* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution and Natural Selection
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
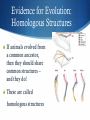
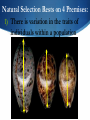
April 11, 2016 TO DO: Notebook, pencil/pen, get your natural selection WS out. WARM UP: Give me an example of Natural Selection and explain how it could happen. HOMEWORK: Weebly Reflections OBJECTIVE: Students will understand the concept of natural selection. Evolution and Natural Selection How species change over time Evolution and Natural Selection Genetic variations are passed on through reproduction Evidence for evolution illustrates how organisms are related Natural selection leads to evolution Our understanding of evolution has changed over time Evolution The theory that organisms today developed from more simple life forms and have changed (evolved) over time. Natural Selection The theory that states that those organisms best adapted to their environment have a better chance of surviving and reproducing. What was Darwin’s hypothesis? Darwin hypothesized that organisms had a common ancestor, but had adapted to their particular environments and changed over time. Darwin published his research in 1859 Natural Selection For natural selection to occur, there must be at least two varieties of a species. For example: the peppered moth Peppered Moths At the beginning of the Industrial Revolution in England, coal burning produced soot that covered the countryside in many areas What do you think happened? Evolution/Natural Selection White moths became easier to see, while the black moths became harder to see. The black moths were more likely to survive and pass on the gene for dark color to their offspring. Over time, the black moths have become more common. Evidence for Evolution: Common Ancestry Common Ancestry: If species evolved from a common ancestor, then they should share common anatomical traits Hawaiian Honeycreeper: family of birds in Hawaii that have similar skeletons and muscles, indicating they are closely related. Over time, their common ancestor evolved into several species, each with a specialized bill for eating certain foods. Just like Darwin’s finches on the Galapagos! Evidence for Evolution: Homologous Structures If animals evolved from a common ancestor, then they should share common structures – and they do! These are called homologous structures Evidence for Evolution Embryo Development What do you notice? List 2 observations Evidence for Evolution: Vestigial Organs Some organisms have structures or organs that no longer have a useful function. These structures or organs may have been useful to the ancestors of a species, but over time have evolved into what we term vestigial organs. Examples of Vestigial Organs Kiwi (flightless bird) Whales (hind leg bones) Humans (tailbone, appendix) Evidence for Evolution Fossils Fossils provide a look into the past Scientists can trace how a species has evolved by studying fossils Wrap Up the Evidence Common Ancestry Homologous Structures Vestigial Organs Embryonic Development Fossils Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 1) There is variation in the traits of individuals within a population Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 1) There is variation in the traits of individuals within a population Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 1) There is variation in the traits of individuals within a population Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 2) There is differential survival and reproduction, i.e., some individuals survive and reproduce, some don’t Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 2) There is differential survival and reproduction, i.e., some individuals survive and reproduce, some don’t Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 2) There is differential survival and reproduction, i.e., some individuals survive and reproduce, some don’t Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 2) There is differential survival and reproduction, i.e., some individuals survive and reproduce, some don’t Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 3) Traits have a genetic basis, or are inherited from parents Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 3) Traits have a genetic basis, or are inherited from parents Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 4) Advantageous traits, which allows organisms to have more offspring, will become more common in the population over time. Examples of Natural Selection: The Evolution of The Polar Bear Our story begins with the Polar Bear’s closest living relative – the Brown Bear The Evolution of The Polar Bear Around 300,000 years ago a small group of Brown Bears became reproductively isolated from the rest of the population The Evolution of The Polar Bear This small founding population of Brown Bears were able to survive and reproduce living in the Arctic Tundra. After MANY generations, a random genetic mutation occurred The Evolution of The Polar Bear Because of the genetic mutation, a litter of Brown Bears exhibited WHITE coloration The Evolution of The Polar Bear How do you think the white fur color affected these bears chances of surviving long enough to have cubs of their own? REMEMBER: Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 1) There is variation in the traits of individuals within a population REMEMBER: Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 2) There is differential survival and reproduction, i.e., some individuals survive and reproduce, some don’t REMEMBER: Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 2) There is differential survival and reproduction, i.e., some individuals survive and reproduce, some don’t X X X X REMEMBER: Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 3) Traits have a genetic basis, or are inherited from parents REMEMBER: Natural Selection Rests on 4 Premises: 4) Advantageous traits, which allows organisms to have more offspring, will become more common in the population over time. X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X What Happened? Through Reproductive Isolation and Natural Selection . . . One Species Evolved Into Another New Species By Adapting To Its New Environment We see this trend again and again in the Animal Kingdom . . . Speciation by means of Reproductive Isolation & Natural Selection! Activity Go to the following website and answer the worksheet. http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/natural-selection You will need to download Java to play this.