* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STEM_Midterm Study Guide_2017
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
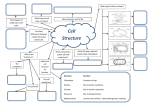
Midterm Study Guide 2017 Lab skills Identify pictures of lab equipment Purpose of various lab equipment Read a graduated cylinder Units for length, volume, and mass Metric conversions The scientific method Parts of an experiment: o Independent variable – where on a graph? o Dependent variable – where on a graph? o Control Creating a graph o Bar o Line Lab safety Chemistry of Life What are the characteristics shared by all living things? Know the 3 Domains of Life and know what type of cells these organisms have. What is the atom? Define o o o o o o Element: Ion: Cation: Anion: Isotope: Electronegativity: How do electron shells fill and how many electrons can be held in the first, second and third shell? What is the valence shell and why are valence electrons so important? Atomic number Mass number Subatomic particles in the atom (know charges of each) Know what an isotope is and be able to identify one (for example: Carbon) What are the four elements that make up 96% of our body mass? Identify a compound How are elements different than compounds? Ionic/Covalent/Hydrogen bonds (know characteristics: i.e. covalent bonds share electrons and are strong/ionic bonds transfer electrons and are weak/hydrogen bonds form between water molecules) What kind of molecule is a water molecule? Why? Three important properties of water. Why are they important to life? Acids and Bases (pH scale) Organic vs. inorganic Functional groups 3 fundamental structures Carbon can form. Difference between a monomer and a polymer. How are they related? 4 Types of carbon based Molecules Monomers of Carbohydrates Polymers of Carbohydrates Examples of Carbs Functions of Carbs Chemical Formula of Pentose/ Hexose (C5H12O5 /C6H12O6) Identify a monosaccharide by a picture (glucose, fructose, galactose) Dehydration Synthesis vs. Hydrolysis Uses of Starch & Glycogen monoglycerides – structure Saturated vs. Unsaturated fatty acid Components of a triglyceride Examples of lipids and their structure Structure of triglycerides and phospholipids Steroids and their structure – what class of organic molecules do steroids belong to? Monomers of Proteins What makes each amino acid different? Total # of amino acids – 20 Amino acids link together via peptide bonds (type of covalent bond) Why is the amino acid sequence important? What is an Enzyme and what is its function? HOW do enzymes work? Answer questions based on a graph of a reaction with/without an enzyme Enzymes are specific**, reusable, and end in –ase. Where does the substrate bind on an enzyme? What affects Enzyme activity (3 factors) Change in Shape = Change in function Activation energy Endergonic vs. exergonic reactions Catalyst/enzyme Coenzyme/cofactor What is a denatured protein Examples of nucleic acids Function of nucleic acids Monomers of Nucleic Acids 3 parts of a nucleotide Polymers are nucleic acids 4 nucleotide bases (A-T; G-C) Purine vs. Pyrimidine Where is Uracil found? Shape of DNA DNA vs. RNA The Cell Prokaryotic/ eukaryotic cells Examples of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Parts of a microscope Calculate total magnification Pant cell vs. animal cell All cell organelles and their functions Cell theory What is the cell membrane made up of? What are the parts of a phospholipid? What does polar mean? What does non-polar mean? Which part of the phospholipid bilayer (cell membrane) is polar? Non-polar? Describe the fluid mosaic model What kinds of molecules are found in the cell membrane? How is the cell membrane selectively permeable? Why is it important to the cell? Difference between passive and active transport Passive transport: HIGH concentration LOW concentration Active transport: LOW HIGH (***REQUIRES ENERGY***) Types of passive transport: o Diffusion o Osmosis o Facilitated diffusion How are diffusion and osmosis similar? Different? Why is passive transport important for the cell? What would happen if all molecules had to be moved by active transport? Hypotonic/isotonic/hypertonic Characteristics of transport proteins Vesicular transport Endocytosis/exocytosis – they require energy!! Types of active transport!! Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis Example of exocytosis in the body (nerve cells) Where does the cell get the energy it needs to function? How many phosphates does ATP have? ADP? ADP low energy molecule ATP high energy molecule What is ADP/ATP? What is their role in the transfer of energy into a form the cell can use? How is energy stored in ATP and then released?? Heterotrophs/autotrophs Photosynthesis/chemosynthesis Cells and Energy Who relies on photosynthesis? Photosynthesis equation – identify names of reactants and products Where does photosynthesis take place? Where does the light-dependent reaction take place? Where does the light-independent reaction take place? What is needed for the light-dependent reaction to take place? What is produced during the light-dependent reaction? What is needed for the light-independent reaction to take place? What is produced during the light-independent reaction? Describe what happens during the light-dependent reaction Describe what happens during the light-independent reaction Difference between photosystem I and photosystem II Where does the electron transport chain (in photosynthesis) get electrons? What is the sun’s role in photosynthesis? What is water’s role in photosynthesis? What happens when electrons are passed down the ETC? What is made when H+ ions move through ATP synthase? (High Low concentration) Describe how energy from sunlight is transferred to ATP and NADPH. How are these molecules used in the light-independent reaction? Describes what happens in the light-independent reactions Cellular Respiration Equation – identify names of reactants and products Where does cellular respiration take place? Aerobic/anaerobic What parts of cell respiration are aerobic/anaerobic? What takes place during glycolysis? What are the products? Where does it occur? What is the purpose of the Krebs cycle? How does pyruvate enter the Krebs cycle? What gas is formed during the Krebs cycle? What other products are formed during the Krebs cycle? And where are they used next? Describe the ETC of cellular respiration What are the roles of NADH and FADH2 in the ETC? What is the role of oxygen in the ETC? Compare cell respiration to photosynthesis. How are they similar? How are they different? Fermentation is an anaerobic process. How does fermentation allow glycolysis to continue? Why and when does fermentation occur? Lactic Acid Fermentation vs. Alcoholic fermentation Compare fermentation to cellular respiration