* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
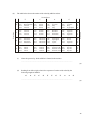
Download 1. The table below refers to some disaccharides, their constituent
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
1. The table below refers to some disaccharides, their constituent monomers and their roles in living organisms. Complete the table by writing in the appropriate word or words in the empty boxes. Disaccharide Constituent monomers One role in living organisms Carbohydrate source in mammalian milk Lactose Glucose + glucose Form in which sugars are transported in plants (Total 5 marks) 2. (a) Explain what is meant by the primary structure of a protein molecule. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Explain the role of hydrogen bonding in maintaining the structure of a globular protein such as insulin. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) 1 (c) Describe how the structure of a fibrous protein, such as collagen, differs from the structure of a globular protein. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 8 marks) 3. Read through the following account of the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account. DNA is a molecule consisting of a long chain of nucleotides, which are joined together by................................... reactions. Each nucleotide in DNA consists of a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group and ................................... .The nitrogenous base may be adenine, guanine, cytosine or .................................... . A molecule of DNA is made up of two polynucleotide chains coiled into a ................................... . The two chains are held together by ................................... bonds between the nitrogenous bases (Total 5 marks) 2 4. Read through the following passage about protein structure, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage. Proteins are composed of long chains of monomers called ..............................................., which are linked together by ........................................................ bonds. These bonds are formed by ..................................................... reactions between adjacent monomers. The primary structure of a protein is the specific sequence of monomers in a polypeptide chain and determines the secondary and tertiary protein structure. The secondary structure of a protein may be a coil, known as an ............................................................... which is held in shape by ............................................................. bonds between different monomers in the chain. (Total 5 marks) 5. The diagram below shows the structure of a nucleotide. A B (a) C Identify the parts labelled A, B and C in the diagram. A ................................................................................................................................ B ................................................................................................................................ C ................................................................................................................................ (3) 3 (b) The sequence of bases from part of a gene is shown below. AGCCGTCCCGTC Write out the sequence of bases on messenger RNA (mRNA) that would be coded for by this part of the gene. .................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Describe what is meant by the semi-conservative replication of DNA. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (4) (d) A quantity of DNA was labelled with radioactive nitrogen. It was then allowed to replicate three times, using non-radioactive nucleotides to synthesise the new DNA strands. What proportion of the final mass of DNA would you expect to be radioactive? Explain your answer. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) 4 (e) In which stage of the cell cycle does replication of DNA take place? ................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 12 marks) 6. The table below refers to two disaccharides, sucrose and maltose. If the statement is correct, place a tick ( ) in the appropriate box and if the statement is incorrect, place a cross ( ) in the appropriate box. Statement Sucrose Maltose Contains glucose Is a reducing sugar Contains glycosidic bonds Is transported in the phloem of flowering plants (Total 4 marks) 5 7. Read through the following account of the properties of water, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account. Water has the chemical formula ………………………………… . Water molecules are described as ………………………………….. because they have a slight positive charge at one end of the molecule and a slight negative charge at the other end. As a result, individual molecules form ………………………………….. bonds with each other. Water is an important ………………………………….. in living organisms because most biochemical reactions take place in aqueous solution. Water also has a high ………………………………….., which means that its temperature remains relatively stable despite large changes in the temperature of the surrounding environment. (Total 5 marks) 8. Explain what is meant by the following terms. (a) Semi-conservative replication of DNA ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. (3) 6 (b) Tertiary structure of a protein ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………….. (3) (Total 6 marks) 9. Give an account of the structure and functions of lipids, including triglycerides and phospholipids. (Allow 3 lined pages) (Total 10 marks) 10. The table below refers to the structure of different types of nucleic acids. If the feature is present, place a ( ) in the appropriate box and if the feature is absent place a cross ( ) in the appropriate box. Feature DNA mRNA Cytosine present Uracil present Pentose sugar present Is single stranded (Total 4 marks) 7 11. Read through the following passage about protein structure, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage. The tertiary structure of a protein depends on its primary and secondary structure. The primary structure is the ………………………………….. of amino acids, which are joined together by ………………………………….. bonds to form a chain. This type of bond is formed when a ………………………………….. reaction takes place between two amino acids. The chain of amino acids may be folded into an alpha helix, held in shape by ………………………………….. bonds. A number of different types of bonds hold the tertiary and quaternary structure in shape. For example, the two peptide chains in insulin are held together by ………………………………….. bonds which form between the ………………………………….. of certain amino acids. (Total 6 marks) 8 12. The diagram below summarises the steps involved in the semi-conservative replication of DNA. Double strand of DNA Step 1 Enzyme A Two strands separated Step 2 Complementary nucleotides line up against each strand Step 3 Enzyme B Nucleotides join to form two new polynucleotide chains Step 4 Two identical DNA molecules formed (a) Describe how Enzyme A separates the two DNA strands in Step 1. ……………………………………………….……………………………………… ……………………………………………….……………………………………… (1) (b) In Step 3 the individual nueleotides are joined up to form a polynucleotide chain by Enzyme B. Name the type of reaction that Enzyme B catalyses. ……………………………………………….……………………………………… (1) (c) Give the phase of the cell cycle during which DNA replication occurs. ……………………………………………….……………………………………… (1) (Total 3 marks) 9 13. The diagram below shows the structure of the cell surface membrane. Carbohydrate Proteins Glycoprotein (a) The cell surface membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer. Explain why tile phospholipids in the bilayer are arranged with the fatty acid tails pointing inwards and the phosphate heads outwards. ……………………………………………….……………………………………… ……………………………………………….……………………………………… ……………………………………………….……………………………………… ……………………………………………….……………………………………… ……………………………………………….……………………………………… ……………………………………………….……………………………………… (3) (b) The diagram has been magnified three million (3 × 106) times. Calculate the width of the cell surface membrane in tin (micrometres). Show your working. Answer ………………………… µm (3) (c) State one function of each of the following components of the cell surface membrane. Carbohydrate ……………………………………………………………………….. Protein ……………………………………………………………………………… (2) (Total 8 marks) 13 14. The table below refers to the formula and structure of some biological molecules. Complete the table by writing in the name, the formula or the structure of the molecule where appropriate in the empty boxes. Name Formula Water H2 O Structure NH2RCHCOOH Fatty acid H H H H H H C C C C C H H H H H O C OH CH 2 OH C H C HO O H OH H C C H OH H C OH (Total 6 marks) 17 15. The diagram below shows the structure of two fatty acids. O C A O H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C H H H H H H H H O B C O H H C H C C H H (a) Give the name of the molecule to which three fatty acids are bonded to form a triglyceride lipid. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) (i) Name the type of fatty acid labelled B. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Describe one way in which the physical properties of a triglyceride composed of fatty acids of type B will differ from a triglyceride of similar molecular size composed of fatty acids of type A. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) 18 (c) Draw a diagram to show the arrangement of phospholipid molecules in a unit (cell) membrane. (2) (Total 5 marks) 16. The diagram below shows the structure of a triglyceride molecule. O H H C O C O H C O C O H C O C H A (a) (i) Name the part of the molecule labelled A. ............................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the type of bond formed between part A and a fatty acid. ............................................................................................................................................... (1) 19 (b) Stearic acid and oleic acid are both examples of fatty acids. Each has a hydrocarbon chain containing 17 carbon atoms. Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid but oleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid. Give two ways in which the structure of a stearic acid molecule differs from the structure of an oleic acid molecule. 1 ............................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................... 2 ............................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Describe two functions of lipids in animals. 1 ............................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... 2 ............................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 8 marks) 20 17. The diagram below shows a stage in the process of translation during protein synthesis. This process is occurring on a ribosome. Amino acids Ribosome Amino acid 4 tRNA molecule 1 3 2 Anticodon GU A GGU AAA G C C AC G GG U Part of a messenger RNA molecule (a) Describe the structure of a ribosome. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (2) 22 (b) The table below shows the anticodons of some tRNA molecules and the specific amino acids that each one carries. tRNA anticodon Amino acid GGU Proline CCA Glycine AAA Phenylalanine CGA Alanine ACC Tryptophan UUU Lysine Using the information in the table, identify amino acids 2 and 3 shown in the diagram on the previous page. Amino acid 2 ......................................................................................................................... Amino acid 3 ......................................................................................................................... (2) (c) During translation, amino acids are linked by a peptide bond. (i) Draw a diagram to show two amino acids linked by a peptide bond. (3) 23 (ii) Name the type of reaction that occurs during the formation of a peptide bond. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 8 marks) 18. Carbohydrates are used as a source of energy. Excess carbohydrate can be stored as glycogen in animal cells. (a) Give two reasons why glycogen is used as a storage molecule. 1 .................................................................................................................................. 2 .................................................................................................................................. (2) (b) The diagram below shows a molecule of maltose. (i) Complete the diagrams below to show the two glucose molecules that will result when this maltose molecule is broken down. (2) 24 (ii) Name the type of chemical reaction that occurs when maltose breaks down. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) 19. The diagram below shows part of a DNA molecule. Y Z X Adenine W (a) (i) Cytosine Name the parts of the molecule represented by each of the following letters. W ...................................................................................................................... X ...................................................................................................................... Y ...................................................................................................................... Z ...................................................................................................................... (4) (ii) Name the type of bond that holds the two strands of DNA together. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 25 (b) The table below shows the amino acids coded by mRNA codons. Second base C A G UUU U UUC UUA UUG Phenylalanine Phenylalanine Leucine Leucine UCU UCC UCA UCG Serine Serine Serine Serine UAU UAC UAA UAG Tyrosine Tyrosine Stop Stop UGU UGC UGA UGG Cysteine Cysteine Stop Tryptophan U C A G CUU CUC C CUA CUG Leucine Leucine Leucine Leucine CCU CCC CCA CCG Proline Proline Proline Proline CAU CAC CAA CAG Histidine Histidine Glutamine Glutamine CGU CGC CGA CGG Arginine Arginine Arginine Arginine U C A G AUU A AUC AUA AUG Isoleucine Isoleucine Isoleucine Methionine ACU ACC ACA ACG Threonine Threonine Threonine Threonine AAU AAC AAA AAG Asparagine Asparagine Lysine Lysine AGU AGC AGA AGG Serine Serine Arginine Arginine U C A G GUU GUC G GUA GUG Valine Valine Valine Valine GCU GCC GCA GCG Alanine Alanine Alanine Alanine GAU GAC GAA GAG Aspartic acid Aspartic acid Glutamic acid Glutamic acid GGU GGC GGA GGG Glycine Glycine Glycine Glycine U C A G (i) Third base First base U Name the process by which mRNA is formed in the nucleus. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Reading from left to right, what is the sequence of amino acids coded by the following length of mRNA? G A U C G U U G U A A G ........................................................................................................................... (1) 26 (iii) A mutation occurred so that the base cytosine was replaced by guanine in this mRNA. Using the information in the table, explain why this mutation could affect the tertiary structure of the protein formed from this mRNA. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 10 marks) 20. The diagram below shows four molecules of water. H H O H H O H O A (a) H H H O Name the type of bond labelled A on the diagram. …………………………………………………………………………………………… (1) (b) Explain why water molecules are described as dipolar. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (2) 27 (c) One of the properties of water is that it has a high specific heat capacity. Explain why this property is important for organisms that live in water. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (2) (Total 5 marks) 21. Protein synthesis involves transcription and translation. (a) (i) Where does transcription take place in a eukaryotic cell? ……………………………………………………………………………………… (1) (ii) Name the type of chemical reaction that occurs when a strand of messenger RNA is formed from individual nucleotides. ……………………………………………………………………………………… (1) (b) The diagram below shows part of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. C (i) G A A C C G C C C G A A U C A C C What is the maximum number of amino acids coded for by this strand of mRNA? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Complete the diagram below to show the sequence of bases on the strand of DNA that coded for this mRNA. (2) 28 (c) A strand of mRNA was found to have 53 codons but the protein produced from it contained only 51 amino acids. Suggest two reasons for this difference. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (2) (d) Describe the process of translation. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (5) (Total 12 marks) 29 22. (a) DNA is replicated by a process called semi-conservative replication. Explain what is meant by the term semi-conservative replication. …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (4) (b) When bacteria grow and reproduce they need a nitrogen source. The nitrogen becomes part of their DNA. Bacteria were placed in a culture medium containing a heavy form of nitrogen. The bacteria were grown and allowed to reproduce for several generations until all the nitrogen in their DNA was heavy nitrogen. The bacteria were removed, washed thoroughly and then divided into five batches labelled A, B, C, D and E. They were then placed in fresh culture medium and allowed to grow for different periods of time. Batch A was placed into fresh culture medium containing heavy nitrogen, and left for four generations. The other four batches were placed into fresh culture medium containing light nitrogen and left for different periods of time. 30 The treatments are shown in the table below. Batch A B C D E First treatment All grown in heavy nitrogen Second treatment Grown in heavy nitrogen for four generations Grown in light nitrogen for one generation Grown in light nitrogen for two generations Grown in light nitrogen for three generations Grown in light nitrogen for four generations The DNA from the five batches of bacteria was then removed, placed on separating solutions and centrifuged (spun). The mass of DNA added to each separating solution was the same. DNA containing different proportions of heavy and light nitrogen can be seen as separate bands after centrifugation. The heavier molecules are lower down in the separating solution than the lighter molecules. The wide bands contain more molecules than the narrow bands. Figure 1 shows an example of the results of centrifuging a mixture of heavy and light DNA. Figure 1 31 Figure 2 shows the results for the batches A, B, C and D. Figure 2 (i) Explain why the DNA from batch B is higher up in the separating solution than the DNA from batch A. ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… (2) (ii) Explain the results for batch C. ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… (3) 32 (iii) On Figure 2, draw in the bands you would expect to see for the DNA separated from the bacteria grown in batch E. (2) (Total 11 marks) 23. The diagram below shows the structure of a human insulin molecule. Each circle represents one amino acid. S S A chain Gly Ile Val Glu Glu Cys Cys Thr Ser Ile Cys Ser Leu Tyr Glu Leu Glu Asn Tyr Cys Asn S S S S Phe Val Asn Glu His Leu Cys Gly Ser His Leu Val Glu Ala Leu Tyr Leu Val Cys Gly Glu Arg Gly Phe Phe Tyr Thr Pro Lys Thr B chain Insulin is a protein that has a tertiary structure and a quaternary structure. (a) (i) Name two types of bond that help to maintain the tertiary structure. 1. ............................................................................................................................ 2. ............................................................................................................................ (2) (ii) What evidence is there in the diagram that insulin has a quaternary structure? ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... (1) (b) (i) All human insulin molecules have the same primary structure. Explain what is meant by primary structure. ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... (1) 33 (ii) When insulin molecules are formed they fold into a specific shape. Explain why all human insulin molecules fold into the same shape. ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) 24. (a) The statements in the table below refer to three biological molecules. If a statement is correct place a tick ( ) in the appropriate box and if a statement is incorrect place a cross ( ) in the appropriate box. Four boxes have already been completed for you. Statement Starch Glycogen Monosaccharide Is a polymer Glycosidic bonds are present Is an energy store in animal cells Has high solubility in water (4) (b) The diagram below represents a polypeptide consisting of amino acids. State the minimum number of bases needed to code for this polypeptide along a strand of mRNA. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) 34 (c) Describe the key stages involved in protein synthesis, from the genetic code in the nucleus to the sequence of amino acids being assembled at the ribosome. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) (d) Explain how the sequence of amino acids determines the shape of a protein. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 12 marks) 25. Carbohydrates and lipids are both sources of energy in the diet. A high carbohydrate intake stimulates the production of fatty acids. Eating excessive amounts of carbohydrates can lead to obesity. 35 (a) (i) The diagram below illustrates part of the structure of a fatty acid with the formula C15H31COOH. Complete the diagram of the molecule. H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H—C— C— C— C— C— C— C— C— C— C— C— C— C— C— C— H (ii) H H H H H H H H H H H H H (2) H State whether this fatty acid is saturated or unsaturated. Give a reason for your answer. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) (i) Explain what is meant by the term risk factor. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain how obesity increases the risk of developing coronary heart disease. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) 36 (c) Energy drinks containing glucose provide a concentrated source of energy that is particularly valuable during exercise. Explain why glucose can provide a quick energy boost during exercise. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 11 marks) 26. (a) The table below refers to the composition of the disaccharides sucrose, maltose and lactose. Place a tick ( ) in the appropriate box or boxes to indicate clearly the monosaccharide or monosaccharides that make up each disaccharide. Monosaccharides Disaccharide Galactose Glucose Fructose Sucrose Maltose Lactose (3) (b) Name the bond that joins two monosaccharides in a disaccharide. ....................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) 37 27. Read through the following passage about protein structure, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage. All amino acids contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and ................................................ The primary structure of a protein is formed when amino acids are joined together by ............................................... bonds. Chains of amino acids may then form a secondary structure such as a spiral shape called the ..............................................., which is maintained by ............................................... bonding. The tertiary structure of a protein is maintained by bonding between the ............................................... of amino acids. (Total 5 marks) 28. Sucrose is a disaccharide made up from one molecule of glucose bonded to one molecule of fructose. Sucrose needs to be digested by the enzyme sucrase before it can be absorbed into the blood. (a) The diagram below illustrates how the enzyme sucrase may catalyse the breakdown of sucrose into glucose and fructose. Sucrose R Glucose Fructose Q Sucrase Use the diagram to identify: (i) reactant Q ........................................................................................................................... (1) 38 (ii) the region labelled R ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) the name of the bond between the glucose and fructose molecules that is broken by the reaction shown in the diagram. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) (i) Explain why sucrase will digest sucrose and not any other disaccharide. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) Name and describe one way that glucose is absorbed across cell membranes. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 29. (a) Maltose is a disaccharide formed by a reaction between two alpha (α) glucose molecules. Complete the word equation below, which represents this reaction. α-glucose + α-glucose –→ maltose + ............................................. (1) 39 (b) Draw the structure of a molecule of alpha glucose. (3) (c) Describe a function of maltose. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) 40 30. (a) In the space below draw a diagram to show two mononucleotides joined together in a single strand of DNA (polynucleotide). Use the symbols shown for each component in your diagram. Phosphate group: Deoxyribose: Base: Covalent bonds: (3) 41 (b) Describe how two strands of DNA are joined to form a DNA molecule and how this molecule is organised in a chromosome. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) (c) The table below shows the percentage content of one of the four bases in a molecule of DNA. Name of base Percentage content Adenine 14 Cytosine Guanine Thymine (i) Use the information in the table to calculate the percentage content of the other three bases in this molecule of DNA. Write your answers in the table. (3) 42 (ii) State what percentage of the bases in this molecule of DNA are purines. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 12 marks) 31. The table below summarises the structure of some of the main chemical compounds found in living organisms. (a) Complete the empty boxes in the table. Chemical Compound One example of the chemical compound found in living organisms Subunits of the chemical Elements contained in the chemical Polysaccharide Protein Enzyme C, H, O, N, S Lipid Phospholipid C, H, O Nucleic acid Nucleotide (7) (b) State one difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fat (lipid). ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) 43 (c) Draw a labelled diagram to show the arrangement of phospholipids and proteins in the fluid mosaic model of a cell membrane. (3) (Total 11 marks) 32. The table below shows population statistics and deaths from coronary heart disease (CHD) for males and females in England during a two year period. Number in the population Number dying from CHD Males 23 922 144 33 879 Females 25 216 687 9 016 (a) (i) For this two year period, calculate the percentage risk of a male dying from CHD. Show your working. (1) (ii) Use the data in the table above to calculate how many times females are less likely to die from CHD than males. (1) 44 (b) Body Mass Index (BMI) can be used to indicate whether a person is overweight. The chart below shows the effect of having a high BMI on the risk of dying of CHD when compared with a control group with a normal BMI of 20. A person with a BMI of 30 is obese. 50 Increase in risk of death due to CHD /% 40 30 20 10 0 20 25 30 35 Body Mass Index (BMI) (i) Describe the trend shown in the chart. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Give the formula used to calculate BMI. (1) 45 (iii) Explain why people who are overweight are more likely to die from CHD. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 8 marks) 33. The function of a protein depends on its shape. (a) (i) Explain what is meant by the primary structure of a protein. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain how the primary structure of a protein is important in determining its shape. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 46 (b) Explain why most enzymes are specific to only one substrate. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Describe the process that converts a genetic sequence on messenger RNA into the primary sequence of a protein. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 9 marks) 47 34. The table below refers to the structure of DNA and RNA. If the statement is correct, place a tick ( ) in the appropriate box and if the statement is incorrect, place a cross ( ) in the appropriate box. Statement DNA mRNA Is double stranded Contains the bases adenine and uracil Contains a pentose sugar Contains phosphodiester bonds (Total 4 marks) 35. Read through the following account of the roles of lipids in living organisms, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account. Lipids have many important roles in living organisms. They are found as small droplets of oil in many cells where they act as an .................................................... Fats are found deposited beneath the skin of animals where they provide .................................................... and .................................................... . In plants, waxes are found on the upper surface of leaves where they act as a .................................................... layer. (Total 4 marks) 48 36. (a) The diagram below shows the structures of two amino acids, alanine and serine. H H N H C O N C CH 3 H H OH H C CH 2 O C OH OH Alanine Serine In the space below, draw a diagram to show a dipeptide formed when these two molecules bond together. (2) 49 (b) Computer-generated models were used to measure the length in nanometres (nm) of a polypeptide containing a large number of amino acids. Measurements were made of the primary and secondary structure of the polypeptide. The models were used to measure the length of the polypeptide at 25 °C and at 55 °C. The results are shown in the table below. Length of polypeptide/nm Structure of polypeptide at 25 °C at 55 °C Primary 505 505 Secondary 48 70 (i) Explain what is meant by the term secondary structure of a protein. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Compare the results obtained at 25 °C with those obtained at 55 °C. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 50 (iii) Suggest why the increase in temperature has this effect on the length of the secondary structure of the polypeptide. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 37. The diagram below shows part of a starch molecule. (a) (i) Name the type of chemical reaction that joins monosaccharides together to form a starch molecule. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the type of chemical bond formed during this reaction. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) State what other molecule is produced in this reaction. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 51 (b) Starch and glycogen are both storage molecules in cells. (i) Explain two ways in which the structure of these molecules makes them suitable for their role as storage molecules. 1 ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................... 2 ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Describe one structural difference between starch and glycogen. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 6 marks) 38. The diagram below shows the pairing between two bases in a DNA molecule. Thymine CH 3 H H N C N C H O N C N H C N C C N C C C N H Deoxyribose O H Deoxyribose (a) (i) Name the base which pairs with thymine. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 52 (ii) Name the base which replaces thymine in RNA. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Apart from other bases, name one chemical group present in DNA not shown on the diagram. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Describe two structural features of DNA which give it the ability to replicate. 1 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... 2 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Give two differences between the processes of DNA replication and transcription. 1 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... 2 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 53 39. Proteins are chains of amino acids and have a wide range of functions in living organisms. (a) (i) The diagram below shows part of the general structure of two different amino acids. Complete the diagram to show how these two amino acids can be joined together. H R N—C— H H R O —C—C H OH (1) (ii) Name the bond that is formed between the two amino acids. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Explain how the specific sequence of amino acids in a protein determines its threedimensional structure. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) 54 (c) Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions within living organisms. The graph below shows the effect of changing enzyme concentration on the rate of reaction. Rate of reaction X Enzyme concentration (i) Explain why increasing the enzyme concentration above point X on the graph does not increase the rate of the reaction further. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) 55 (ii) Outline the practical procedures that could have been used to obtain the results shown on the graph. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 10 marks) 40. Read through the following passage about water, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage. A water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom held together by ........................................ bonds. There is an unequal distribution of charge over the molecule. This is called a ........................................ and results in water being a good ........................................ for many substances such as sodium ions. Bonds called ........................................ bonds form between water molecules. As a result water has a high ................................................................ meaning that a lot of energy is needed to cause a small rise in temperature. (Total 5 marks) 56 41. (a) The diagram below represents a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule. X A C C Y A G U (i) Name the type of bond labelled Y. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the molecule that is attached to position X during protein synthesis. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 57 (iii) Explain the meaning of the term anticodon. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) State two ways in which the structure of a tRNA molecule differs from the structure of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. 1 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... 2 .................................................................................................................................. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) 58 42. (a) DNA in eukaryotic organisms is a double helix. Bases on one strand bond to bases on the second strand to form base pairs. During protein synthesis, one strand of DNA (the coding strand) acts as a template to make mRNA. The second strand is known as the noncoding strand. The base sequence of a small section of the coding strand of a DNA molecule is shown below. AGACTTGCAACTTGACATGTA (i) How many codons are shown in this sequence? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Give the sequence of the first five bases that would be present in each of the following: 1. the mRNA molecule transcribed from this DNA strand ........................................................................................................................... 2. the non-coding strand of this DNA ........................................................................................................................... (2) 59 (b) A sample of DNA from a locust was analysed to determine the percentage of each base present. The percentage of adenine was found to be 29.4%. Calculate the percentage of cytosine in this sample. Show your working and give an explanation for your answer. Percentage of cytosine = ............................................................................................. Explanation: ................................................................................................................ ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) (Total 8 marks) 60 43. Proteins have a wide range of functions in living organisms. The function of a protein is related to its precise three dimensional shape, which is determined by its specific sequence of amino acids. The diagram below shows a model of a typical protein molecule. (a) (i) Complete the diagram below to give the structure of the amino acid glycine. H C H (2) 61 (ii) Explain how a specific sequence of amino acids can form the precise three dimensional shape of a protein molecule. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (b) The following DNA base sequence codes for part of a protein molecule. TACGGTATGCCAACCTTC (i) State the number of amino acids coded by this section of DNA. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the process involved in converting a base sequence of DNA into a base sequence of messenger RNA (mRNA). ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Give the complementary mRNA sequence to the DNA sequence above. ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 9 marks) 62 44. (a) The following table contains some statements about the properties of polysaccharides, lipids and proteins. Complete the table by placing a if a statement is correct and a if it is incorrect. Polysaccharides Lipids Proteins Are polymers Have ester bonds Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen Form components making up the structure of cell membranes (6) (b) Give one difference between the following pairs of molecules: (i) Saturated and unsaturated lipids ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (ii) Glycogen and starch ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 63 45. Read through the following passage about lipids, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the passage. Lipids contain the elements hydrogen, carbon and oxygen joined together by ............................................... bonds. Triglycerides are lipids that consist of three ............................................... molecules joined to a ............................................... molecule. These molecules are joined together by a chemical process called a ............................................... reaction. Triglycerides that have double bonds between carbon atoms are known as ............................................... triglycerides. (Total 5 marks) 46. Adipose tissue contains stored triglycerides. Describe the structure of a triglyceride. ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................... (Total 3 marks) 64 47. (a) The diagram below shows the structure of a triglyceride. Ch2 O Bond A CHO CH2 O O C O C O C triglyceride (i) Name Bond A on the diagram. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the type of reaction that will break down the triglyceride into its constituent parts during digestion by lipase enzymes. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Name two products formed when triglycerides are completely digested. 1 ........................................................................................................................ 2 ........................................................................................................................ (2) (iv) Some triglycerides have several double bonds (C C), others have none. Describe one way in which the physical property of triglycerides which include several double bonds will differ from triglycerides which have no double bonds. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) 65 (b) Lipids in membranes have an additional chemical group attached. (i) Name the chemical group which is added to the lipids in membranes. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain how adding this extra chemical group allows the formation of a cell membrane. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 48. The diagram below illustrates part of a glycogen molecule. CH2OH CH2OH C H C HO (a) O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O CH2OH O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O CH2OH O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O CH2OH O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O CH2OH O H H OH H C C H OH H C C C O O H OH H C C H OH H C OH State the role of glycogen in the human body. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) An enzyme is used to break the bonds holding the monomers (glucose molecules) together. (i) In the space below draw one of the monomers that would result from this reaction. 66 (2) (ii) Explain why this enzyme will not break the bonds in a protein molecule. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) 67 (c) Explain the advantages, to living organisms, of using enzymes in biological reactions. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 49. (a) Insulin and collagen are both proteins that have a primary structure made up of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. (i) Explain what is meant by the term primary structure of a protein. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Name the type of reaction that occurs when a peptide bond is broken causing a dipeptide to split into two amino acids. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 68 (b) Insulin and collagen both contain the amino acids glycine and serine. The diagram below shows a dipeptide formed from these two amino acids. Complete the diagram to show the structure of serine when the peptide bond breaks. H H O H H O N—C—C—N—C—C H OH H CH2 OH H H O N—C—C + H OH H Glycine Serine (1) (Total 3 marks) 50. (a) The diagram below shows the structure of a mononucleotide from a DNA molecule. A B Name the parts of the mononucleotide labelled A and B. A .............................................. B .............................................. (1) 69 (b) The table below shows the percentage of different bases present in the DNA from two organisms. Percentage of each base present Organism Yeast Cow (i) Adenine Guanine Thymine Cytosine 31 19 31 19 29 Complete the table to show the percentage of adenine, guanine and cytosine in the DNA of a cow. (1) (ii) Explain how you worked out the percentage of guanine present in the DNA of a cow. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) 70 (c) DNA and messenger RNA (mRNA) have different properties. DNA is very stable but mRNA breaks down quickly and most of it will be broken down within a day of it being produced. Suggest why it is important for DNA to be more stable than mRNA. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) Protein synthesis involves transcription and translation. Describe the process of transcription. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) (Total 12 marks) 71 51. (a) Name a component of DNA that contains nitrogen. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) When bacteria are grown in conditions containing a heavy form of nitrogen, they will incorporate the heavy nitrogen into their DNA each time DNA replication occurs. After many replications in these conditions, all the nitrogen in the bacterial DNA will be of the heavy form. If the bacteria are then switched to conditions containing a light form of nitrogen, this will become incorporated each time DNA replication occurs. The diagram below shows the changes in the DNA composition, over two DNA replications, after the bacteria have been transferred from conditions containing heavy nitrogen to conditions containing light nitrogen. Complete the diagram to show the DNA composition in the third generation. KEY = Heavy nitrogen = Light nitrogen ...................................................................................................................................................... DNA before replication in light nitrogen conditions ...................................................................................................................................................... DNA after the first replication in light nitrogen conditions ...................................................................................................................................................... DNA after the second replication in light nitrogen conditions ...................................................................................................................................................... DNA after the third replication in light nitrogen conditions ...................................................................................................................................................... (2) 72 (c) Name an enzyme involved in DNA replication. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) The table below shows nine bases from a DNA template strand. Complete the table by giving the corresponding bases on the complementary DNA strand. DNA template strand A G C T T A C C A Complementary DNA strand (1) (e) Genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, are caused by mutations in the sequence of bases found in DNA. Explain how a gene mutation may result in a protein that does not function normally. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) (Total 10 marks) 73 52. Read through the following account on lipids, then write on the dotted lines the most appropriate word or words to complete the account. Lipids are insoluble in water because they are ...................................................... A triglyceride is one type of lipid. A triglyceride consists of one .................................................... molecule with three ..................................................... molecules joined to it by ..................................................... bonds. Triglycerides have important roles in living organisms, including waterproofing and ...................................................... (Total 5 marks) 53. Lactose is a sugar found in human milk. (a) Lactose is a disaccharide that can be hydrolysed to its two monosaccharides, galactose and glucose. (i) The diagram below shows lactose being hydrolysed. Complete the diagram by drawing the missing components of the monosaccharide galactose in the left-hand box and the monosaccharide glucose in the right-hand box. Lactose CH 2 OH HO CH 2 OH O H H O H H O H OH H H OH CH 2 OH H OH H H OH OH CH 2 OH O Galactose O Glucose (2) 74 (ii) Explain the term hydrolysis. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Galactosaemia is a rare and potentially serious inherited condition. It is caused by a recessive allele that reduces the ability of the body to break down galactose. A couple is expecting a second child. Neither parent has galactosaemia but their first child does have galactosaemia. (i) Using the symbols G and g, complete the genetic diagram below to show the probability of the couple’s second child not having galactosaemia. Parents’ genotypes .......................................... .......................................... Parents’ gametes Possible genotypes of second child .................. .................. .................. .................. Probability of their second child not having galactosaemia ............................. (3) 75 (ii) The couple wanted confirmation that their second unborn child did not have galactosaemia. To do this, fetal cells were taken, the DNA extracted and the alleles associated with galactosaemia were sequenced. A mutation was found in one of these alleles but the protein produced by this allele was the same as the protein produced by the normal allele. The couple were told this could be explained by the degenerate nature of the genetic code. Explain how the degenerate nature of the genetic code could allow the mutated allele to produce the same protein as a normal allele. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (iii) Outline the ethical issues related to genetic screening of a fetus for inherited disorders such as galactosaemia. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 12 marks) 54. Carbohydrates are compounds that include monosaccharides, disaccharides and 76 polysaccharides. (a) (i) The table below lists some features of four carbohydrates. Put a cross in the box to indicate that the feature is present in the carbohydrate. The first row has been done for you. Feature Glucose Glycogen Maltose Starch 1–4 glycosidic bonds present 1–6 glycosidic bonds present Made up of many monomers (4) (ii) Name the disaccharide made up of α-glucose and galactose. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) The diagram below shows a disaccharide molecule. CH2 OH CH 2 OH O H H H H OH O OH H OH H H O HO H OH H H OH Draw the molecules resulting when this disaccharide molecule is split into its two component monosaccharides. (2) (iv) Name this type of reaction. ........................................................................................................................... (1) 77 (b) Explain the advantages of glycogen as an energy storage molecule in the human body. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 11 marks) 78