* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell organelles
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
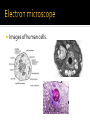
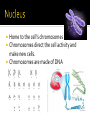
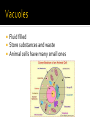
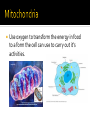
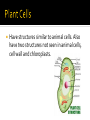
the basic unit of structure and function of life. living units able to make more of themselves(replicate). different depending on their function Cells that do not have membrane bound structures. bacteria Cells that have membrane bound structures Most cells are microscopic Red blood cells are the smallest cells in your body. 2,000 RBC’s are needed to go across your thumb. Images of human cells. Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs. Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids The sequence of amino acids determines each protein’s unique 3-dimensional structure and its specific function. Encloses the cell. It acts like a gatekeeperallowing some materials to pass through it, but not others. 1st line of defense Mostly water with other substances dissolved in it. Similar to gelatin (jello) Organelles are in the cytoplasm Home to the cell’s chromosomes Chromosomes direct the cell activity and make new cells. Chromosomes are made of DNA Found inside the nucleus Responsible for making ribosomes Ribosomes are the protein builders or the protein synthesizers of the cell. They are like construction guys who connect one amino acid at a time and build long chains. You might find them floating in the cytoplasm They are also on the endoplasmic reticulum. Endoplasmic reticulum with attached ribosomes is called rough. Fluid filled Store substances and waste Animal cells have many small ones Use oxygen to transform the energy in food to a form the cell can use to carry out it’s activities. Produce important products for the cell, including proteins and lipids(fats). Serves as the delivery system for the cell Help package products(proteins) from the ER and distribute them around the cell or outside of it. Have structures similar to animal cells. Also have two structures not seen in animal cells, cell wall and chloroplasts. Outer barrier provides extra support for the cell and gives it a shape. Cell wall is made of cellulose, a fiber that is the main component of paper and wood. Food making structures of plant cells. Contain chlorophyll Photosynthesis Sunlight + carbon dioxide + water forms Glucose and oxygen Every cell is a busy place Many chemical activities occur such as…. 1. Releasing energy from food 2. Making proteins and other chemicals the cell needs. 3. Getting rid of wastes Function Description Example Antibody Antibodies bind to specific foreign Immunoglobulin G (IgG) particles, such as viruses and (illustration) bacteria, to help protect the body. Enzyme Enzymes carry out almost all of the Phenylalanine hydroxylase thousands of chemical reactions that (illustration) take place in cells. They also assist with the formation of new molecules by reading the genetic information stored in DNA. Messenger Messenger proteins, such as some Growth hormone (illustration) types of hormones, transmit signals to coordinate biological processes between different cells, tissues, and organs. Structural component These proteins provide structure and support for cells. On a larger scale, they also allow the body to move. Transport/storage These proteins bind and carry atoms Ferritin (illustration) and small molecules within cells and throughout the body. Actin (illustration)