* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell: basic unit of structure and function of life. Prokaryotic: cells that
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
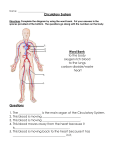
Cell: basic unit of structure and function of life. Prokaryotic: cells that do not have membrane bound structures. Eukaryotic: cells that have membrane bound structures Unicellular: made of only one cell Multicellular: made of many cells Cell membrane: encloses the cell and acts like a gatekeeper-allowing some materials to pass through it, but not others. Cytoplasm: a gel like fluid, it takes up most of the space inside the cell. It holds the organelles Organelles: carry out the activities that keep the cell alive. Nucleus: a structure usually located near the center of an animal cell. It controls cell activity. Nuclear membrane: It surrounds and protects the nucleus. Nucleolus: located in the nucleus and responsible for making ribosomes. Vacuoles: fluid filled structures temporarily store different substances needed by the cell. Mitochondria: use oxygen to transfer energy in food to a form that the cell can use to carry out its activities. Endoplasmic reticulum: produce important products for the cell, including proteins and lipids. Golgi bodies: Help package products from the endoplasmic reticulum and distribute them around the cell. Cell wall: This outer barrier provides extra support for the cell and gives it a shape. Chloroplasts: food making structures of plant cells that contain the green pigment, Chlorophyll. Photosynthesis: food making process in plants. Tissue: groups of cells that work together to do a specific job. Organ: a structure made up of two or more tissues that work together to carry out a specific job. Organ system: made up of all the organs that work together to do a specific job. Digestive system: organ system that breaks down food into a form the body can use. Diaphragm: large domed muscle that separates chest and abdomen and plays a large role in breathing. Digestion: process of breaking down food into a form the body can use. Epiglottis: This flap of tissue prevents swallowed food from entering the tube to your lungs. Esophagus: tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach. Heart: part of the circulatory system that pumps blood throughout the body. Large intestine: part of the digestive system where water is absorbed from solid waste. Lungs: pair of organs in respiratory system where carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged. Trachea: part of the respiratory system, the windpipe. Alveoli: tiny air sacs in the lungs where gases are exchanged. Bronchi: two large tubes that branch off the trachea into the lungs. Plasma: the liquid part of blood that supports the other parts. Platelets: cell pieces that help blood to clot where there is an injury. Mouth: opening that animals use to take in food. Anus: the opening at the end of the digestive system, where wastes are released. Artery: a vessel in the circulatory sytem that carries blood away from the heart. Rectum: final section of the large intestine, ending in the anus. Respiratory system: organ system that takes oxygen into the body and releases carbon dioxide and water. Small intestine: organ in the digestive system that completes digestion and absorbs nutrients. Stomach: part of the digestive system where food is stored and partially digested before it enters the small intestine. Vein: in the circulatory sytem, vessel that carries blood towards the heart. Capillaries: tiny vessels in the human body. Red blood cells: specialized blood cells that carry oxygen and carbon dioxide. White blood cells: help you fight disease Nervous system: controls and coordinates your body’s activites and helps you sense and respond to changes in your environment. Central nervous system: made up of your brain and spinal cord. Cerebrum: control center of your thoughts and voluntary actions. Brain stem: base of your brain it controls vital and continual processes such as breathing, the beating of your heart, and digestion. Cerebellum: helps with balance and coordination. Spinal cord: bundle of nerves that goes from the brain stem down the center of your back.