* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane Concept Map
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
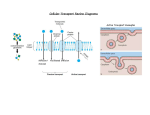
Cellular Transport Review Diagrams Active Transport Examples Diffusion/ Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Cell Transport Concept Map Name Date Cell transport involves the exchange of molecules through the Against the concentration gradient (low to high) Down the concentration gradient (high to low) large molecules transported by requires small molecules move through moved by of water in out Small molecules move through Larger molecules move through examples Example: Example: also called Word Bank: Active Transport Passive Transport Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion ATP Energy Glucose/Amino Acids/Ions Wastes/Secretions Cell Membrane (2X) Osmosis Food/Bacteria Proteins (2X) Endocytosis Exocytosis Cell Transport Concept Map Answer Key Exchange of molecules through the cell membrane Against the concentration gradient (low to high) Down the concentration gradient (high to low) active transport passive transport large molecules transported by requires small molecules move through energy - ATP proteins moves by endocytosis diffusion exocytosis of water in out small molecules move through larger molecules move through examples glucose, amino acids, ions (Ca, Na) Example: food for unicellular organisms; bacteria that cause infection Example: Wastes, Secretions: Enzymes, Hormones, Insulin proteins Cell membrane also called facilitated diffusion osmosis