of the Altantic and Pacific Oceans Cooler water advected along eastern boundary and equatorial currents Circulation of the Ocean Wind Driven Currents Gyres: closed surface currents occupying major ocean basins Forced by overlying pressure systems Subpolar low pressure system Subtropical high pressure system Circulation of the Ocean Thermohaline Circulation Global Conveyor Belt Driven by density variations salinity and temperature Circulation of the Ocean Thermohaline Circulation Driving mechanism: deep water formation (DWF) Water is advected north into the Labrador and GIN seas where its cooled Relatively cold salty water creates unstable surface layer and sinks North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) DWF occurs in North Atlantic but not North Pacific Vertical Profile of Ocean Mixed(Surface) Layer: warm low-density water Responds to annual cycle of insolation: thinnest in summer and thickest in winter Thermocline: layer in which temperatures decreases greatly with depth Deep Water Layer: cold-high density water