* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Targets of Opportunity
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical warfare wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapons in World War I wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Fluorochemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Oil refinery wikipedia , lookup
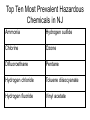
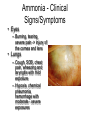
Targets of Opportunity Steven M Marcus Medical Director NJ Poison Information & Education System New Jersey Medical School Chemical Agents used during WWI include: chlorine, phosgene, and nitrogen mustard gases. These chemical lead to 100,000 deaths and 1.2 million casualties. Nazis killed millions of civilians with Zyklon B gas (HCN) in WWII. Agent Orange (a dioxin and defoliant) was used in the Vietnam War, which may have lead to skin cancer in our veterans. Chemical Terrorist Events • 1985 - Covenant Group found to possess 33 gallons of cyanide • 1992 - Police prevent Neo-Nazis from using cyanide in synagogue • 1994 - Aum Shinrikyo uses sarin in Matsumoto – 7 dead, 280 injured In 1995 in Tokyo, Sarin (very potent organophosphate nerve gas) caused 12 deaths and 5,500 injuries. More Chemical Terrorism • Copycat attacks in Japan using cyanide, phosgene, and pepper spray • FBI thwarts possible sarin attack in Disneyland • 1997 - Sydney, Australia – chlorine bombs in shopping centers injure 14 500 evacuated Types - Chemical Agents • Nerve Agents Soman, VX • Blood agents • • • • Pulmonary Intoxicants Miscellaneous Vesicants Riot Control Spray • Incapacitating Agents Tabun, Sarin, Hydrogen Cyanide, Cyanogen Chloride Phosgene, Chlorine Ammonia Mustard, Lewisite Mace ®, Pepper BZ The Bhopal Disaster: Twenty years ago an explosion at a chemical factory sent 27 tons of poisonous methyl isocyanate wafting over the slumbering residents of Bhopal, India. The aftermath was apocalyptic. Between 7,000 and 10,000 people died in the three days after the explosion and 15,000 more have died since. There is virtually no location in the state of NJ beyond the range of toxicity from an explosion in a chemical storage or production plant! Top Ten Most Prevalent Hazardous Chemicals in NJ Ammonia Hydrogen sulfide Chlorine Ozone Difluoroethane Pentane Hydrogen chloride Toluene diisocyanate Hydrogen fluoride Vinyl acetate Chlorine • Used in swimming pools and laboratories • Industrial exposures may produce large numbers of casualties Chlorine - Civilian Uses • • • • Chlorinated lime (bleaching powder) Water purification Disinfection Synthesis of other compounds – synthetic rubber – plastics – chlorinated hydrocarbons • Don’t try this at home! (bleach + acid) Historical Exposures • 1996 Bethlehem, Pa 13 pool victims • 1998 Rome, Italy 282 pool victims • Diyarbakir, Turkey 2000 106 victims leaking tanker car Chlorine - Characteristics • Properties – Greenish-yellow gas, pungent odor – Chlorine + water = HCl + Free O2 30x more irritating to lungs than HCl • Effects – Eye irritation, cough, SOB, and wheezing – delayed ARDS Chlorine - Tissue Effects • Topical rather than systemic • In central airways - from HCl – necrosis, sloughing • In peripheral airways – oxygen free radicals – react with sulfhydryl groups, disulfide bonds – damage to alveolar-capillary membrane Chlorine - Clinical Effects • Mild Exposure – – – – suffocation, choking sensation ocular, nasal irritation chest tightness, cough exertional dyspnea • Moderate Exposure – above sx + hoarseness, stridor – pulmonary edema within 2-4 hours Chlorine - Clinical Effects • Severe Exposure – severe dyspnea at rest – may cause pulmonary edema within 30-60 min – copious upper airway secretions – sudden death may occur from laryngospasm Clinical Considerations • These agents cause pulmonary edema – damage alveolar-capillary membrane • Latent Period – symptom onset may be delayed hours to days – objective signs appear later than symptoms • Sudden Death may occur – laryngeal obstruction (edema/spasm) – bronchospasm Clinical Considerations • Infectious Bronchitis / Pneumonitis common – usually occurs 3-5 days post-exposure – fever, elevated WBC, infiltrates NOT always infection – prophylactic antibiotics NOT indicated • Effects exacerbated by exertion – compensatory mechanisms overwhelmed – strict rest, even if asymptomatic • No specific therapy exists Ammonia • Colorless, watersoluble, alkaline gas • Pungent odor • Wide industrial use • Used to make fertilizer, explosives, dyes, and plastics Ammonia - Characteristics • Household ammonia pH < 12 - limited damage • Anhydrous ammonia pH > 12 - severe damage • Rapidly absorbed by mucosal surfaces (eyes, throat, and lungs) • Corrosive produced when combined with water Liquefaction necrosis Ammonia - Clinical Signs/Symptoms • Eyes – Burning, tearing, severe pain -> injury of the cornea and lens • Lungs – Cough, SOB, chest pain, wheezing and laryngitis with mild exposure – Hypoxia, chemical pneumonia, hemorrhage with moderate - severe exposures Ammonia - Clinical Signs/Symptoms • Skin – Pain, blister formation, deep burns • Gastrointestinal (ingestion) – Severe mouth pain, cough, and abdominal pain – Nausea and vomiting – Edema to lips and mouth (leading to airway obstruction) – Esophageal strictures and perforation Hydrogen flouride • Production of electronic circuits • Etching: glass, metal, stone and porcelain • Cleaning products: wheel and chrome cleaners • Rust removers Hydrogen fluoride • • • • • Dissolved in water as hydrofluoric acid Weak acid Volatizes easily Local and systemic effects Delayed symptoms HF-clinical effects • Local: pain out of proportion to apparent injury • Systemic: hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia and hyperkalemia HF-therapy • • • • Decontamination Calcium compresses Nebulized calcium? Eye wash Fluoride Release Leads to Evacuation of Texas Neighborhood International Fluoride Information Network July 10, 2003 Yesterday, July 9, an explosion occurred at a Texas oil refinery which resulted in the release of an unspecified, but potentially large amount of hydrogen fluoride. According to the article which appeared in today's Corpus Christi Caller Times, a seven block area adjacent to the plant was soon evacuated after winds blew the HF gas in its direction. "The unpublicized usage of deadly hydrofluoric acid at half of all refineries is endangering refinery communities...The environmental hazards of HF as used at refineries have to do with the high volumes utilized, the potential for high temperatures and pressures to be involved in a release, and the tendency of HF, once released to the environment, to form deadly gas clouds that do not easily diminish...This makes it an extremely dangerous material to be utilized at refineries in highly populated areas. The danger posed is thought by many experts to be as severe as the accident in Bhopal, India in which thousands were killed at a Union Carbide chemical plant in 1984." 14 feared killed in refinery blast Rescuers search for survivors at oil plant in Texas Thursday, March 24, 2005 BY PAM EASTON Associated Press TEXAS CITY, Texas -- A thunderous explosion tore through a BP oil refinery yesterday, shooting flames and billowing smoke into the sky and showering the area with ash and chunks of charred metal. At least 14 were believed dead and more than 100 were injured.