* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Cell Structure Induction Booklet
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
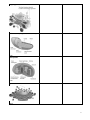
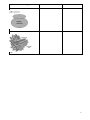
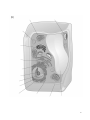
Cell ultrastructure Name…………………………………………………………………………… Living organisms consist of cells 1. Living organisms consist of cells. Cells are complex and busy places. You will know many of the structures from your work at KS3 and KS4, but we need to go much further at A Level. Carry out research and complete the following table giving details of the cell ultrastructure. AO1 [24] Membrane bound organelles Describe the structure Summarise the function Plasma (cell surface) membrane Size: Nucleus Nuclear envelope Nucleus Size: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Nucleolus Rough: Smooth: Size: 2 Golgi apparatus Size: Mitochondria (singular mitochondrion) Size: Chloroplasts Size: Lysosomes Size: 3 Non-membrane bound organelles Describe the structure Summarise the function Ribosomes Size: Centrioles Size: 4 Organelles – structure and function 2. Using your new found knowledge label the organelles typically found within (a) animal cells and (b) plant cells on the diagrams below. 5 6 Cells and living processes 3. State two functions of the cytoskeleton inside animal cells. AO1 [2] 4. Suggest why nerve cells have an unusually well developed cytoskeleton. AO2 [1] 5. Suggest why most plant cells have a poorly developed cytoskeleton. AO2 [1] 6. Suggest why chloroplasts are moved around plant cells. AO2 [1] 7. Suggest why white blood cells need to be able to move. AO2 [1] 8. Cells can be Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic. Find out about the differences between these cell types and summarise in the table below. AO1 [16] Eukaryotic cell Prokaryotic cell Cell wall present/type Nuclear envelope Golgi apparatus Undulipodium/flagellum Ribosomes (size and location) DNA / type of DNA Carries out respiration Chloroplasts Size of cell 7 9. The Figure below is a diagram of a bacterium as seen under an electron microscope. (i) Name the structures labelled A and B. A ........................................................... B ........................................................... AO1 [2] (ii) It has been suggested that the mesosome has the same role as mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. Suggest the role of the mesosome in prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria. ................................................................................................................................................................... AO2 [1] (iii) Eukaryotic cells, such as Euglena, contain membrane-bound organelles. Each organelle has a specific function in the cell. State the process that is carried out in each of the organelles. Ribosome .................................................................................................................... ....... Chloroplast .................................................................................................................... AO1 [2] 8