* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The lymphatic system consists of lymphatic vessels and
Survey
Document related concepts
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
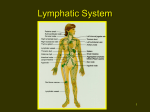
The lymphatic system consists of lymphatic vessels and associated lymphoid organs. LEARNING OBJECTIVE [ edit ] Describe how the lymphatic system consists of lymphatic vessels and associated lymphoid organs KEY POINTS [ edit ] Lymphatic vessels are thin-walled, permeable vessels with valves to prevent backflow of lymph. Lymphatic vessels function in picking up excess tissue fluid and returning it to the bloodstream, a process essential to preventedema. A lymph node is an organized collection of lymphoid tissue, through which the lymph passes on its way to returning to theblood. Lymph nodes are located at intervals along the lymphatic system. TERMS [ edit ] lymph node small oval bodies of the lymphatic system, distributed along the lymphatic vessels, that are clustered in the armpits, groin, neck, chest, and abdomen. They act as filters, with an internal honeycomb of connective tissue filled with lymphocytes and macrophages that collect and destroy bacteria, viruses, and foreign matter from lymph. When the body is fighting an infection, these lymphocytes multiply rapidly and produce a characteristic swelling of the lymph nodes. edema an excessive accumulation of serum in tissue spaces or a body cavity lymph A colorless, watery, bodily fluid carried by the lymphatic system, that consists mainly of white blood cells. lymphocyte A type of white blood cell or leukocyte that is divided into two principal groups and a null group: B-lymphocytes, which produce antibodies in the humoral immune response, T-lymphocytes, which participate in the cell-mediated immune response, and the null group, which contains natural killer cells, cytotoxic cells that participate in the innate immune response. Give us feedback on this content: FULL TEXT [edit ] Lymphatic Vessels The lymphatic system is a collection system which starts in the tissue space as initial lymph collectors that have fenestrated openings to allow fluid and particles to enter. These initial lymph collectors are valveless vessels and go on to form the precollector vessels which have rudimentary valves (which are not considered to be fully functional). These Register for FREE to stop seeing ads structures go on to form increasingly larger lymphatic vessels which form co-laterals and have lymph-angions (lymph hearts). The lymphatic system, once thought to be passive, is now known to be an active pumping system with active pumping segments with a function similar to that of peristalsis. Lymph hearts have stretchreceptors and smooth muscle tissue embedded in their walls. The lymphatic vessels make their way to the lymph nodes and from the lymph nodes the vessels form into trunks which connect to the internal jugular group of veins in the neck, as shown in . The lymphatic system This diagram shows the network of lymph nodes and connecting lymphatic vessels in the human body. Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Lymphatic organs play an important part in the immune system, having a considerable overlap with the lymphoid system. Lymphoid tissue is found in many organs, particularly the lymph nodes, as well as in the lymphoid follicles associated with the digestive system such as the tonsils. Lymphoid tissues contain lymphocytes, but they also contain other types of cells for support. The system also includes all the structures dedicated to the circulation and production of lymphocytes (the primary cellular component of lymph), which includes thespleen, thymus, bone marrow, and the lymphoid tissue associated with the digestive system.